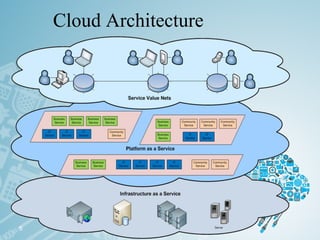
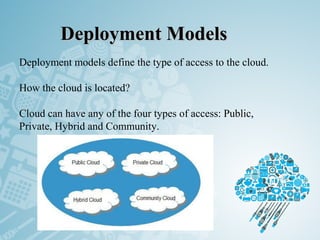
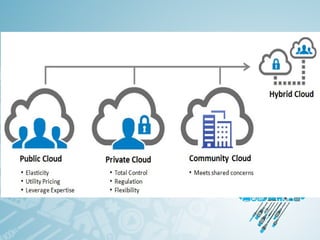
Cloud computing refers to storing and accessing data and programs over the Internet instead of a local computer's hard drive. It offers various online services through a network of remote servers. There are different types of cloud services and deployment models depending on who can access the cloud - public, private, hybrid or community. The main cloud service models are Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). While cloud computing provides benefits like flexible access to data and lower costs, it also poses security and privacy risks if data is not properly protected on remote servers.