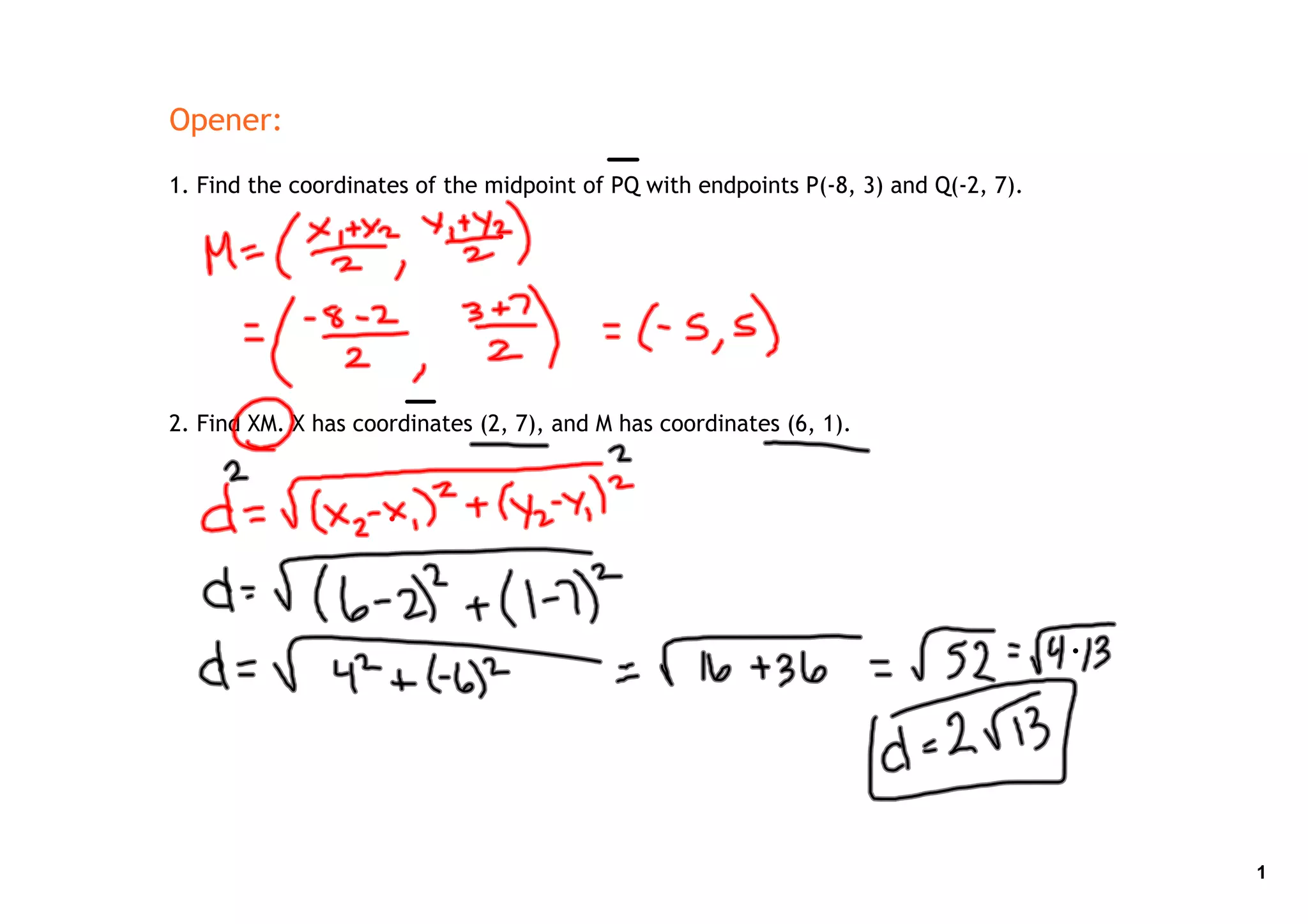
1. The document provides instructions and examples for solving problems involving midpoint and distance formulas, as well as transformations in the coordinate plane. Practice problems are given for finding midpoints and distances between points, as well as homework instructions.
