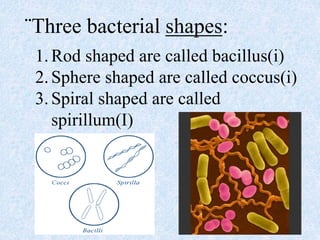
Bacteria are classified into two kingdoms: eubacteria and archaebacteria, with characteristics including unicellularity and prokaryotic structure. They reproduce asexually via binary fission and exchange genetic material through conjugation, leading to antibiotic resistance. Bacteria can be beneficial, such as those involved in food fermentation and nitrogen fixation, while others can be harmful pathogens.