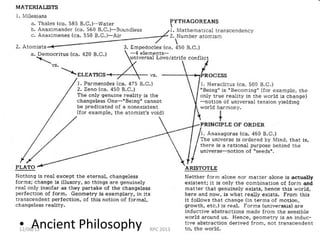
The document discusses ancient Greek philosophers who lived before Socrates, known as the Pre-Socratics. Three philosophers from Miletus - Thales, Anaximander, and Anaximenes - believed the basic substance of the universe was water, infinity, and air respectively. Parmenides argued that change and motion are illusions and all is permanent. Heraclitus believed all is in flux. Empedocles said nature's source cannot be a single element. Anaxagoras believed seeds were ordered by intelligence. Pythagoras and his followers studied mathematics and believed the universe followed musical and numerical laws, discovering the Pythagorean theorem relating triangle side lengths.