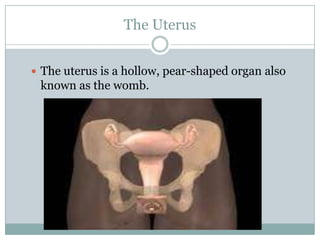
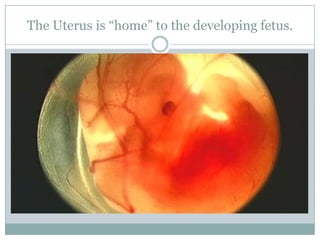
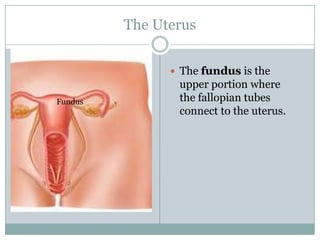
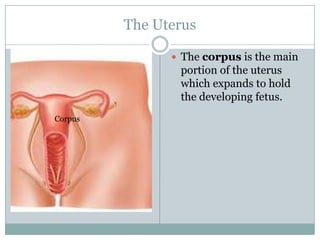
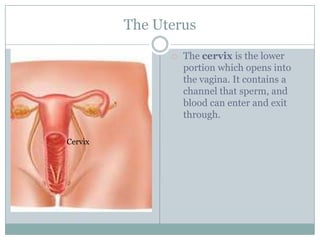
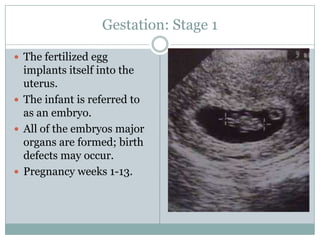
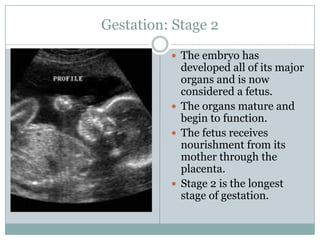
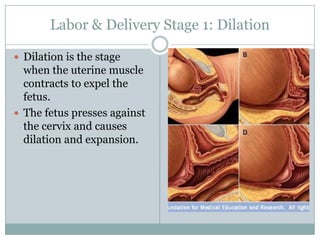
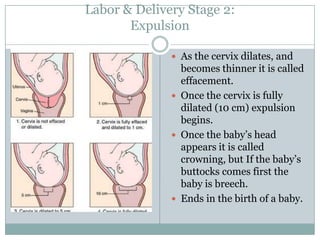
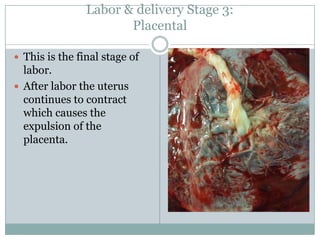
The document summarizes key aspects of the female reproductive system including the uterus, gestation, and the three stages of labor and delivery. The uterus has three main parts - the fundus, corpus, and cervix. Gestation lasts 40 weeks and has two stages: embryo development and fetal development. Labor and delivery involves three stages - dilation of the cervix, expulsion of the baby, and expulsion of the placenta.