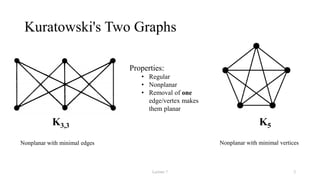
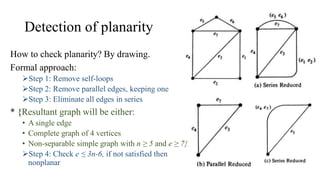
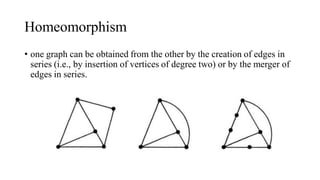
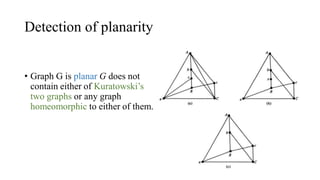
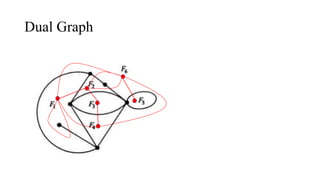
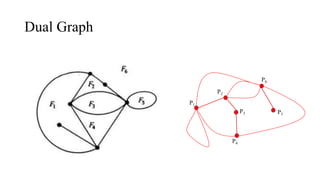
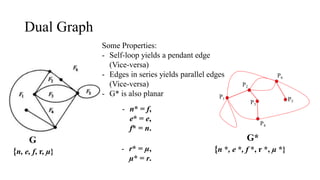
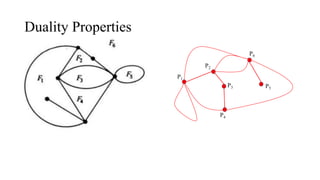
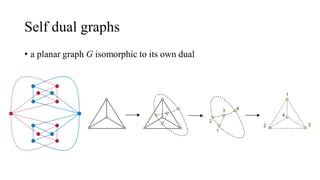
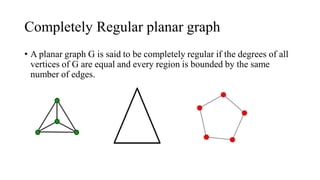
The document discusses planarity and dual graphs, focusing on Kuratowski's two graphs and properties of nonplanar graphs that become planar upon the removal of edges or vertices. It outlines a formal method for checking graph planarity and defines key concepts such as dual graphs, thickness, crossing number, and self-dual graphs. Additionally, it highlights the relationships between graph properties and conditions for planarity.