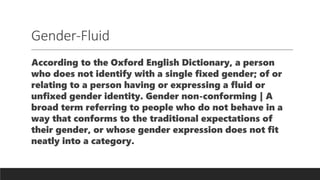
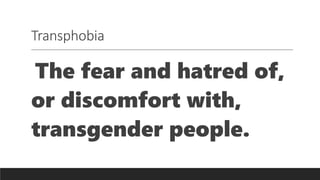
The document discusses the diversity of human sexuality, including various sexual orientations, gender identities, and the social constructs associated with them. It emphasizes that sexuality is a core aspect of identity, while rigid beliefs about gender can marginalize those who do not conform to traditional norms. The document also outlines important terms related to LGBTQ+ identities and highlights that understanding one's sexual orientation and gender identity can be a complex, evolving process.