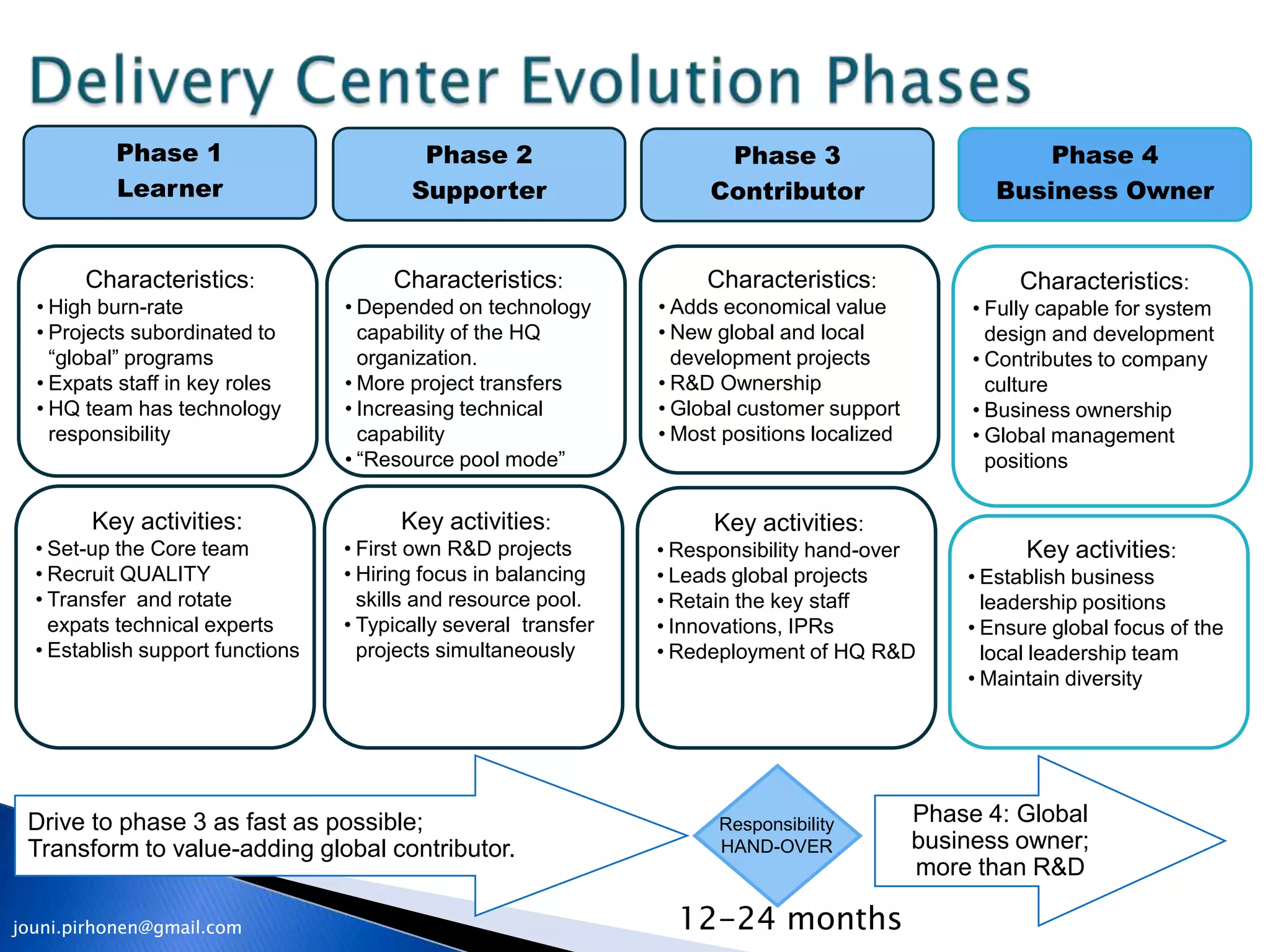
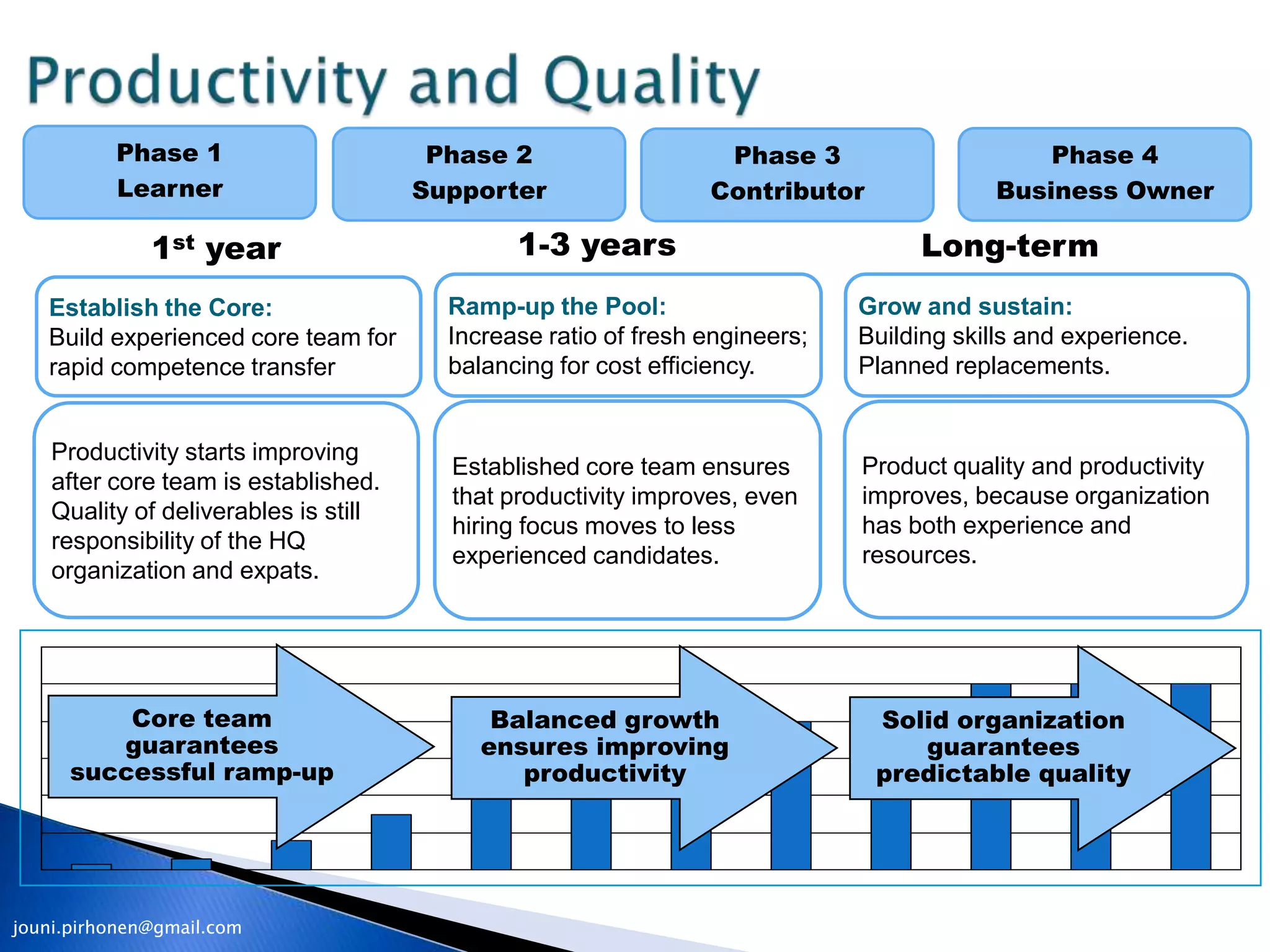
The document outlines a 4-phase model for developing knowledge-intensive organizations globally: 1) Learner phase focuses on establishing an experienced core team, 2) Supporter phase increases local hiring while retaining core team, 3) Contributor phase hands over responsibility to local team, and 4) Business Owner phase establishes local leadership and operational accountability. Key aspects include balancing global costs, skills, and risks while transferring tacit knowledge through expatriate assignments and competence development.