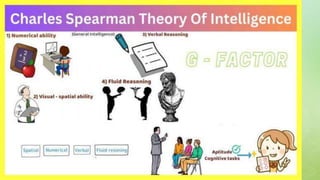
Charles Spearman, a British psychologist, introduced the concept of general intelligence, or g factor, which underlies various cognitive skills, including verbal, spatial, numerical, and mechanical abilities. His two-factor theory distinguishes between general intelligence ('g') and specific abilities ('s'), with the latter being linked to distinct tasks. The document outlines various types of intelligence, such as numerical, visual-spatial, verbal reasoning, fluid and crystallized intelligence, highlighting the interplay between these cognitive capabilities.