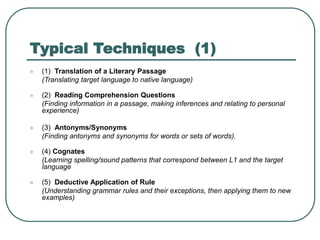
The document discusses the Grammar-Translation method of teaching foreign languages. Some key features of this method are that classes are taught in the native language with little use of the target language, vocabulary is taught through lists, extensive grammar rules are explained, reading difficult texts is emphasized early, and translation exercises are a core technique. Typical techniques used include translating passages, reading comprehension questions, working with antonyms/synonyms, learning cognates, applying grammar rules, fill-in-the-blank exercises, memorization, and composition.