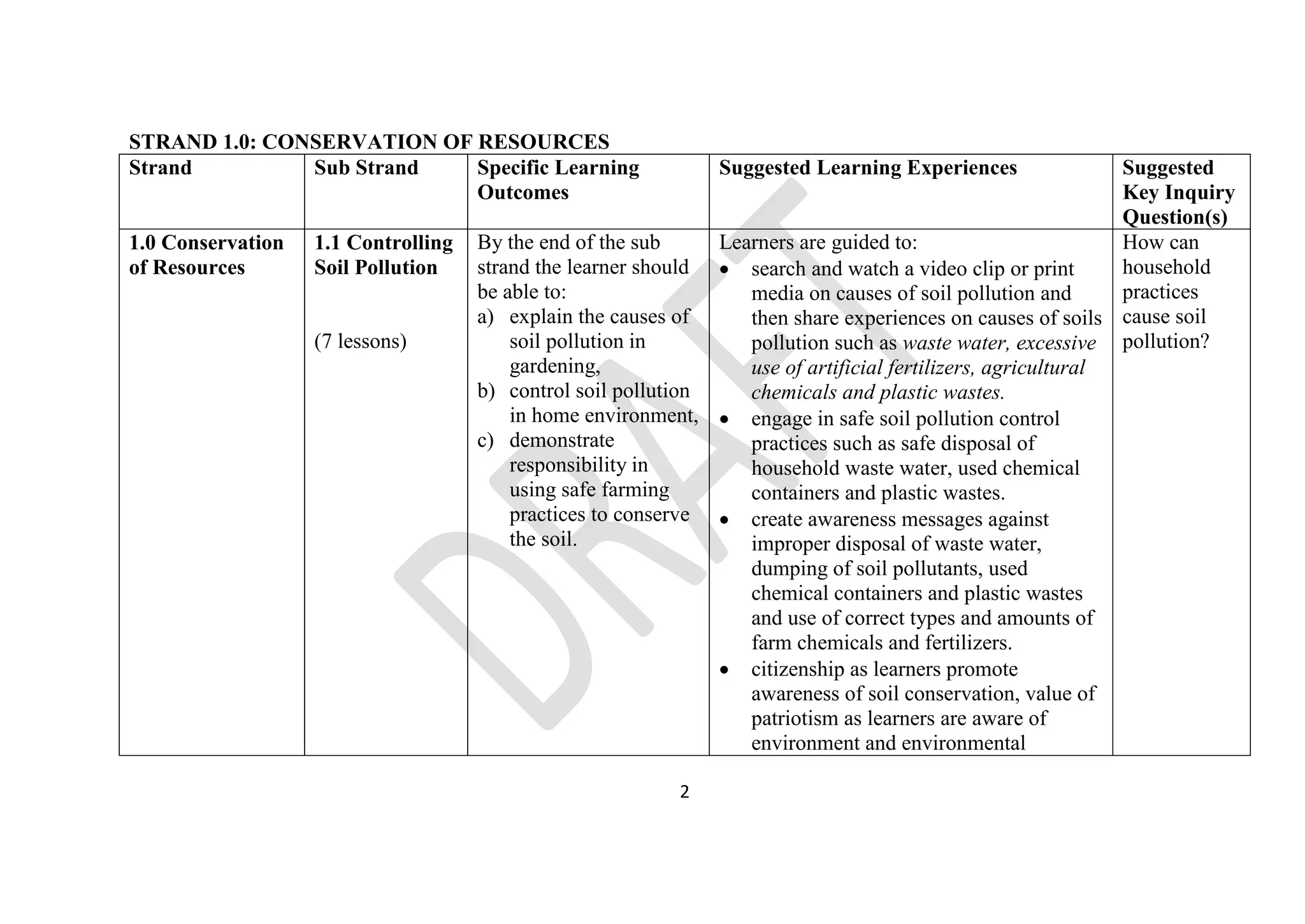
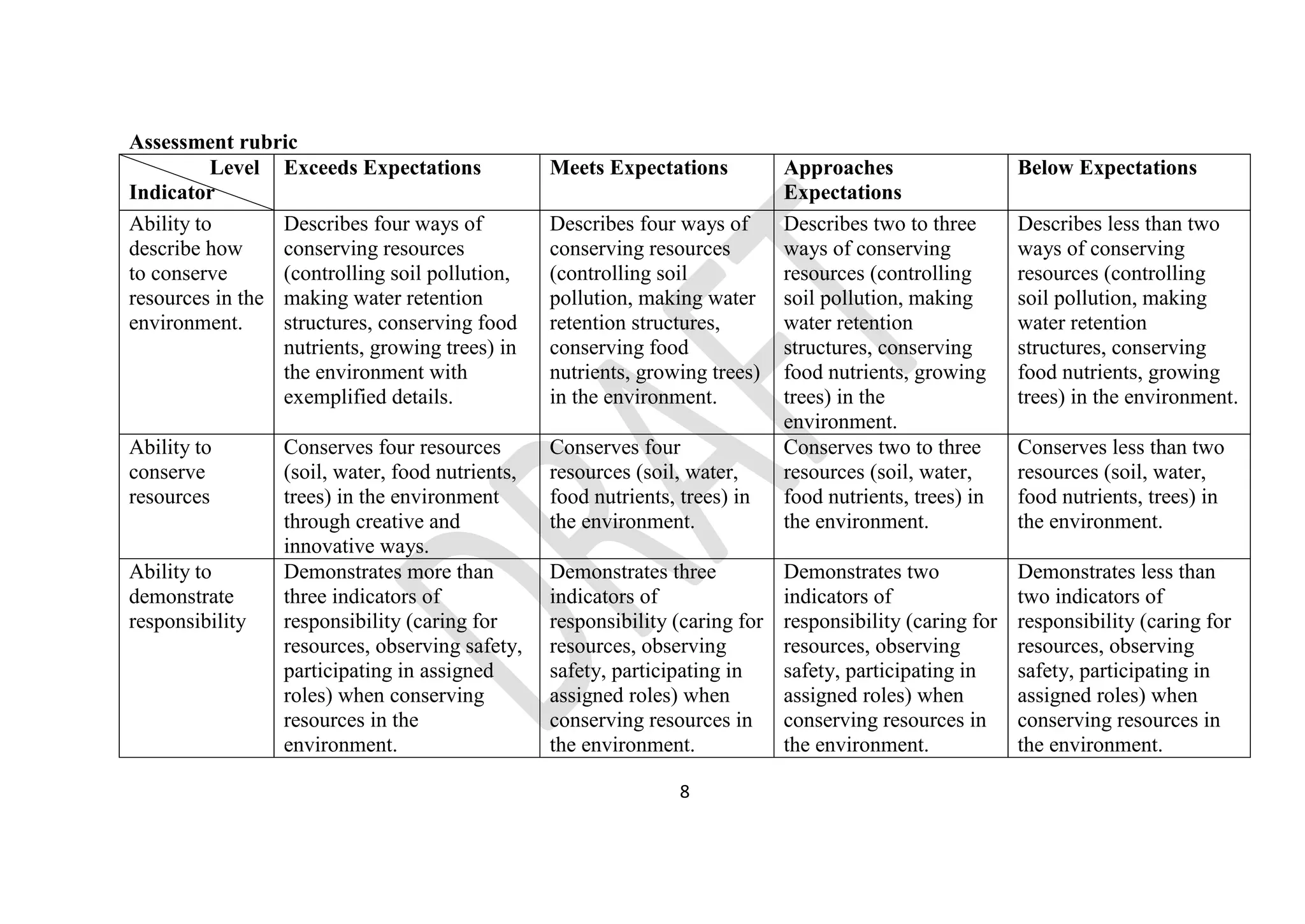
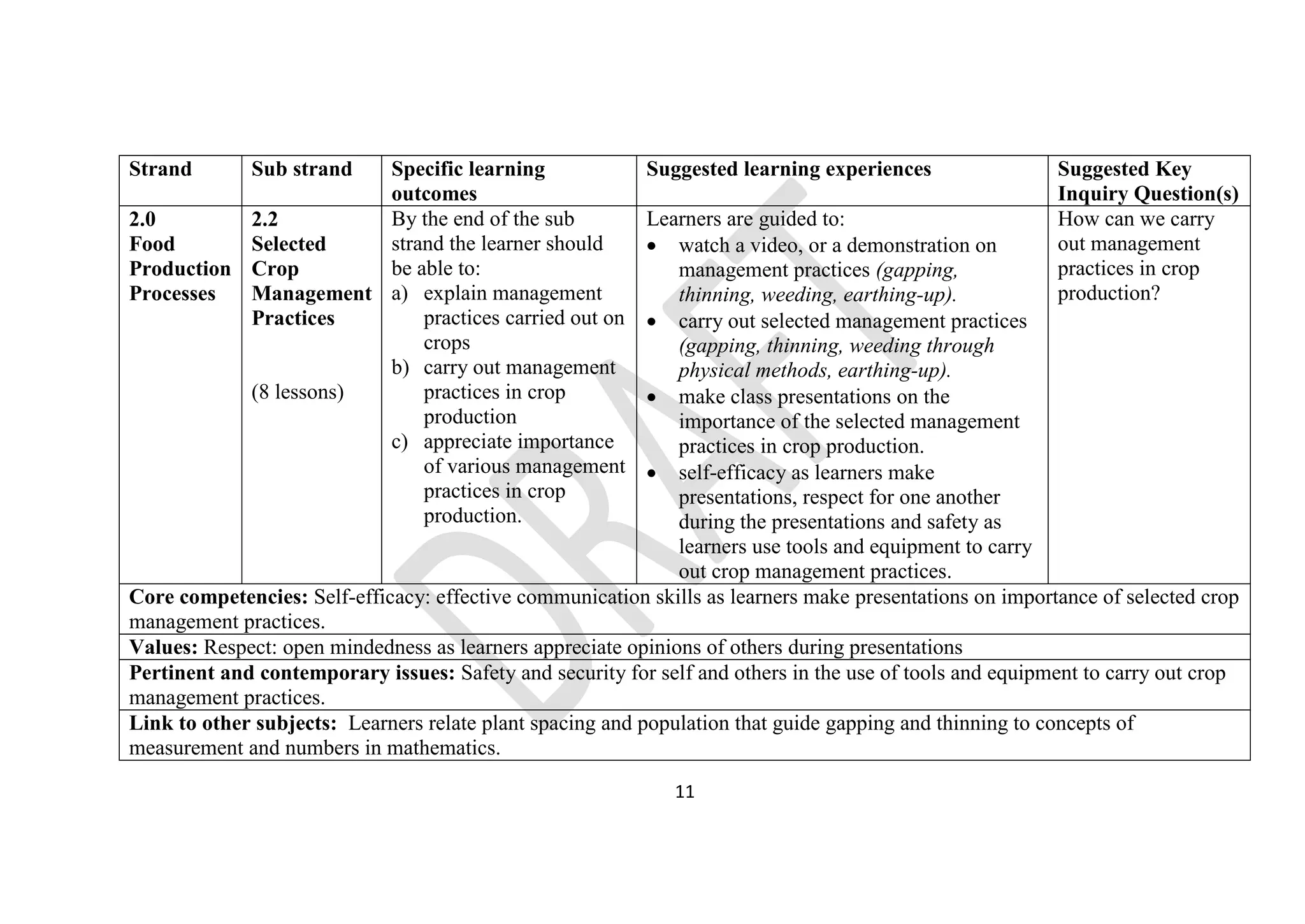
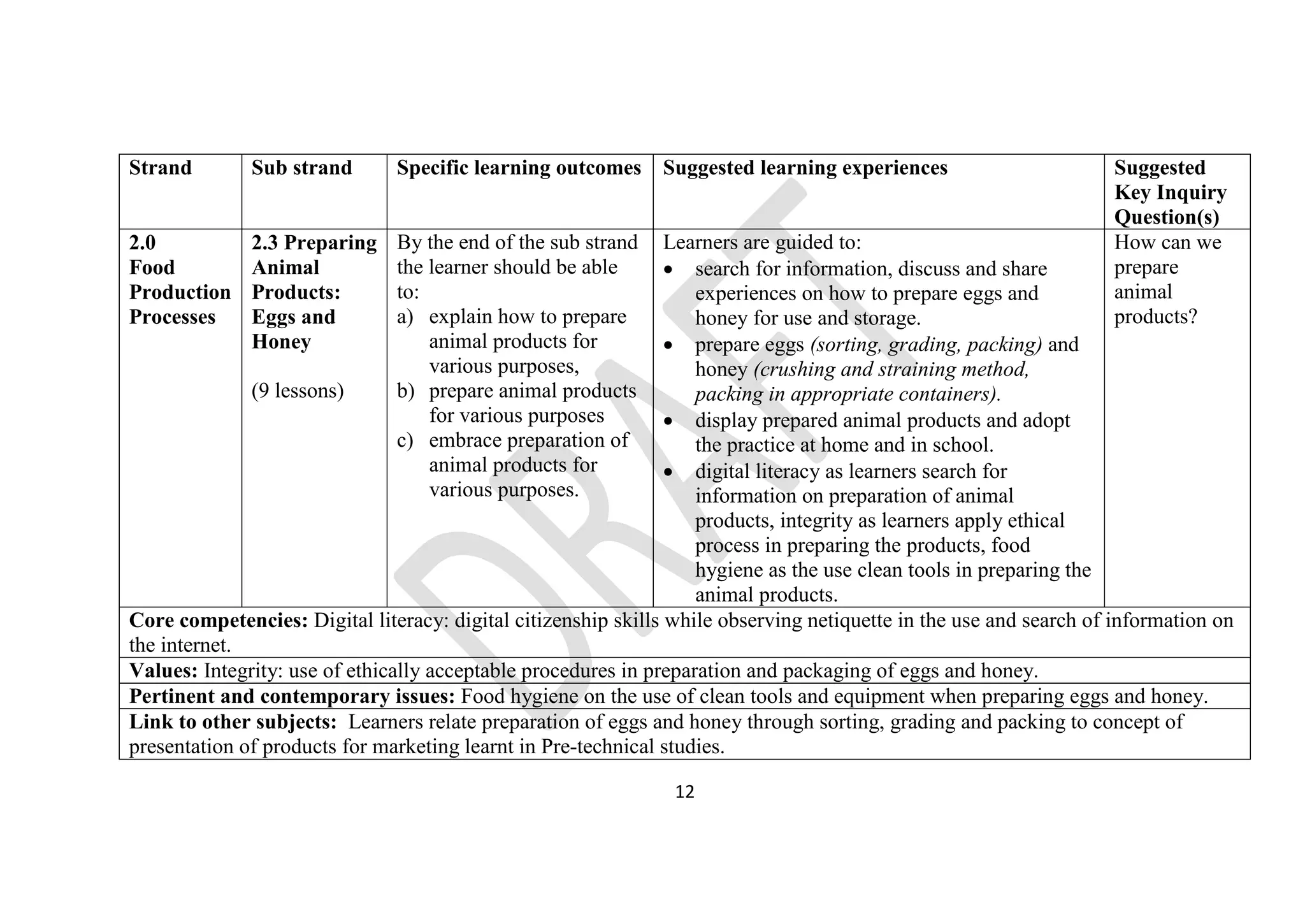
The document provides details on the junior school curriculum for agriculture and nutrition in Kenya. It includes 4 strands divided into sub-strands with specific learning outcomes. Strand 1 focuses on conservation of resources, including controlling soil pollution, constructing water retention structures, conserving food nutrients, and growing trees. Strand 2 covers food production processes such as preparing planting sites and managing crops. Strand 3 addresses hygiene practices like animal rearing and laundry. Strand 4 involves production techniques including sewing, constructing gardens, adding value to crops, and making soap.