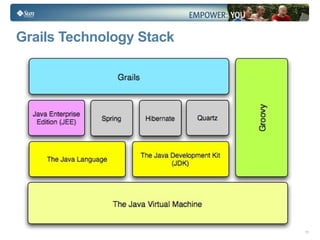
- Groovy is a dynamic language that runs on the Java Virtual Machine and has seamless integration with Java.
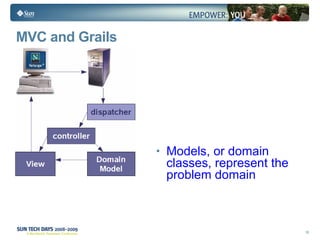
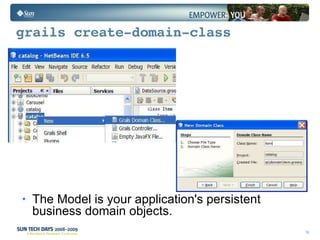
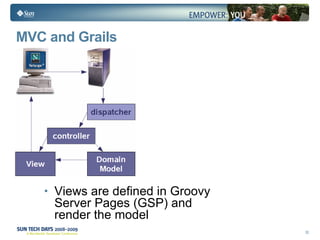
- Grails is an open source web application framework built on Groovy that follows conventions over configuration (CoC) and don't repeat yourself (DRY) principles.
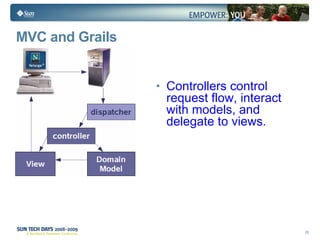
- Grails uses conventions to define a model-view-controller (MVC) structure and provides dynamic scaffolding to generate basic CRUD operations for domain classes.




![A Valid Java Program import java.util.*; public class Erase { private List<String> filterLongerThan(List<String> strings, int length) { List<String> result = new ArrayList<String>(); for (String n: strings) if (n.length() <= length) result.add(n); return (result); } public static void main(String[] args) { List<String> names = new ArrayList<String>(); names.add("Ted"); names.add("Fred"); names.add("Jed"); names.add("Ned"); System.out.println(names); Erase e = new Erase(); List shortNames = e.filterLongerThan(names, 3); System.out.println(shortNames); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/groovygrailsnetbeans-12517452668498-phpapp03/85/Agile-web-development-Groovy-Grails-with-Netbeans-5-320.jpg)
![A Valid Groovy Program import java.util.*; public class Erase { private List<String> filterLongerThan(List<String> strings, int length) { List<String> result = new ArrayList<String>(); for (String n: strings) if (n.length() <= length) result.add(n); return (result); } public static void main(String[] args) { List<String> names = new ArrayList<String>(); names.add("Ted"); names.add("Fred"); names.add("Jed"); names.add("Ned"); System.out.println(names); Erase e = new Erase(); List shortNames = e.filterLongerThan(names, 3); System.out.println(shortNames); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/groovygrailsnetbeans-12517452668498-phpapp03/85/Agile-web-development-Groovy-Grails-with-Netbeans-6-320.jpg)
![The Groovy Way def names = ["Ted", "Fred", "Jed", "Ned"] println names def shortNames = names.findAll{ it.size() <= 3 } print shortNames](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/groovygrailsnetbeans-12517452668498-phpapp03/85/Agile-web-development-Groovy-Grails-with-Netbeans-7-320.jpg)









![grails domain class Define relation between objects with attributes hasMany , belongsTo static hasMany = [ item: Item ] Groovy hashmap Address String street String zip static hasMany = [item:Item] 1 M Item String name String description Address address](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/groovygrailsnetbeans-12517452668498-phpapp03/85/Agile-web-development-Groovy-Grails-with-Netbeans-23-320.jpg)

![grails create-controller Controller made up of action methods Grails routes requests to the action corresponding to URL mapping Default action is index class Item Controller { def index = { redirect(action:list,params:params) } def list = { if(!params.max) params.max = 10 [ itemList: Item.list( params ) ] } def show = {... Actions http://host/catalog/item/list](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/groovygrailsnetbeans-12517452668498-phpapp03/85/Agile-web-development-Groovy-Grails-with-Netbeans-27-320.jpg)

![grails controller class Item Controller { def index = { redirect(action:list,params:params) } def list = { if(!params.max) params.max = 10 [ itemInstanceList: Item.list ( params ) ] } def show = {... returns an ArrayList of item objects retrieved from the item database table itemInstanceList variable is made available to the view](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/groovygrailsnetbeans-12517452668498-phpapp03/85/Agile-web-development-Groovy-Grails-with-Netbeans-29-320.jpg)



![Presenter’s Name [email_address] Carol McDonald Java Architect Tech Days 2009](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/groovygrailsnetbeans-12517452668498-phpapp03/85/Agile-web-development-Groovy-Grails-with-Netbeans-36-320.jpg)
