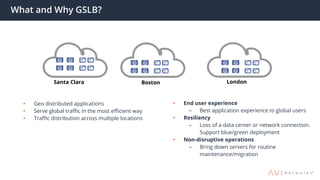
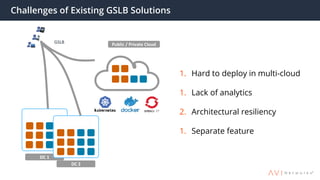
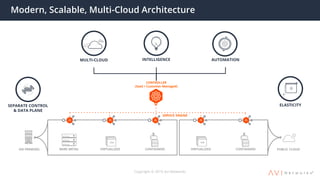
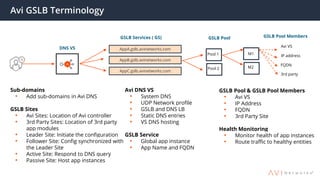
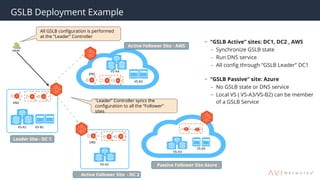
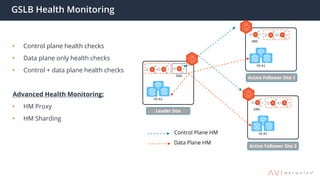
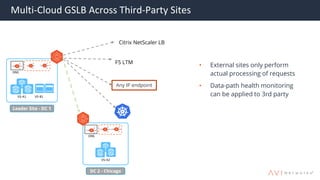
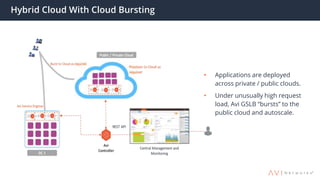
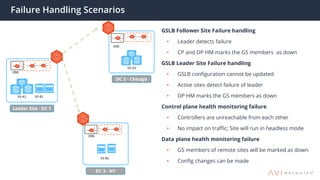
The document provides an overview of multi-cloud global server load balancing (GSLB) by Avi Networks, highlighting its use cases such as multi-cloud deployments, cloud bursting, and failure handling. It discusses the architecture, health monitoring requirements, and the challenges of existing GSLB solutions, emphasizing the benefits of resilience, non-disruptive operations, and analytics. The document also outlines the roles of leader and follower sites in GSLB configurations and the implications of site failures on traffic management.