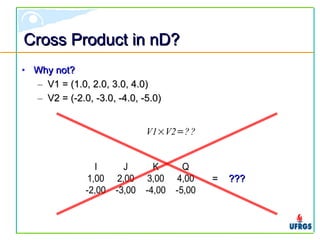
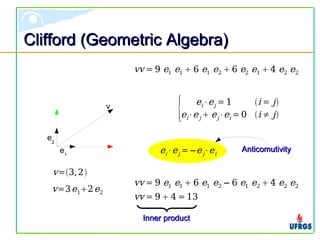
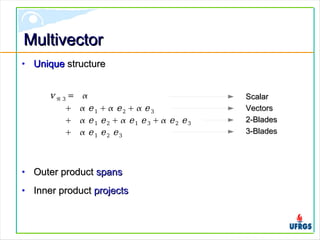
The document discusses geometric algebra, which provides a unified mathematical framework for geometry. It introduces multivectors as the unique structure in geometric algebra, formed from outer and inner products of basis vectors. Operations on multivectors like products, inversions, and joins are described. Implementations of geometric algebra aim to efficiently represent multivectors with minimal memory. The document argues geometric algebra can eliminate diverse mathematical descriptions by providing a single framework for geometric applications.













![Future ReadingsFuture Readings [Dorst,[Dorst, 02a02a] [Vaz,] [Vaz, 9797]]
• Projection of blades andProjection of blades and RejectionRejection
• ReflectionReflection
• RotorsRotors
• ModelsModels
– HomogeneousHomogeneous model / Plücker coordinatesmodel / Plücker coordinates
– ConformalConformal modelmodel
• QuaternionsQuaternions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/geometric-algebra-1224338640583032-8-130422103942-phpapp01/85/Geometric-algebra-1224338640583032-8-17-320.jpg)
![GA FrameworksGA Frameworks
• GAViewerGAViewer: Geometric algebra computations and visualize: Geometric algebra computations and visualize
• GAPGAP: Geometric Algebra Package: Geometric Algebra Package [[Zaharia, 03Zaharia, 03]]
• GAIGEN: Code generator to Geometric AlgebraGAIGEN: Code generator to Geometric Algebra [[FontijneFontijne]]
• GluCat:GluCat: template classes to Clifford algebrastemplate classes to Clifford algebras
• GAGL:GAGL: Geometric Algebra to OpenGLGeometric Algebra to OpenGL
• GEOMA: C++ Template Classes for Geometric AlgebrasGEOMA: C++ Template Classes for Geometric Algebras](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/geometric-algebra-1224338640583032-8-130422103942-phpapp01/85/Geometric-algebra-1224338640583032-8-18-320.jpg)
![Multivector ImplementationsMultivector Implementations
• GAGLGAGL
– Vector[8]Vector[8]
– Only in 3D.Only in 3D.
• GEOMAGEOMA
– Matrix [2Matrix [2kk
][2][2kk
]] where k = gradewhere k = grade
• GluCat:GluCat: ????
• GAPGAP
scalar , e1 , e2 , e3 ,
e1∧e2 , e1∧e3 , e2∧e3 ,
e1∧e2∧e3
scalar , e1 , e2 , e3 , e1∧e2 , e1∧e3 , e2∧e3 , e1∧e2∧e3
HMV HMV HMV
EBLADE EBLADE EBLADE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/geometric-algebra-1224338640583032-8-130422103942-phpapp01/85/Geometric-algebra-1224338640583032-8-19-320.jpg)
![Clean Multivector ImplementationClean Multivector Implementation
• Think OOThink OO with low memory usagewith low memory usage
• Two ClassesTwo Classes
– GAMultivectorGAMultivector
– GASpaceGASpace
• Inside GAMultivectorInside GAMultivector
– double[length]: where length is adouble[length]: where length is a compile timecompile time methodmethod
length=1∑
k=1
n
Cn ,k](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/geometric-algebra-1224338640583032-8-130422103942-phpapp01/85/Geometric-algebra-1224338640583032-8-20-320.jpg)

![So...So...
““... that it provides a single, simple mathematical framework... that it provides a single, simple mathematical framework
which eliminates the plethora of diverse mathematicalwhich eliminates the plethora of diverse mathematical
descriptions and techniques...”descriptions and techniques...”
[McRobie and Lasenby, 1999][McRobie and Lasenby, 1999]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/geometric-algebra-1224338640583032-8-130422103942-phpapp01/85/Geometric-algebra-1224338640583032-8-22-320.jpg)
