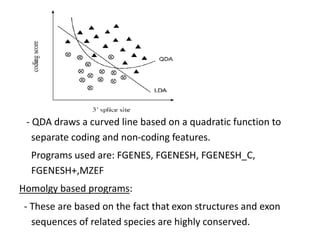
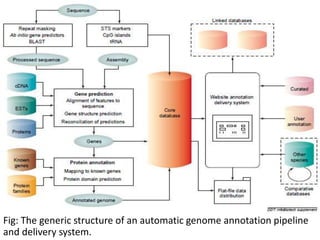
Genome annotation is the process of analyzing genomic DNA sequences to extract biological meaning and context. It involves two main steps - structural annotation, which locates gene elements like exons and introns, and functional annotation, which predicts the functions of gene products. Computational tools are crucial given the vast amounts of sequence data. They use various approaches like identifying open reading frames, conserved sequences, statistical patterns and sequence similarities to model gene structures and infer functions. The results are then integrated into automated annotation pipelines to generate comprehensive and reliable gene annotations for genomes.