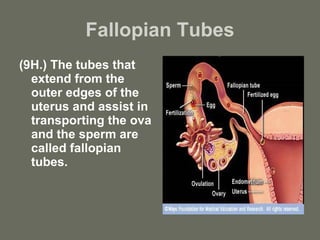
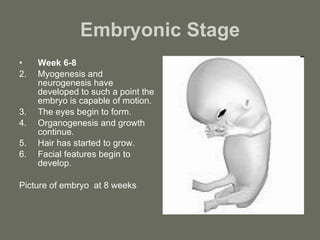
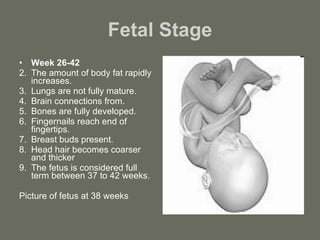
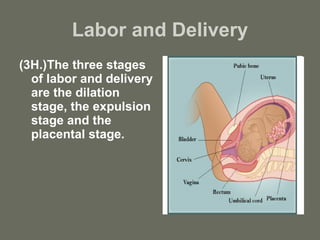
The document summarizes the key stages of pregnancy and labor. It describes the fallopian tubes and their role in transporting eggs and sperm. It then explains the three months of gestation, including the embryonic and fetal stages and key physical developments. Finally, it outlines the three stages of labor: the dilation stage where the cervix dilates; the expulsion stage where the baby is pushed through the birth canal; and the placental stage where the placenta is delivered.