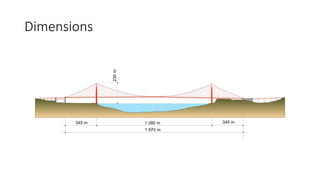
The Golden Gate Bridge is a suspension bridge connecting San Francisco to Marin County, declared one of the wonders of the modern world. Completed in 1937, it was the longest suspension bridge until 1964 and features a clearance of 67 meters to allow large ships to pass. The bridge is also known for its challenging construction conditions, including high winds and seismic risks, and has become a popular site for pedestrians and cyclists.