This document provides information on several Spanish grammar topics in 3 paragraphs or less:
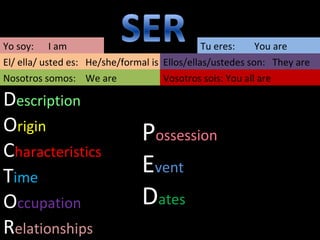
1) It discusses question words like qué and cuál, forms of the verb ser for expressing "to be", and the verb gustar for expressing likes.
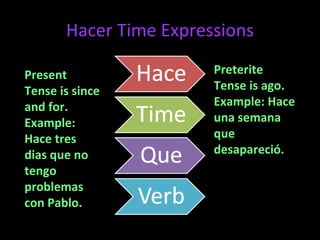
2) It covers the imperfect tense, common triggers used with that tense, and the construction "acabar de" for expressing recent actions.
3) The final paragraph discusses reflexive verbs, tu commands, double object pronouns, and their placement.