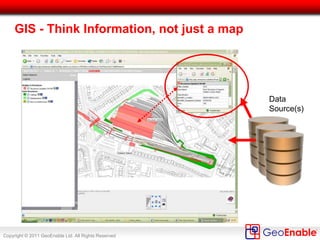
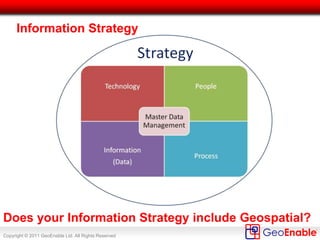
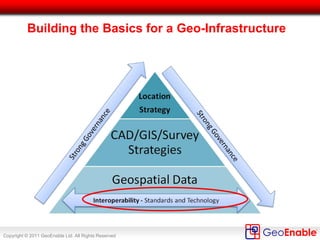
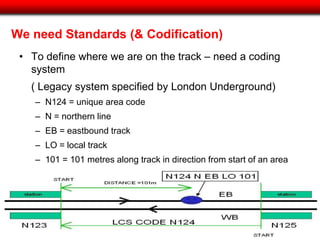
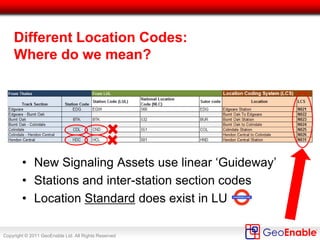
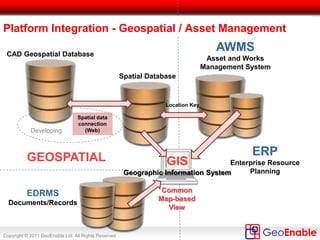
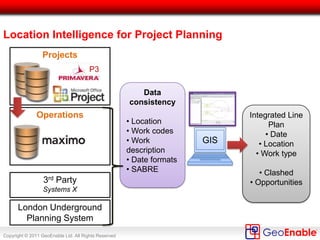
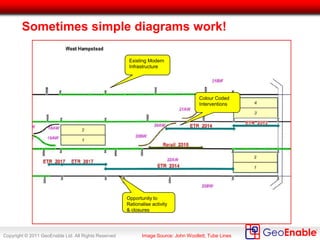
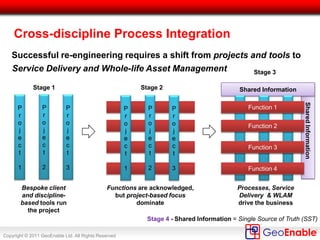
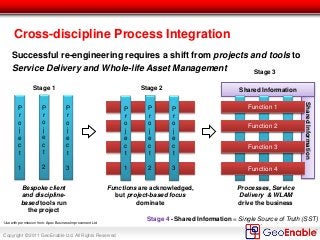
The document discusses the integration of geospatial information systems (GIS) with asset management, specifically in the context of Tube Lines, a company tasked with modernizing London's underground infrastructure. It outlines the benefits of geo-enablement, including improved planning, visualizing assets, and identifying trends through location intelligence. Key topics include location coding standards, the necessity of metadata for interoperability, and steps towards effective geo-enablement in asset management processes.