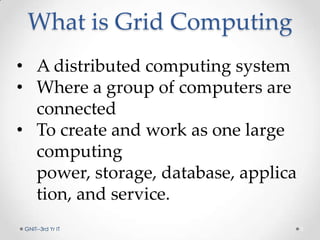
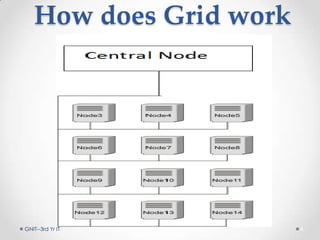
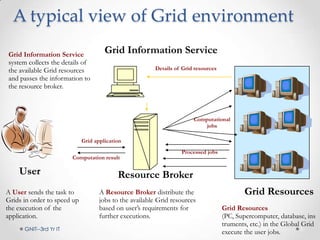
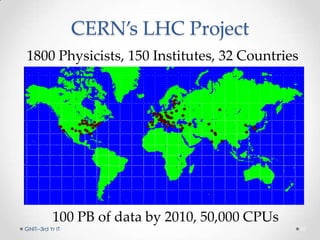
Grid computing is a distributed computing system where a group of connected computers work together as a single large computing resource. It allows users to submit tasks that are divided into independent subtasks and distributed across available grid resources. Key benefits include solving larger problems faster through collaboration and making better use of existing hardware. While standards are still evolving, grid computing has enabled projects like the Large Hadron Collider which involves over 1,800 physicists across 32 countries.






![References
[1]www.ieeexplore.ieee.org
[2]www.gridcomputing.com
[3]www.researchgate.net
[4]www.ibm.com
[5]www.home.cern.ch
GNIT--3rd Yr IT 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gridcomputiingfinal-140331115211-phpapp01/85/Grid-computing-12-320.jpg)
