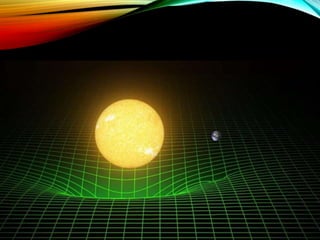
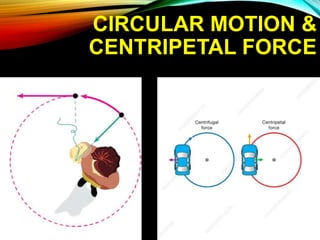
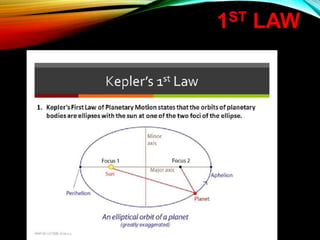
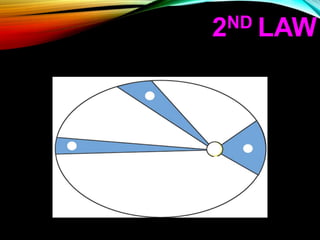
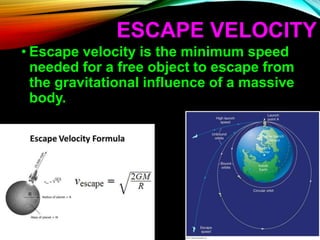
Gravitation is a universal force acting between all objects with mass or energy, governed by Newton's law of universal gravitation, which states that the force is proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the distance squared. Key concepts include the role of gravitons as hypothetical particles of gravity, the elliptical orbits of planets described by Kepler's laws, and the distinction between mass and weight, with weight varying based on location. Additionally, gravitational potential energy and escape velocity are important aspects of the force of gravity.