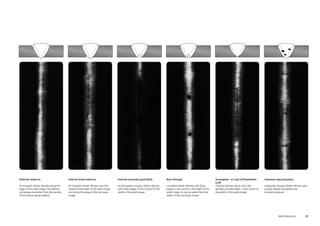
This document provides a reference guide for radiographers to interpret welds. It contains descriptions and examples of various types of discontinuities that can be detected in radiographic images of welds, including mismatches, lack of penetration, inclusions, cracks, porosity, and other defects. The guide defines each discontinuity type and provides details on their visual appearance on radiographs to aid in identification.