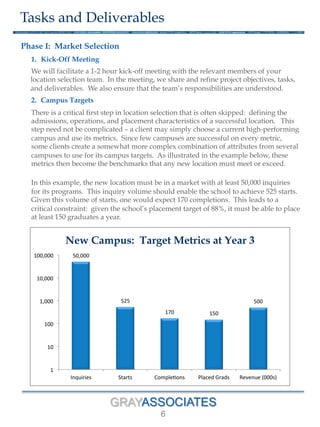
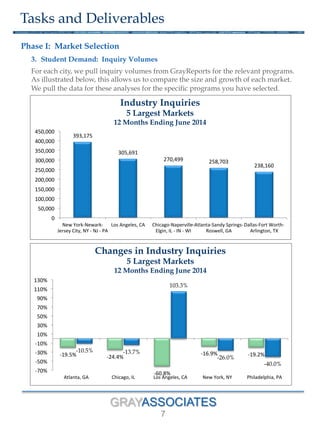
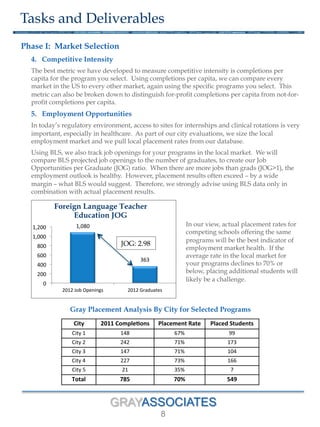
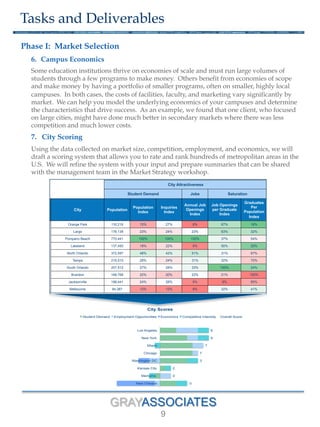
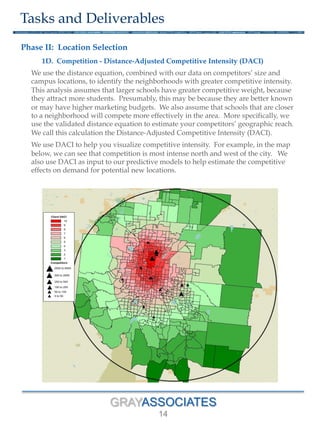
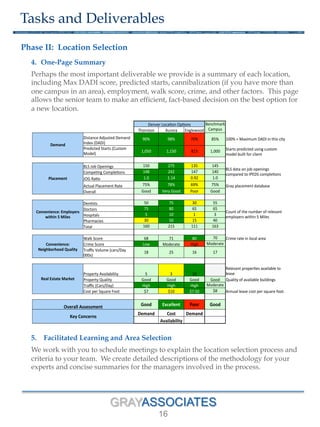
The document outlines a methodology for selecting optimal locations for educational campuses, focusing on market and location selection. It emphasizes analyzing geographic markets based on characteristics such as student demand, competition, and local employment opportunities using advanced analytics and databases. The process involves multiple phases, including workshops for team collaboration and decision-making based on data-driven insights.