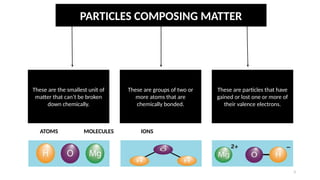
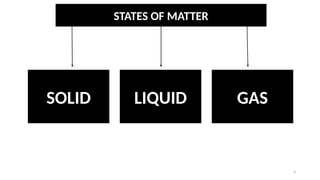
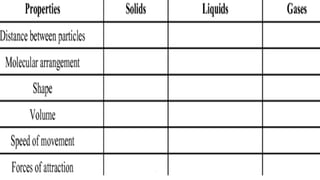
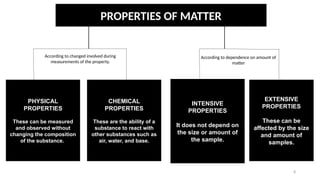
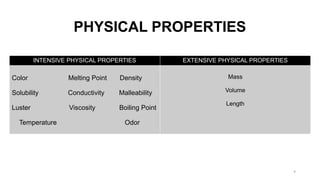
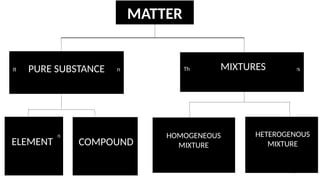
The document discusses the nature of matter, detailing its composition consisting of atoms, molecules, and ions, and the various states of matter, including solid, liquid, gas, plasma, and Bose-Einstein condensate. It explains different properties of matter such as physical and chemical properties, and the distinction between pure substances and mixtures, including methods for separating mixtures. Additionally, it covers the application of these concepts in consumer products, particularly household cleaning agents and personal care products.