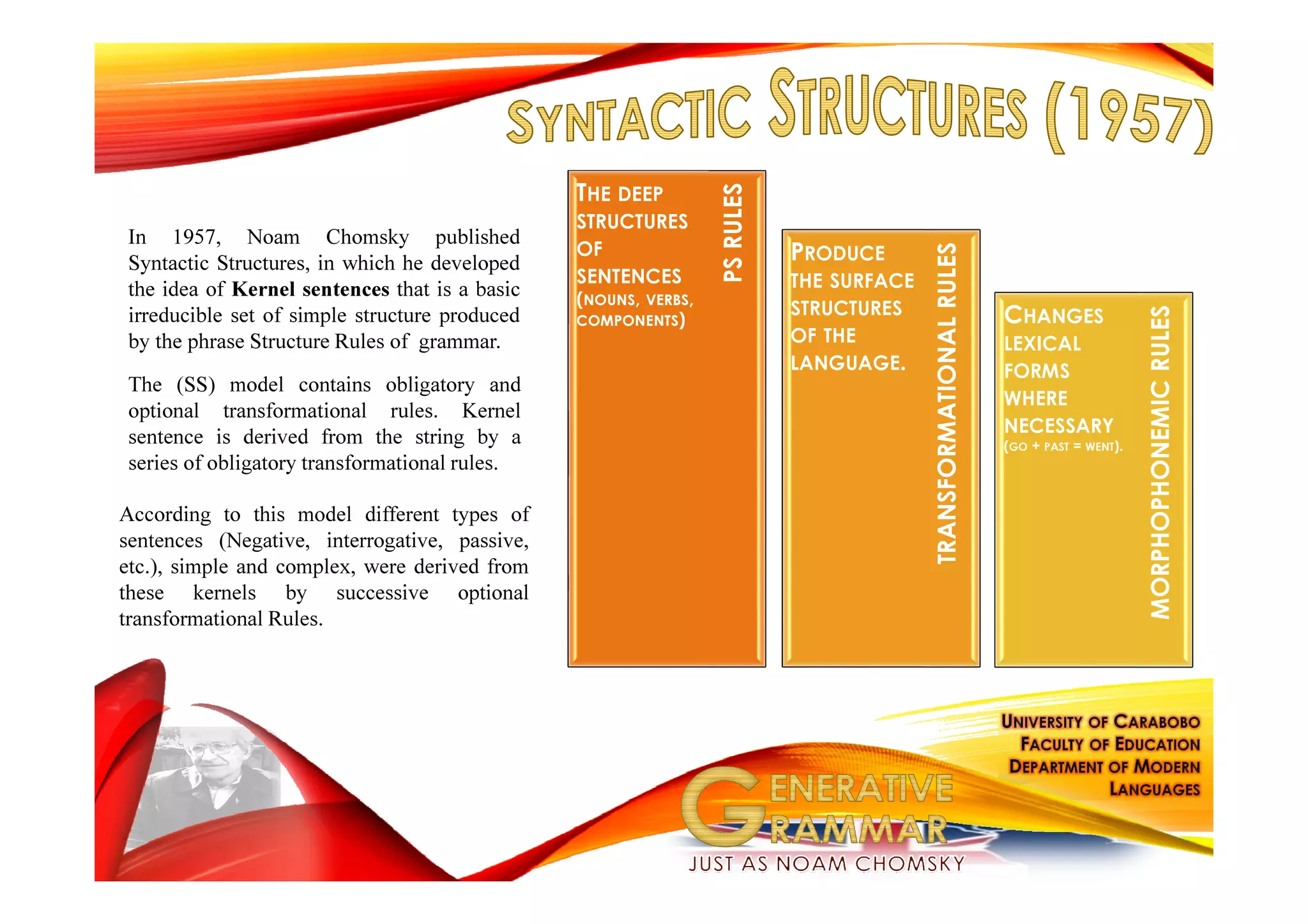
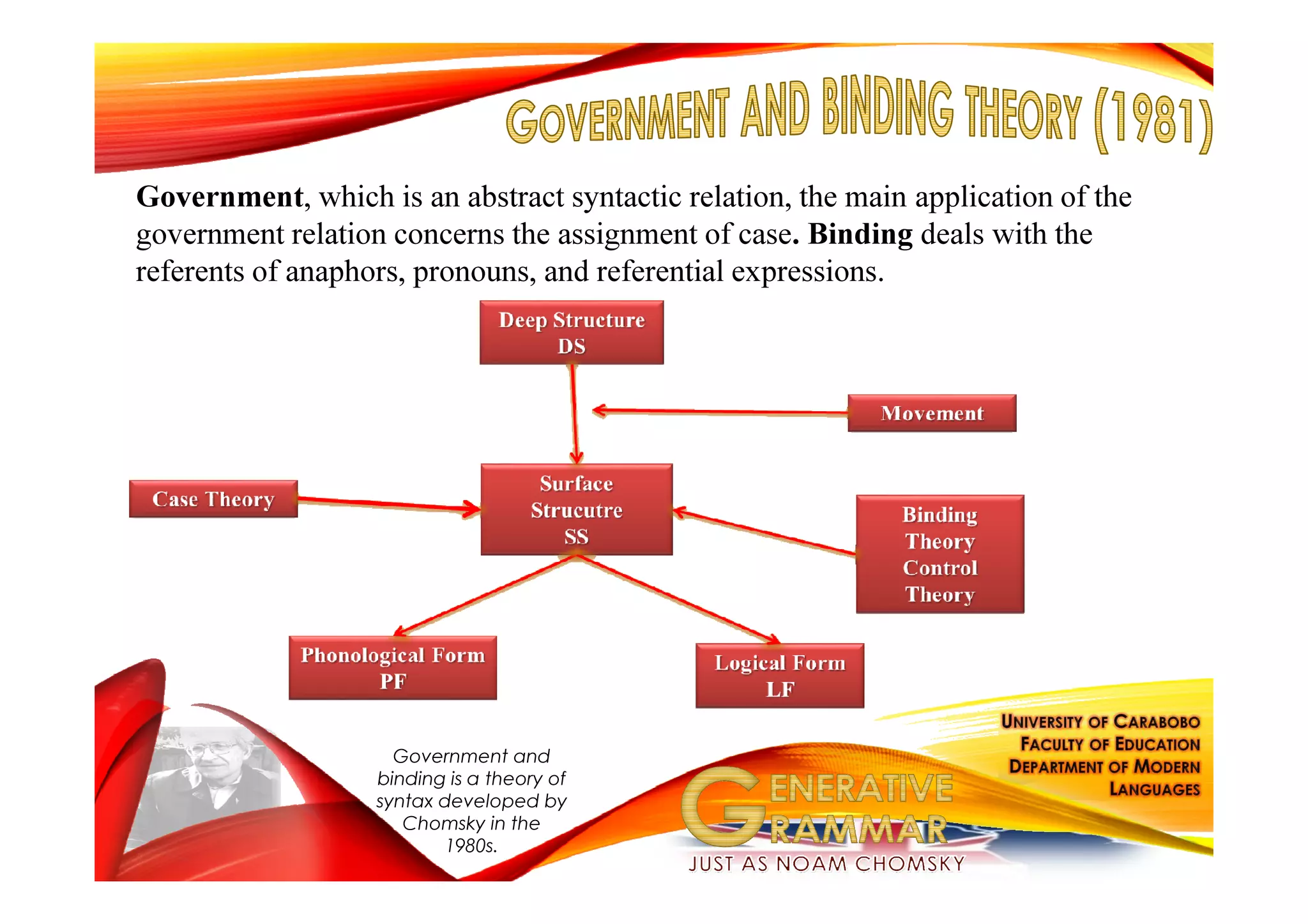
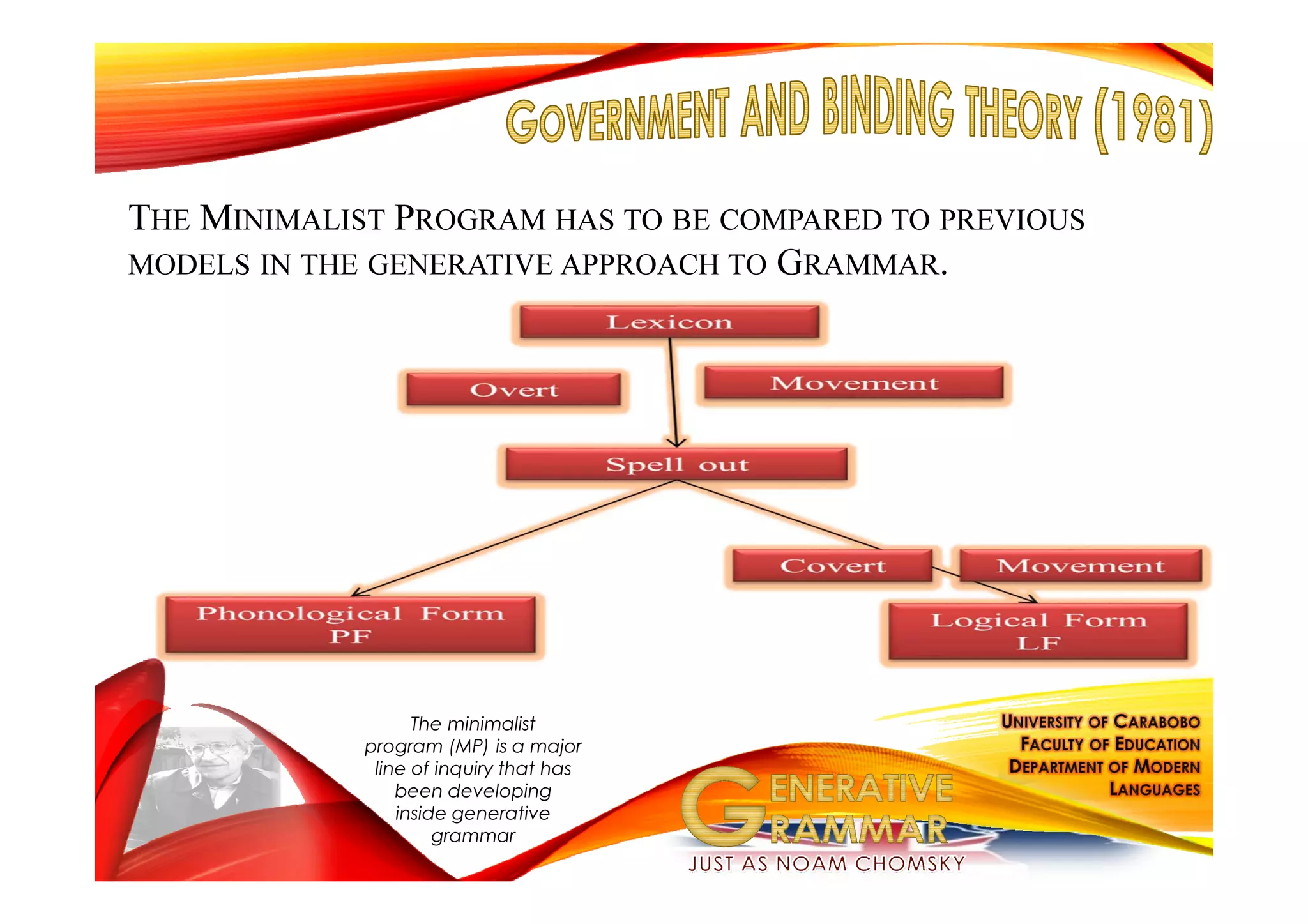
