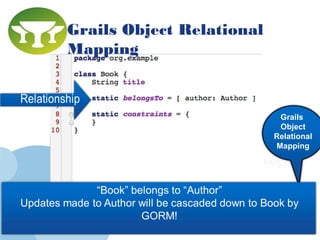
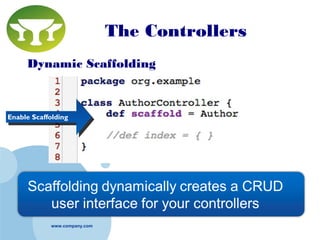
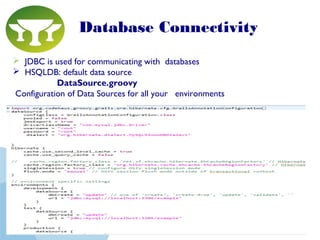
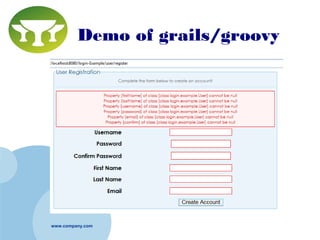
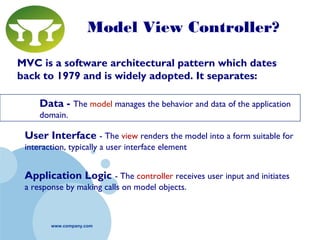
Grails is a web application framework built on Groovy and Java that follows the conventions of the Model-View-Controller (MVC) pattern. It aims to improve developer productivity over traditional Java frameworks by eliminating XML configuration files in favor of conventions, providing automated scaffolding for rapid prototyping, and including a complete development environment out of the box. Key features of Grails include its object-relational mapping (ORM) functionality, tag libraries for views, and ability to define domain classes, controllers, and services to build the model, controller and service layers of an application respectively.










![www.company.com
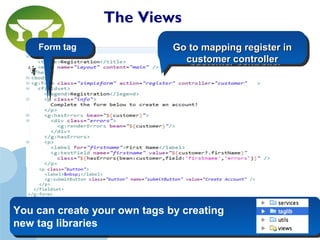
The Views
grails generate-views [domain class]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/grails-framework-presentation-160920095230/85/intoduction-to-Grails-Framework-12-320.jpg)