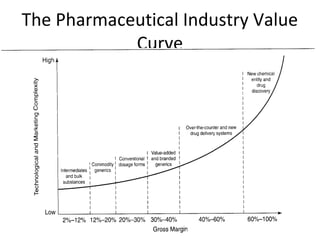
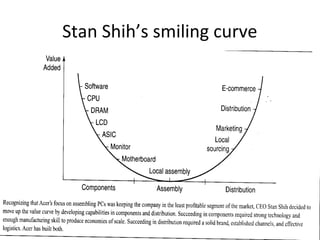
This document provides an overview of healthcare systems and medical equipment companies globally. It then focuses on General Electric Medical Systems (GEMS):
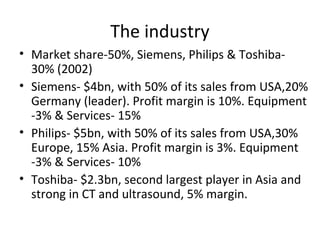
- GEMS is a $8 billion division of GE and the largest medical equipment company with 50% market share. It grows around 16% annually.
- 60% of GEMS' revenue comes from equipment sales and 40% from services. It spends 7-9% of sales on R&D and has an operating margin of 18%.
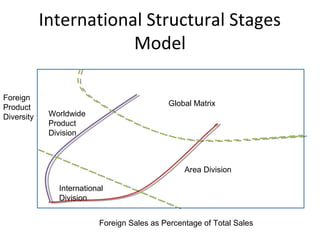
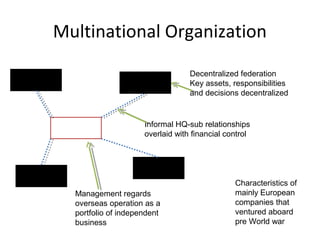
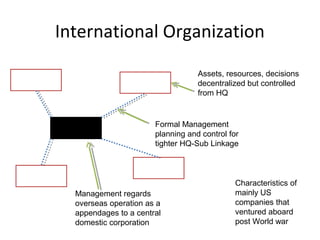
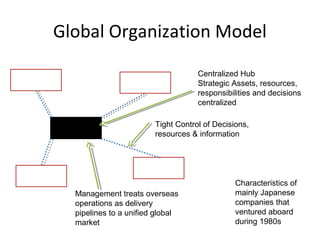
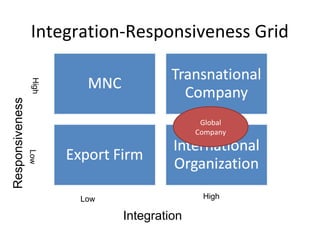
- The document also discusses various models of international organization structures and the characteristics of multinational, global, international, and transnational companies.