1) Bees play a crucial role in pollinating many crops and enabling the production of a wide variety of foods.
2) However, bee populations have been declining rapidly due to factors like pesticide use, habitat loss, and parasites.
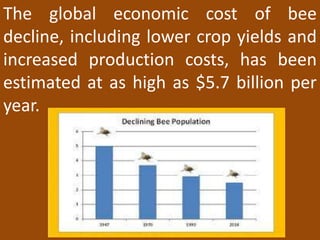
3) This bee decline poses a major threat to global food security and agriculture as one third of food crops depend on bee pollination. Protecting bee habitats and limiting pesticide use is vital.











![1] Global warming, which has caused
flowers to bloom earlier or later than
usual. When pollinators come out of
hibernation, the flowers that provide
the food they need to start the season
have already bloomed.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gem-ppt-36-beesandenvironment-160506124034/85/Gem-ppt-36-bees-and-environment-13-320.jpg)
![2] Pesticide use on farms. Some toxic
pesticides meant
to kill pests can
harm the honey
bees needed for
pollination.
Many pesticides
banned by other
countries because they harm bees are still
available in the United States.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gem-ppt-36-beesandenvironment-160506124034/85/Gem-ppt-36-bees-and-environment-14-320.jpg)
![3] Habitat loss
brought about
by development,
abandoned farms,
growing crops
without leaving
habitat for wildlife,
and growing gardens with flowers that
are not friendly to pollinators.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gem-ppt-36-beesandenvironment-160506124034/85/Gem-ppt-36-bees-and-environment-15-320.jpg)
![4] Parasites such as harmful mites: The
deadly link between the worldwide
collapse of honeybee colonies and a
bloodsucking parasite has been revealed by
scientists. They
have discovered
that the mite has
massively and
permanently
increased the global prevalence of a fatal
bee virus.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gem-ppt-36-beesandenvironment-160506124034/85/Gem-ppt-36-bees-and-environment-16-320.jpg)
![How We Can Protect Bees
1] Policy makers
must take action
to protect the
bees and other
pollinators that
help keep fresh
food on our
table.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gem-ppt-36-beesandenvironment-160506124034/85/Gem-ppt-36-bees-and-environment-17-320.jpg)
![2] Farmers must be rewarded for practices
that help wild bee populations thrive, such as
leaving habitat for bees in
their surrounding fields,
alternating crops so bees
have food all year long, and
not using harmful pesticides.
Assistance should be provided
to farmers who plan to
support a wider variety of
pollinators beyond just bees.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gem-ppt-36-beesandenvironment-160506124034/85/Gem-ppt-36-bees-and-environment-18-320.jpg)
![3] Bee research by the U.S.
Department of Agriculture (USDA) and
the Environmental Protection Agency
(EPA) must be strengthened,
and must also
be broadened to
include research
on pollinators
besides honey
bees.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gem-ppt-36-beesandenvironment-160506124034/85/Gem-ppt-36-bees-and-environment-19-320.jpg)
![4] An Integrated Pest
Management (IPM) techniques
should be used to minimize
pesticide use and risk to bees.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gem-ppt-36-beesandenvironment-160506124034/85/Gem-ppt-36-bees-and-environment-20-320.jpg)









