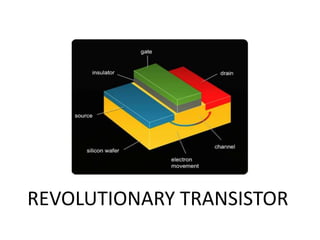
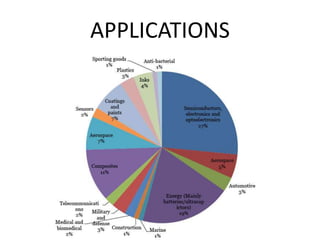
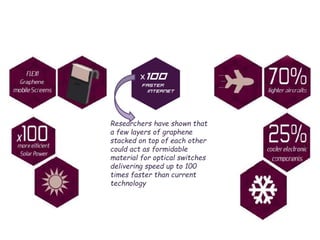
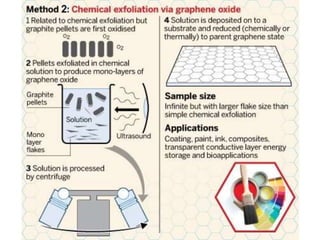
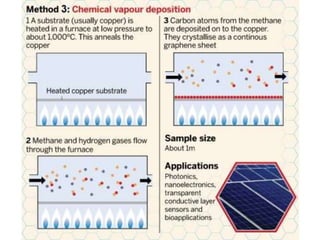
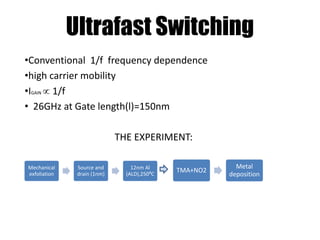
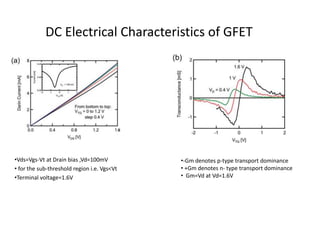
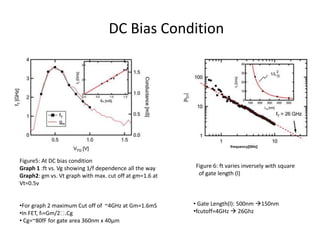
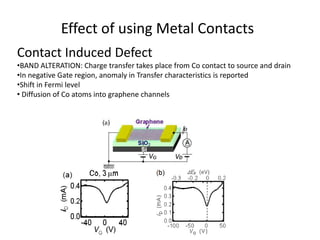
The document discusses graphene and its potential use in transistors. It describes graphene as a single sheet of carbon atoms arranged in a honeycomb lattice. Researchers have shown that stacking a few layers of graphene could enable optical switches that are 100 times faster than current technologies. The document also details experiments where graphene field-effect transistors were fabricated with gate lengths down to 150nm, achieving a cutoff frequency of 26GHz. Scaling to smaller gate lengths allows higher frequencies, with cutoff frequency scaling inversely with the square of the gate length. Graphene has potential for high-frequency and versatile applications due to its high carrier mobility and small channel lengths.