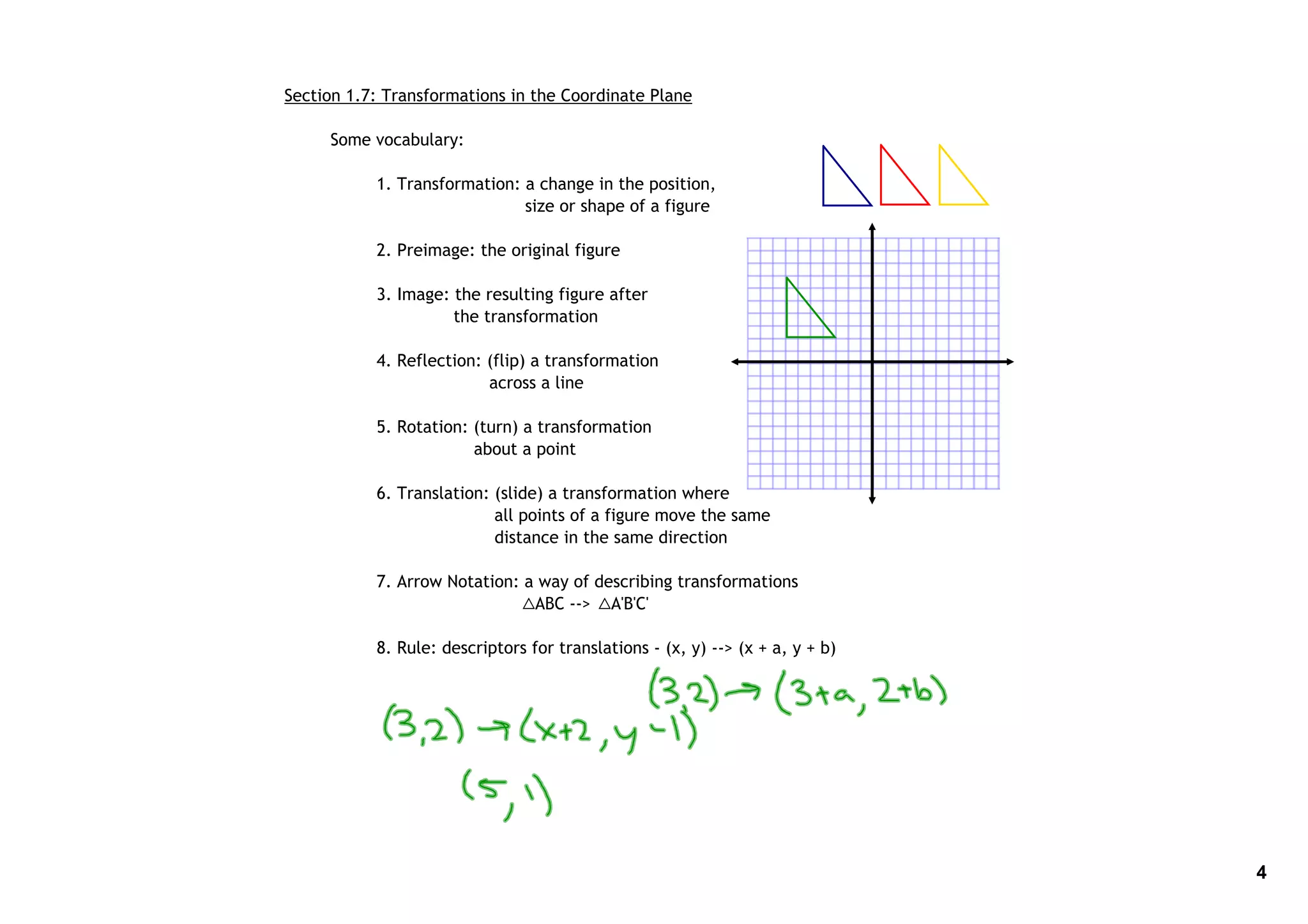
2. Key terms related to transformations are defined, including reflection, rotation, translation, arrow notation, and the rule for describing translations.
3. Examples are given of transformations, including reflections across lines and rotations about points. Formulas and notation for describing translations are also provided.