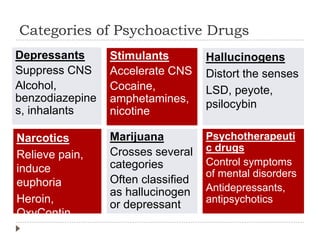
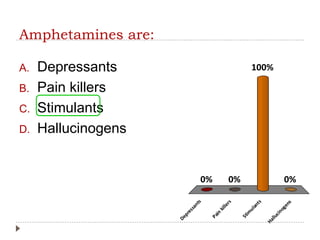
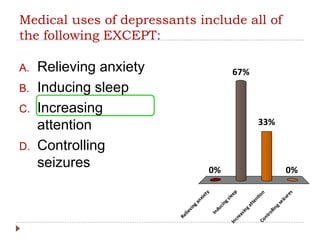
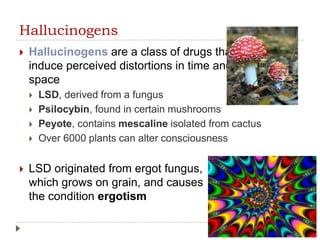
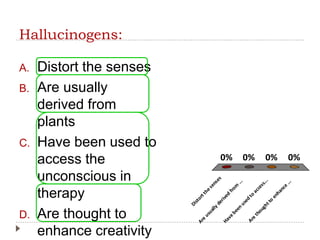
This document provides an overview of key concepts and definitions related to psychoactive drugs and substances. It begins with definitions of terms like drug, psychoactive drug, misuse, abuse, addiction, dependency, and substance use disorder. It then covers historical perspectives and categories of drugs, including depressants, stimulants, narcotics, hallucinogens, and sedative-hypnotic drugs. For each drug category, brief histories are provided on substances like alcohol, marijuana, opium, morphine, heroin, cocaine, amphetamines, barbiturates, benzodiazepines, and inhalants. Medical uses are discussed along with notes on popularization and criminalization of certain drugs over time.