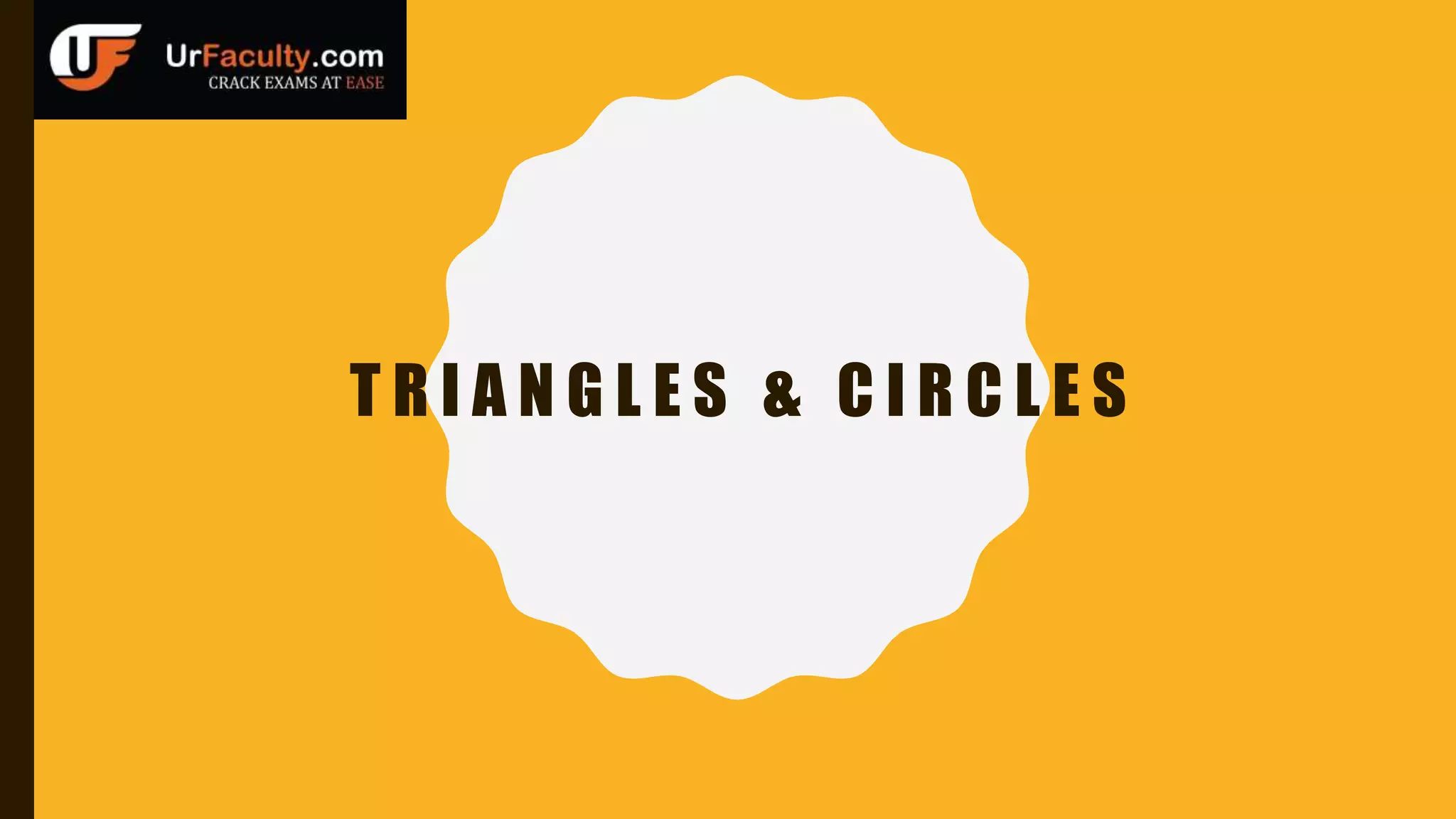
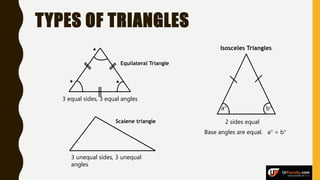
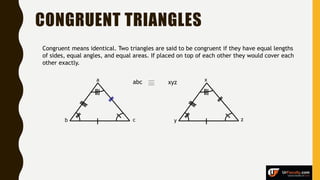
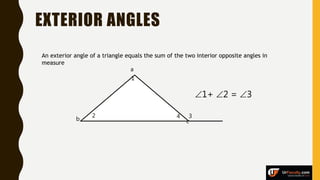
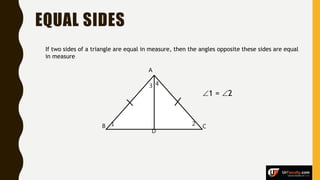
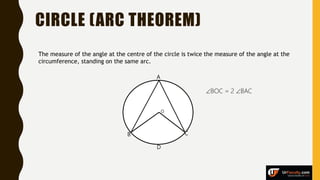
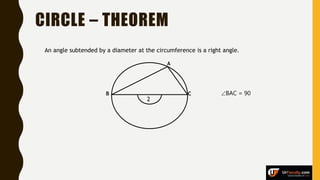
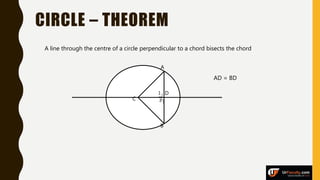
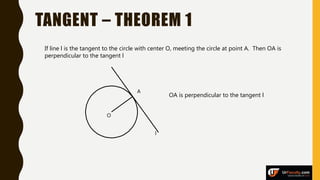
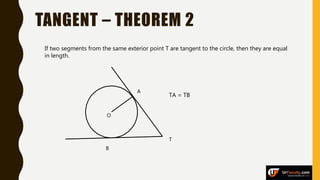
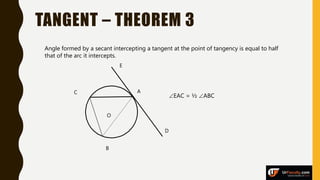
The document provides an overview of various types of triangles, including equilateral, isosceles, and scalene triangles, along with the properties of congruent triangles. It also discusses key circle theorems, such as the relationship between angles at the center and circumference, properties of tangents, and chord bisection by a diameter. These geometric principles are significant in understanding triangle and circle properties.