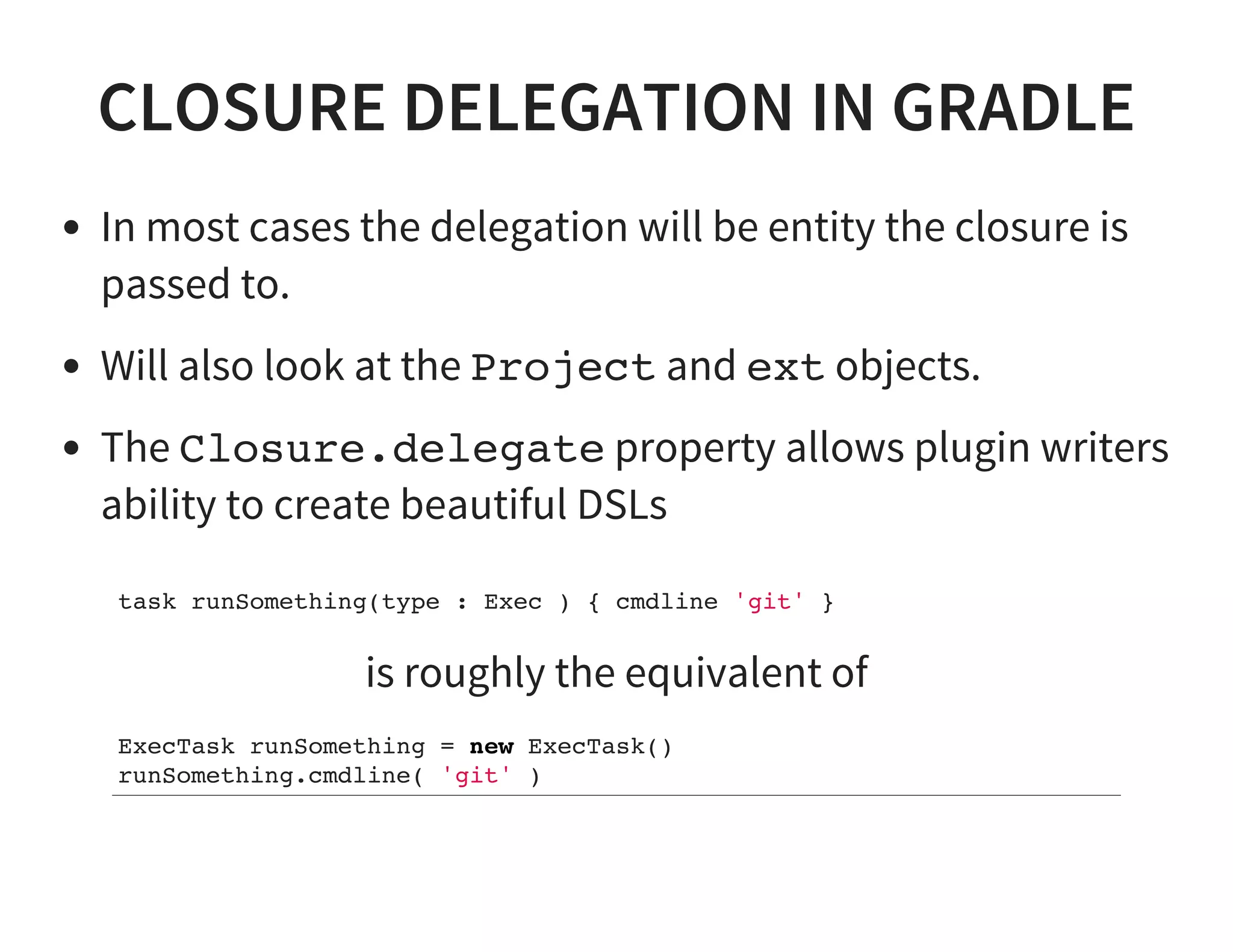
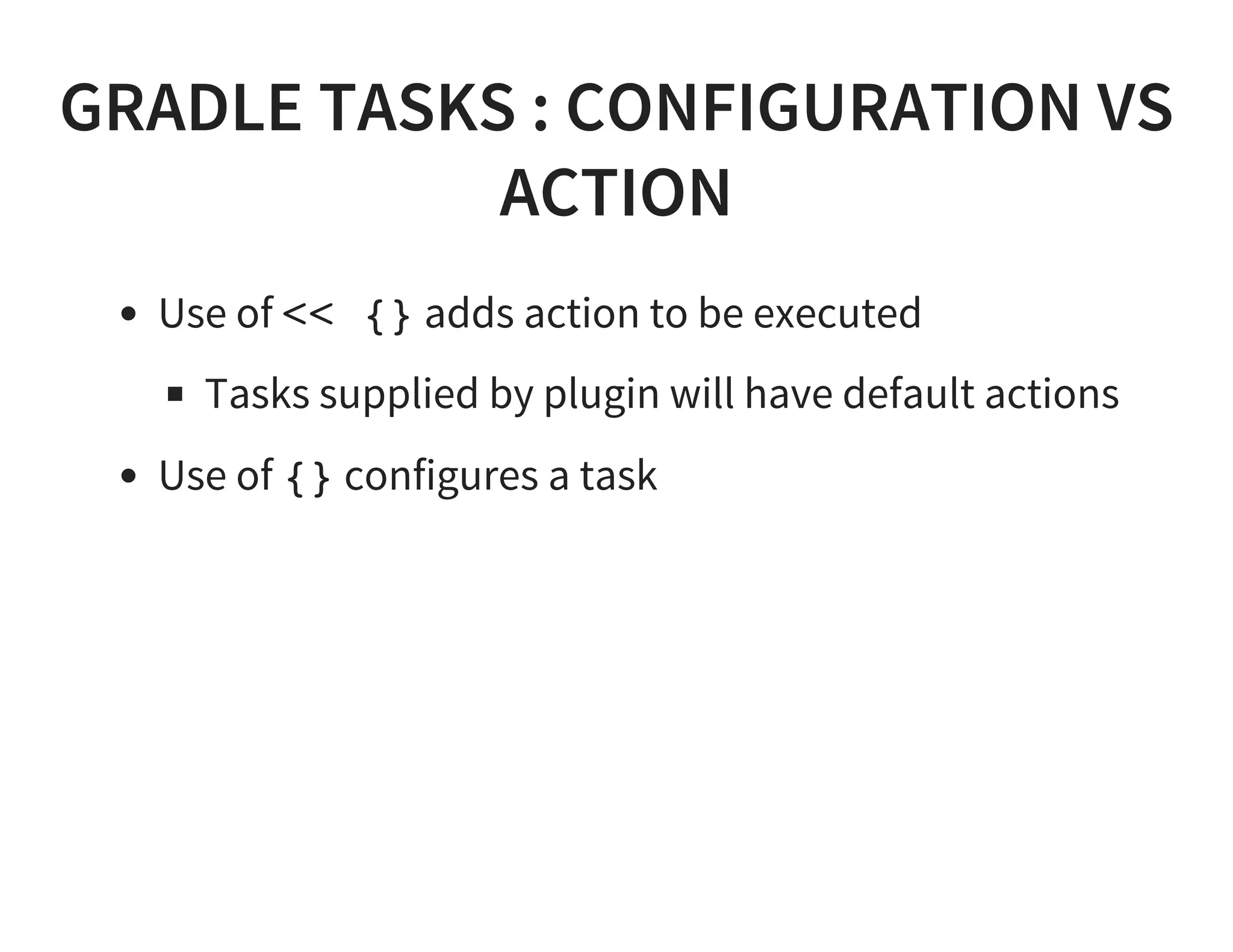
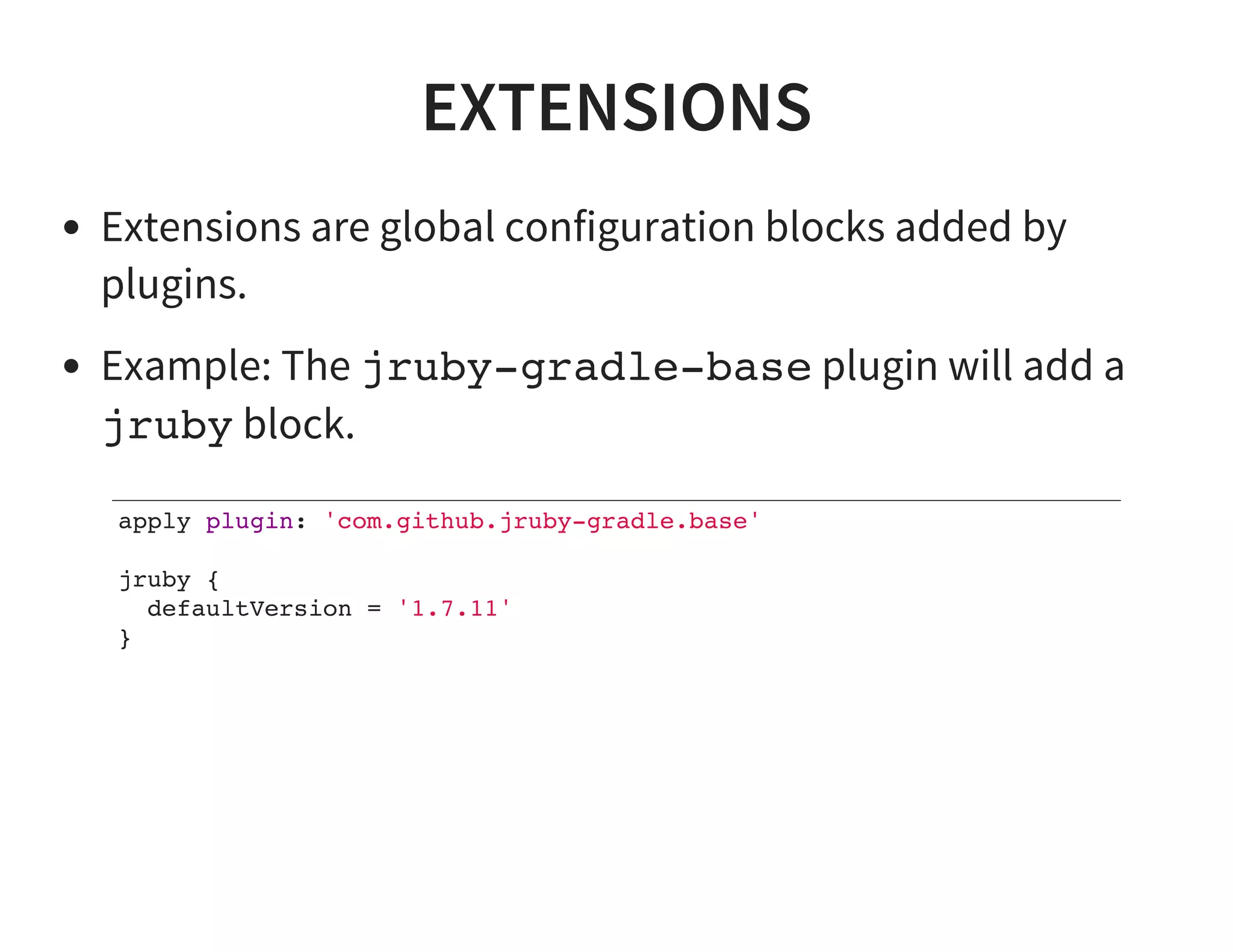
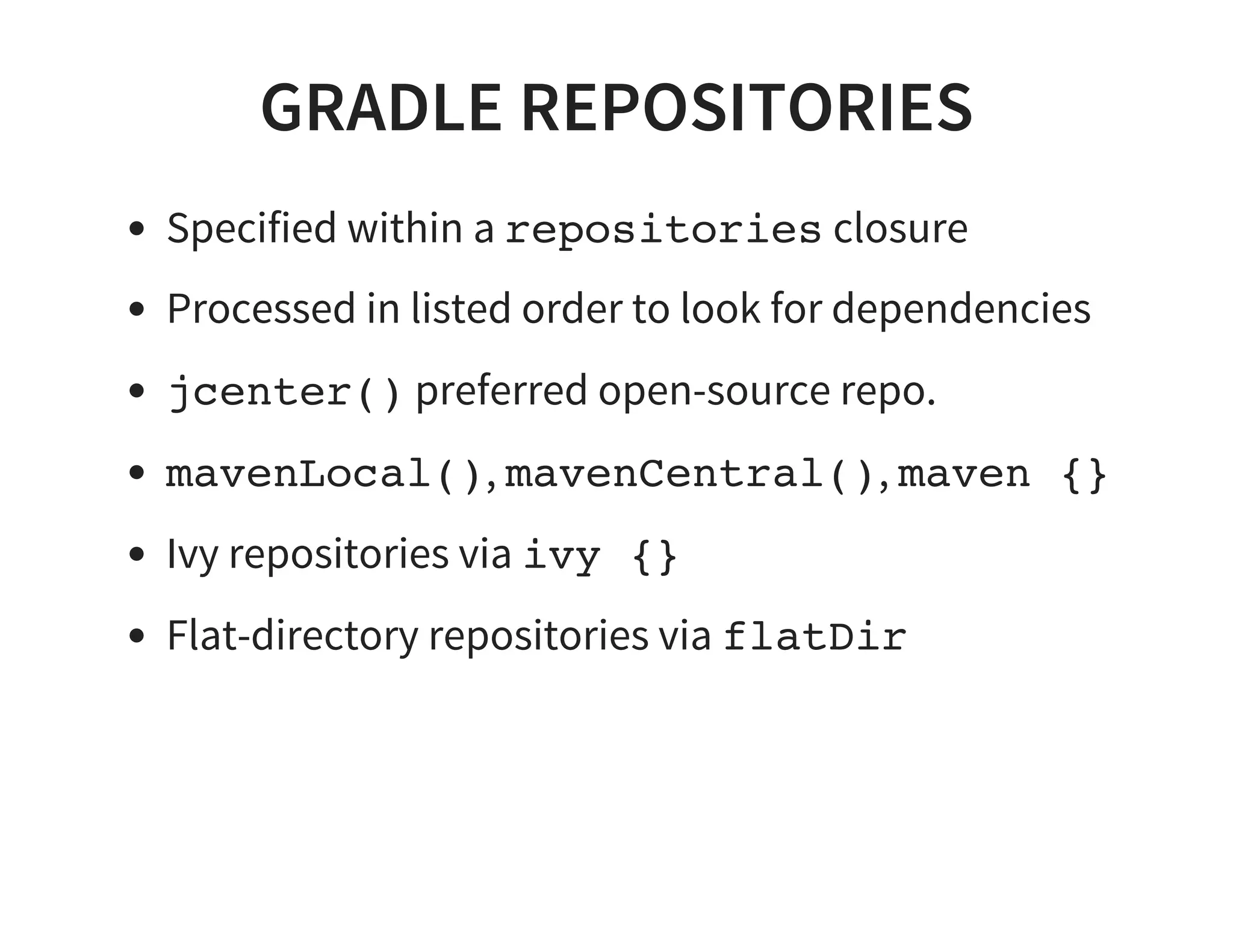
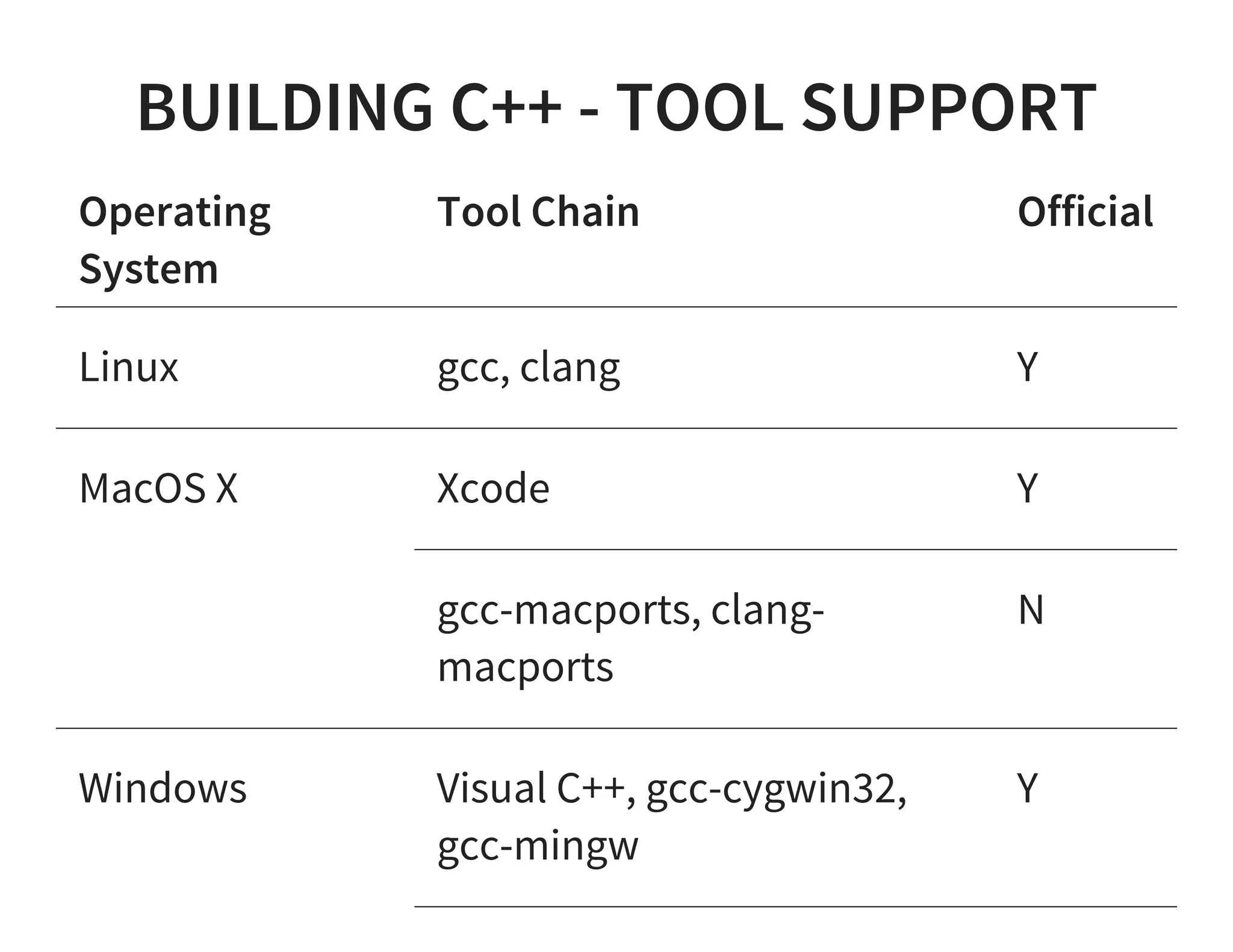
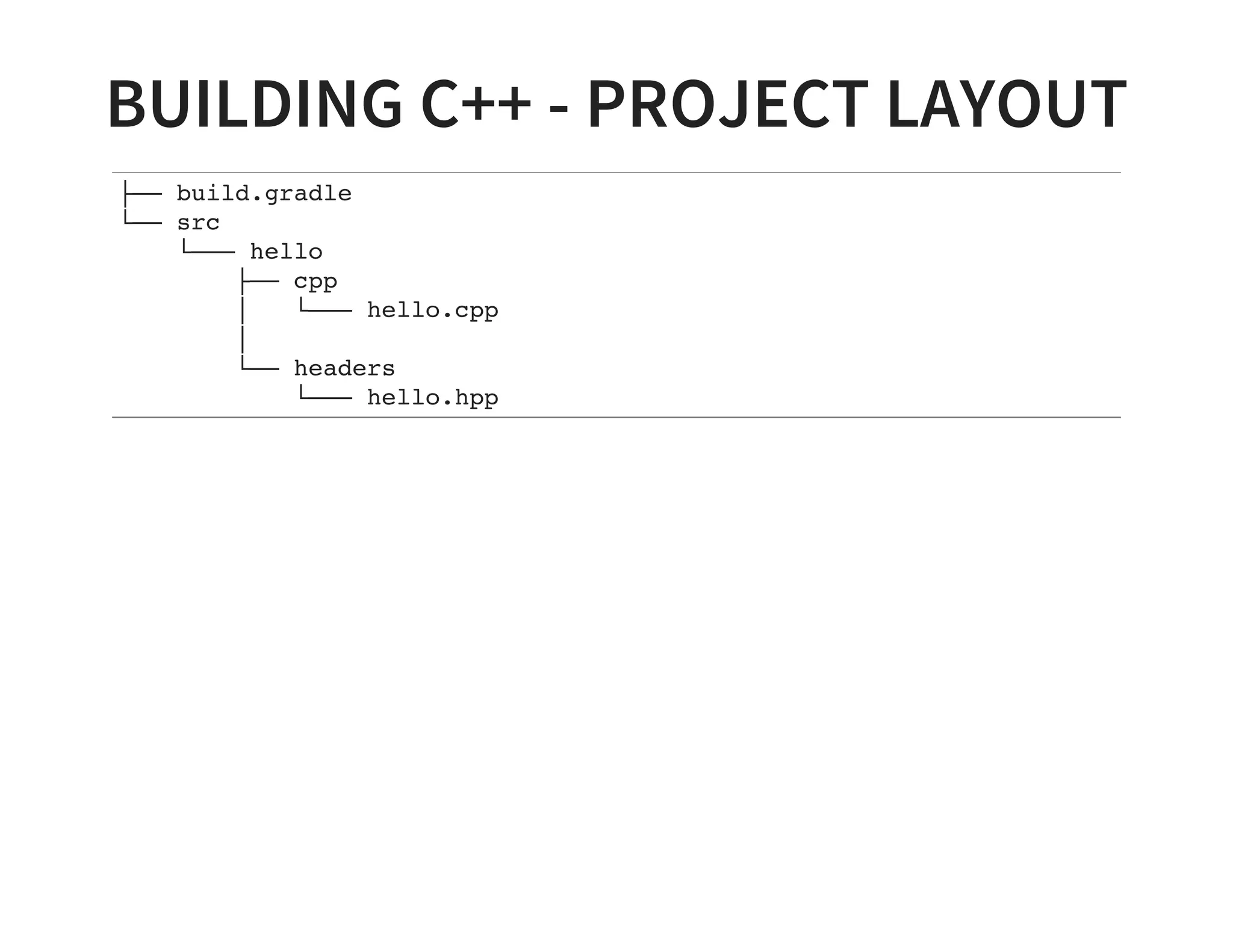
This document discusses using Gradle for building projects in multiple languages. Gradle's domain specific language is based on Groovy, which allows for concise syntax. Gradle supports building Java, C++, Ruby, and other languages through plugins. It can also be used to build documentation and publish artifacts to repositories. Migrating from other build systems like Ant, Maven, and Make to Gradle is also discussed.






![MAPS IN GROOVY
Hashmaps in Groovy are simple to use
def myMap = [ plugin : 'java' ]
Maps are easy to pass inline to functions
project.apply( plugin : 'java' )
Which in Gradle can become
apply plugin : 'java'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gradleinapolyglotworld-151019215831-lva1-app6892/75/Gradle-in-a-Polyglot-World-8-2048.jpg)
![LISTS IN GROOVY
Lists in Groovy are simple too
def myList = [ 'clone', ''http://github.com/ysb33r/GradleLectures' ]
This makes it possible for Gradle to do
args 'clone', 'http://github.com/ysb33r/GradleLectures'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gradleinapolyglotworld-151019215831-lva1-app6892/75/Gradle-in-a-Polyglot-World-9-2048.jpg)