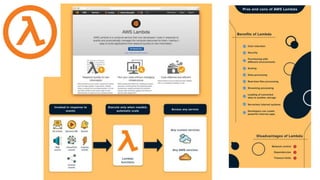
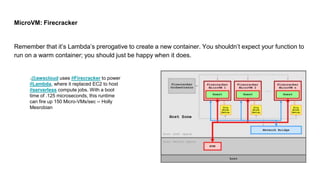
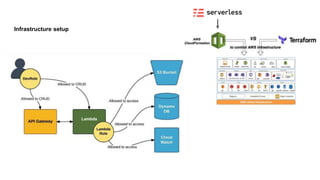
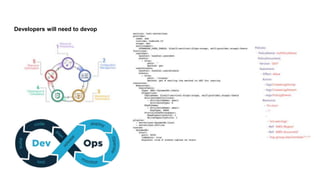
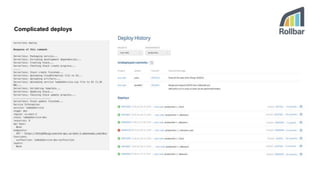
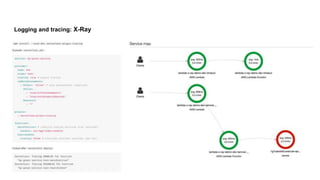
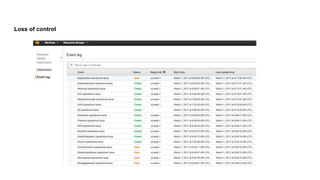
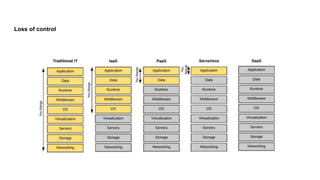
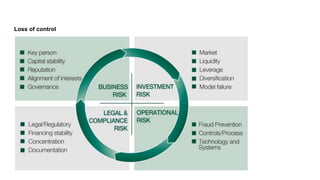
This document discusses the threats and opportunities of going serverless on AWS. It covers limitations on deployment package sizes for Lambda functions, how Firecracker is used to power Lambda, and that serverless may be cheaper but not necessarily simpler due to underlying complexity. It also discusses development patterns like microservices and monolithic approaches. Frameworks like AWS SAM and the Serverless Framework are presented. Considerations around infrastructure setup, local development environments, security, logging/tracing, and loss of control are also covered. Opportunities of serverless like automated infrastructure management and cost/time savings are highlighted.