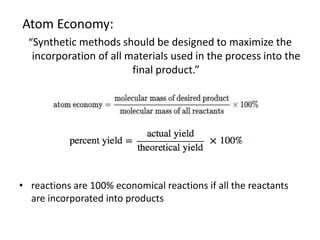
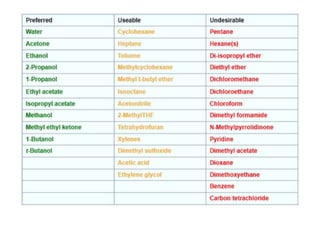
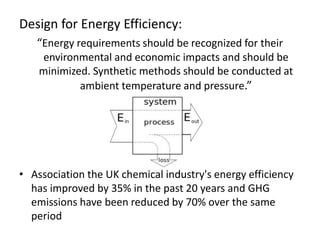
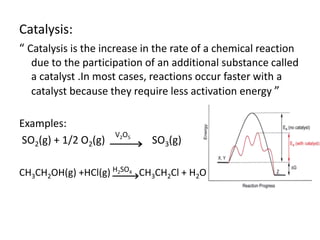
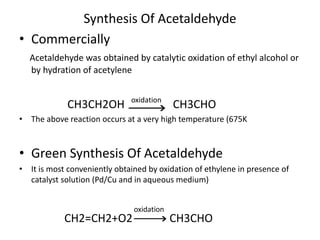
Green chemistry aims to reduce the environmental impact of chemical processes and products. It focuses on 12 principles including prevention of waste, safer solvents and auxiliaries, atom economy, and designing for energy efficiency and safer chemicals. Examples include using ozone instead of chlorine to disinfect water and oxidizing ethylene to produce acetaldehyde through a catalytic process with lower temperature and hazards compared to traditional methods. Green chemistry provides fundamental approaches to preventing pollution through safer, more sustainable design of chemical products and processes.