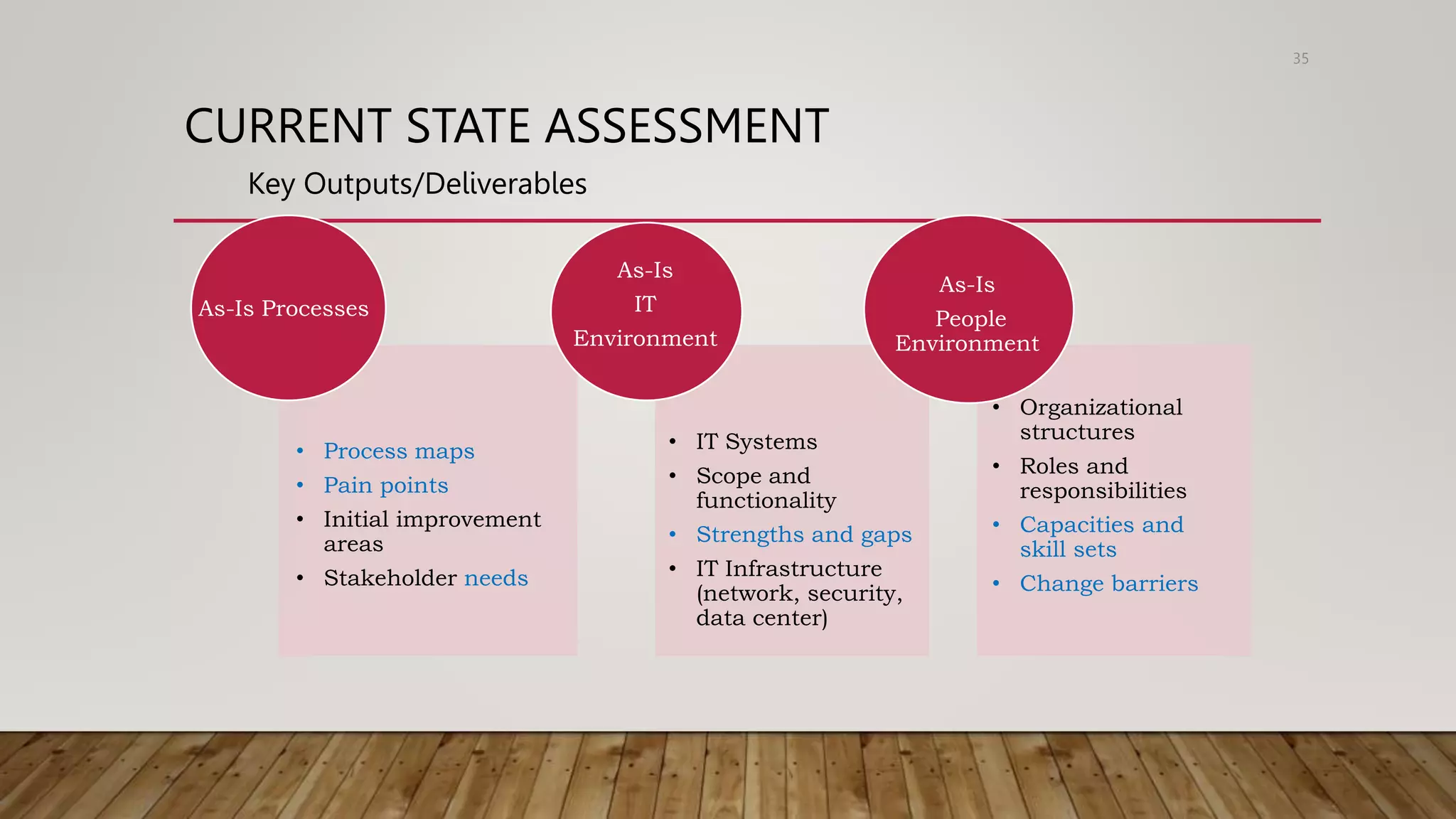
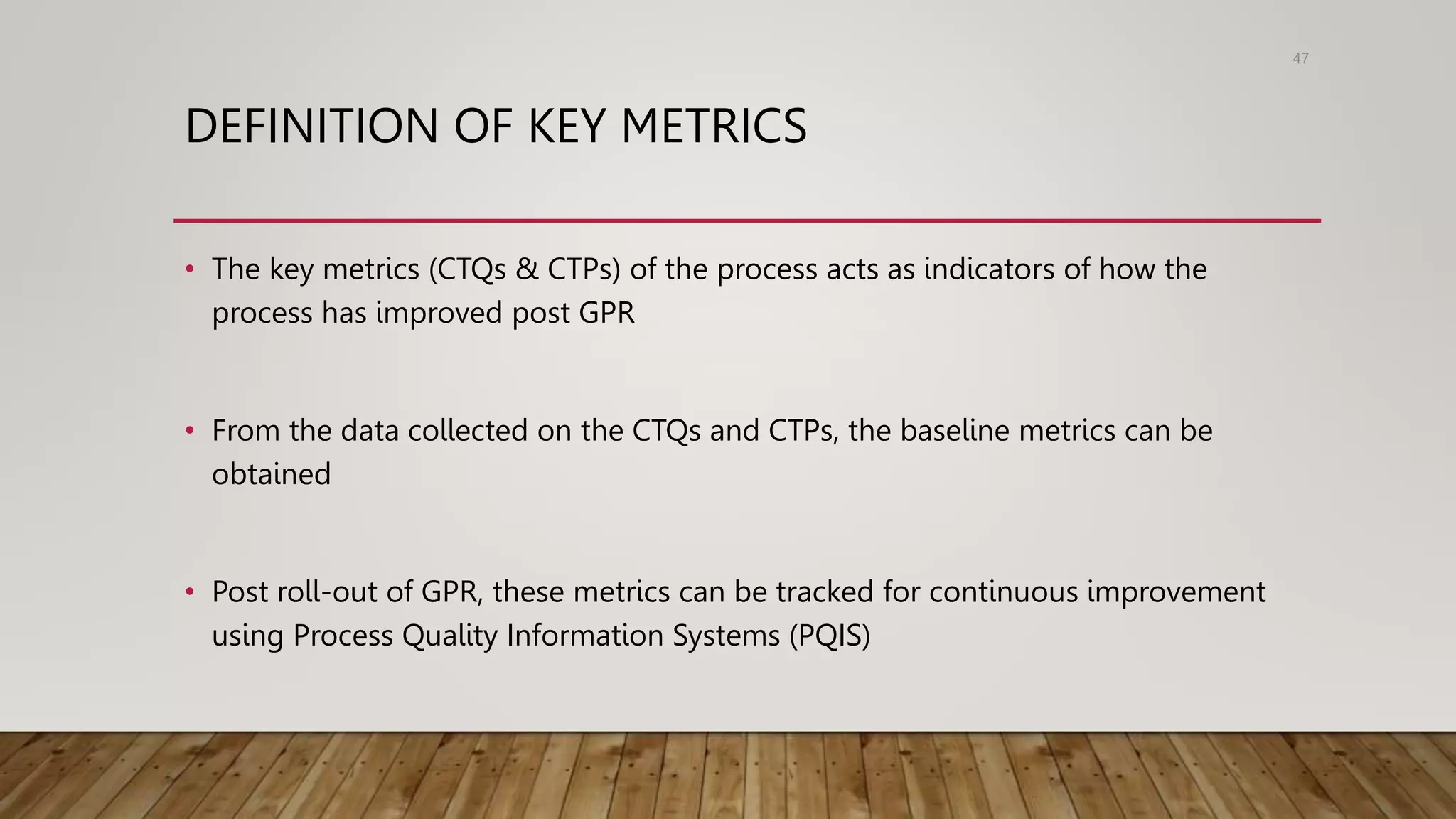
The document discusses government process reengineering (GPR). It defines GPR as the fundamental rethinking and radical redesign of government processes to achieve dramatic improvements in key performance areas like cost, quality, service, and speed. GPR is undertaken to address problems and needs of the organization or its customers, with the aim of improving overall service quality. Current government processes are described as inefficient due to issues like outdated legislation, department-centric rather than citizen-centric focus, complex rules, and large volumes of forms. The document outlines the GPR approach of assessing the current or "as-is" state, defining the ideal or "to-be" state, and measuring performance improvements.