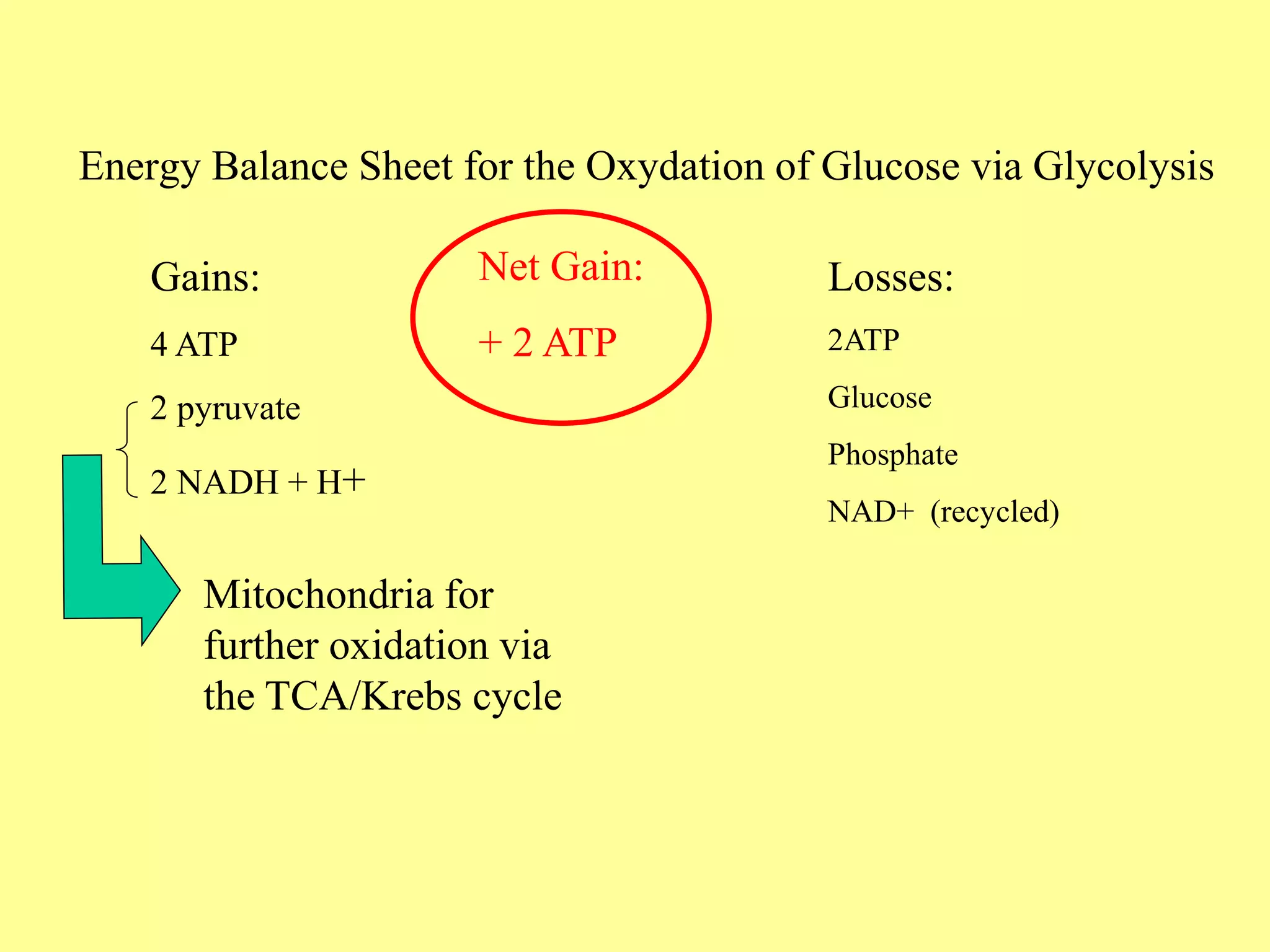
Glycolysis is the breakdown of sugars like glucose and fructose to extract energy. It occurs in the cytoplasm of cells and involves a series of 10 enzyme-catalyzed reactions. Glycolysis converts glucose into pyruvate, producing a small amount of ATP directly. It also generates NADH which drives ATP production during later stages of cellular respiration. Glycolysis is the first step in extracting energy from glucose under both aerobic and anaerobic conditions.