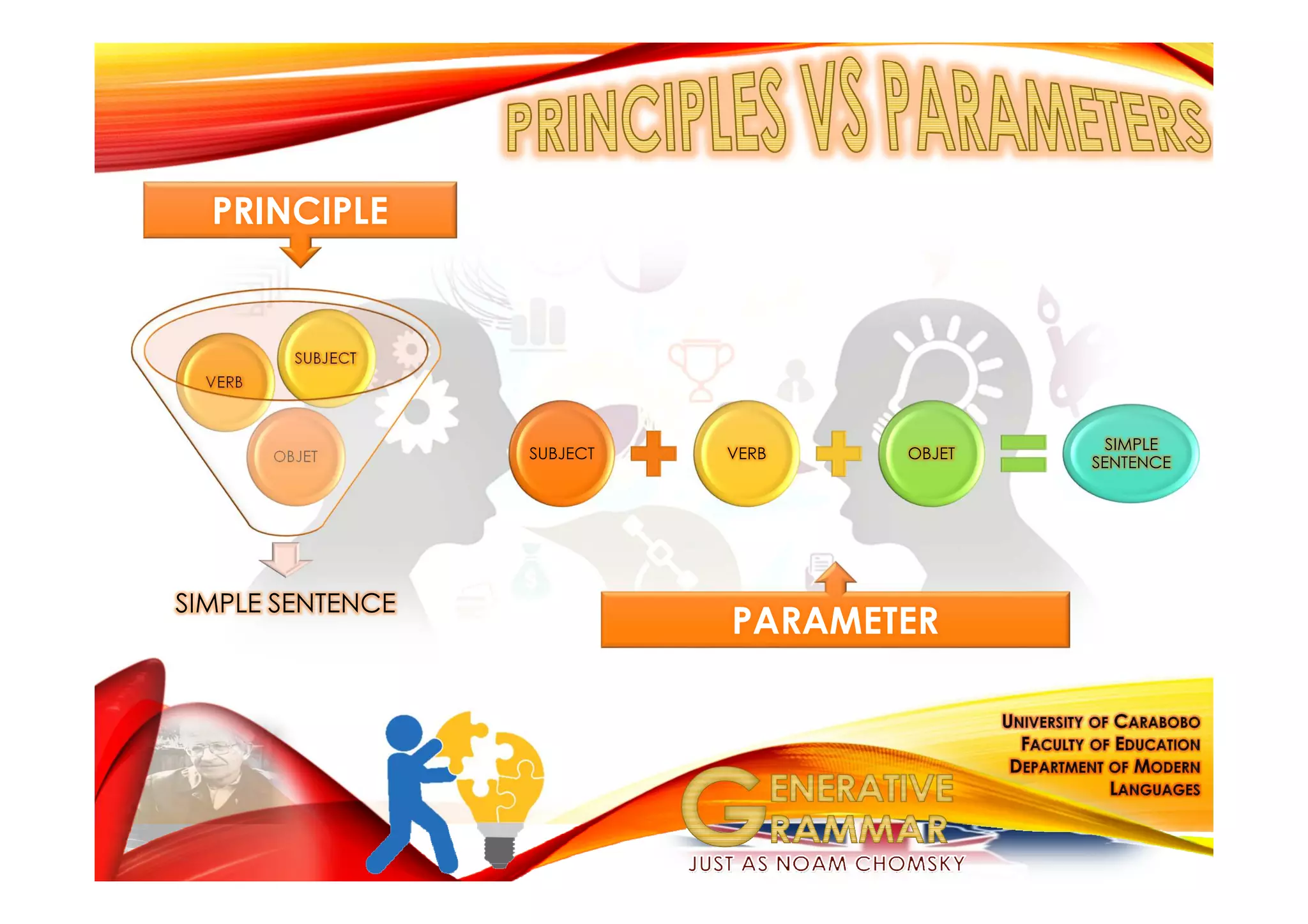
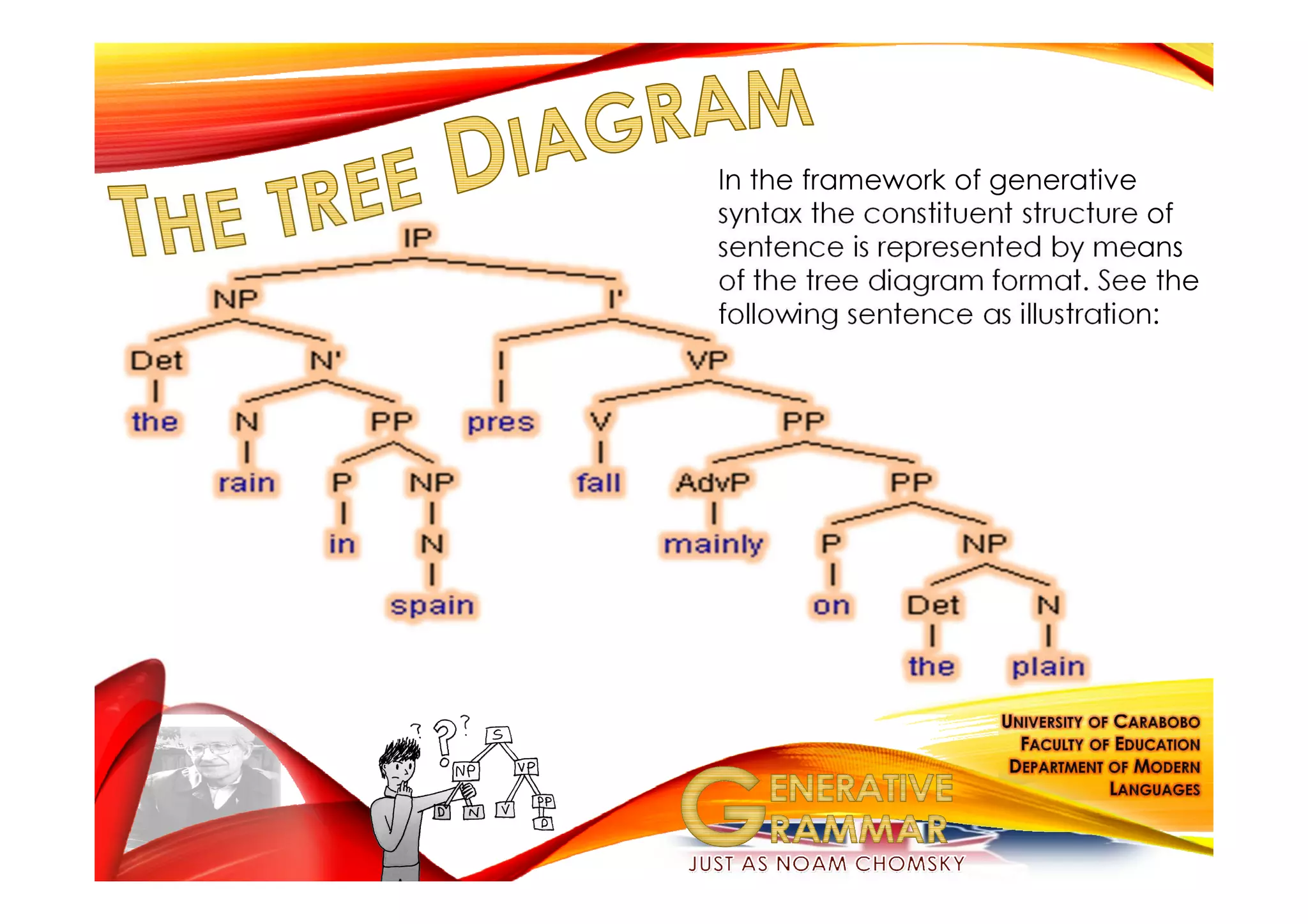
Generative grammar, as defined by Noam Chomsky, is a framework for understanding the rules that govern the formation of grammatical sentences. It encompasses various components, including syntax, semantics, and phonology, and introduces concepts like kernel sentences, deep structures, and the minimalist program for language theory. Chomsky's work seeks to describe children's innate knowledge of language and the underlying principles that all human languages share.