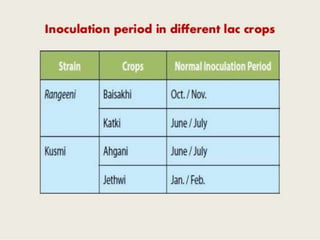
Lac is a resinous secretion produced by lac insects that is cultivated for commercial use. The document outlines the history, cultivation methods, host plants, and uses of lac. Key points include that lac cultivation involves selecting and pruning host trees, inoculating them with broodlac bundles, harvesting immature resin or mature broodlac, and that the main host plants are Butea monosperma, Ziziphus mauritiana, and Flemigia semialata. Lac has various applications in products like paints, electrical goods, and cosmetics.