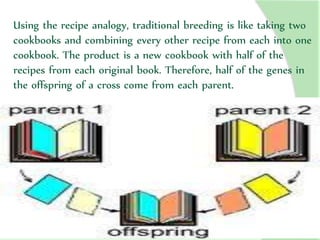
This document summarizes information about genetic engineering. It defines genetic engineering as the process of manually adding new DNA to an organism to give it new traits. It provides examples of genetically engineered crops like plants resistant to insects or herbicides. It compares genetic engineering to traditional breeding and outlines the basic steps of genetic engineering including identifying the desired gene, cloning it, and inserting it into a recipient organism. It discusses advantages like medical and agricultural benefits and disadvantages like potential unknown environmental impacts. It provides examples of specific genetically engineered crops like golden rice and pesticide-resistant rape plants. It also discusses debates around the safety of GMOs.