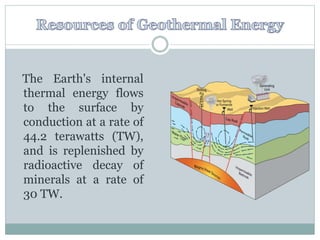
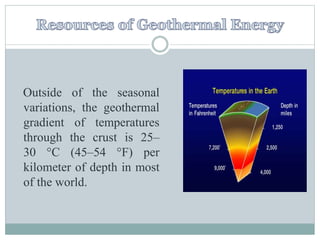
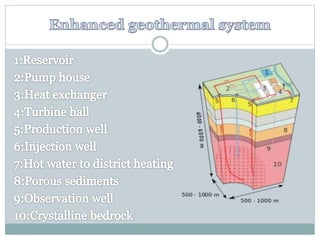
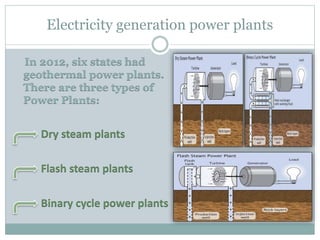
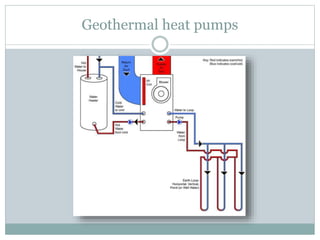
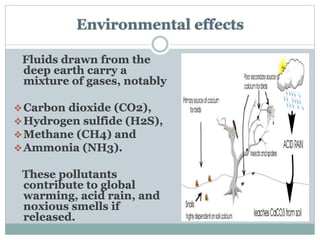
Geothermal energy is the thermal energy from the Earth's surface, utilized for heating and electricity generation since ancient times, with its first dedicated power plant established in Italy in 1911. As of 2010, 10,715 megawatts of geothermal power are operational across 24 countries, primarily in the USA, Philippines, and Indonesia, contributing to greener electricity production compared to fossil fuels. However, geothermal plants can still emit greenhouse gases, albeit at much lower levels than traditional energy sources.