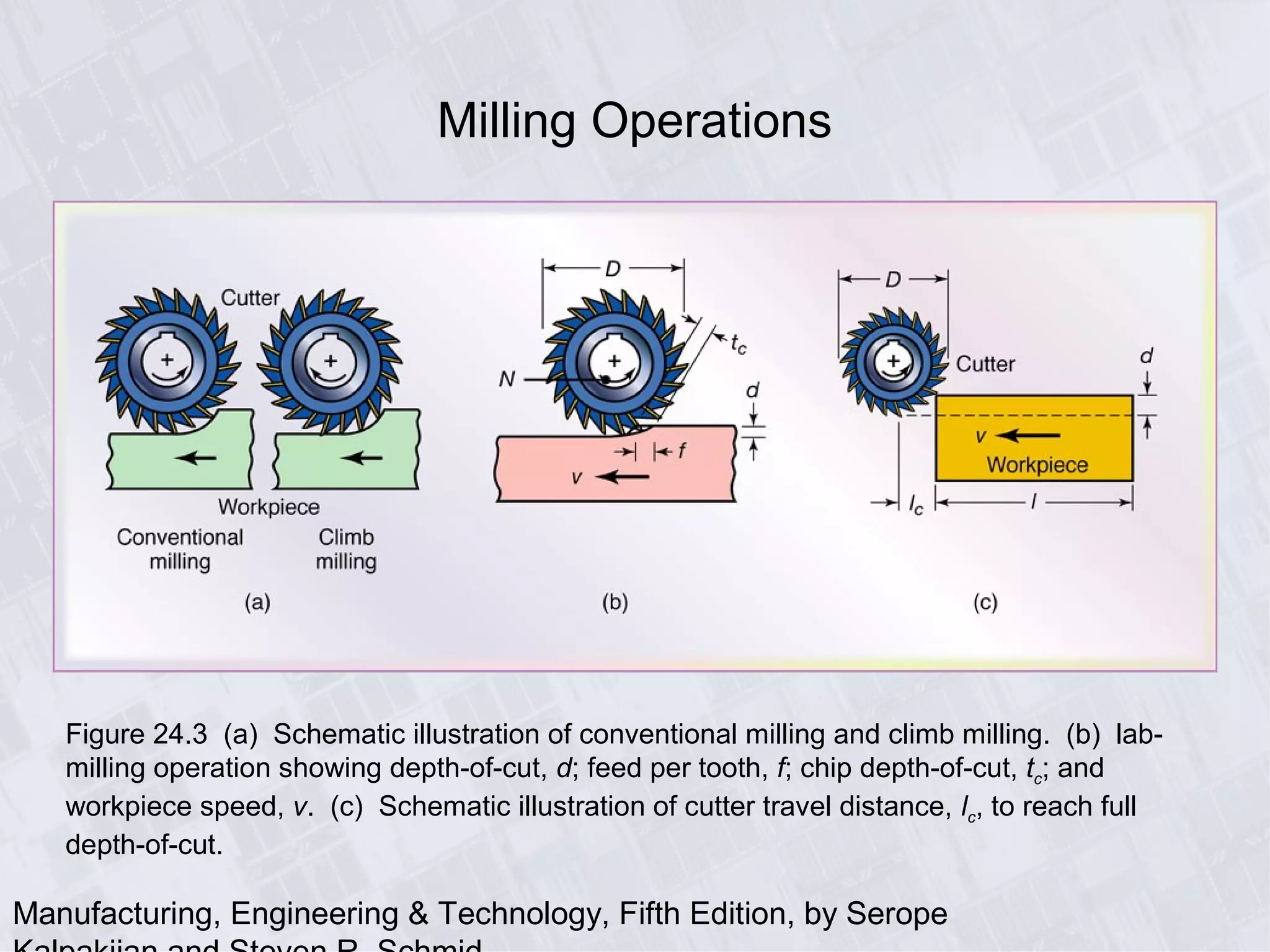
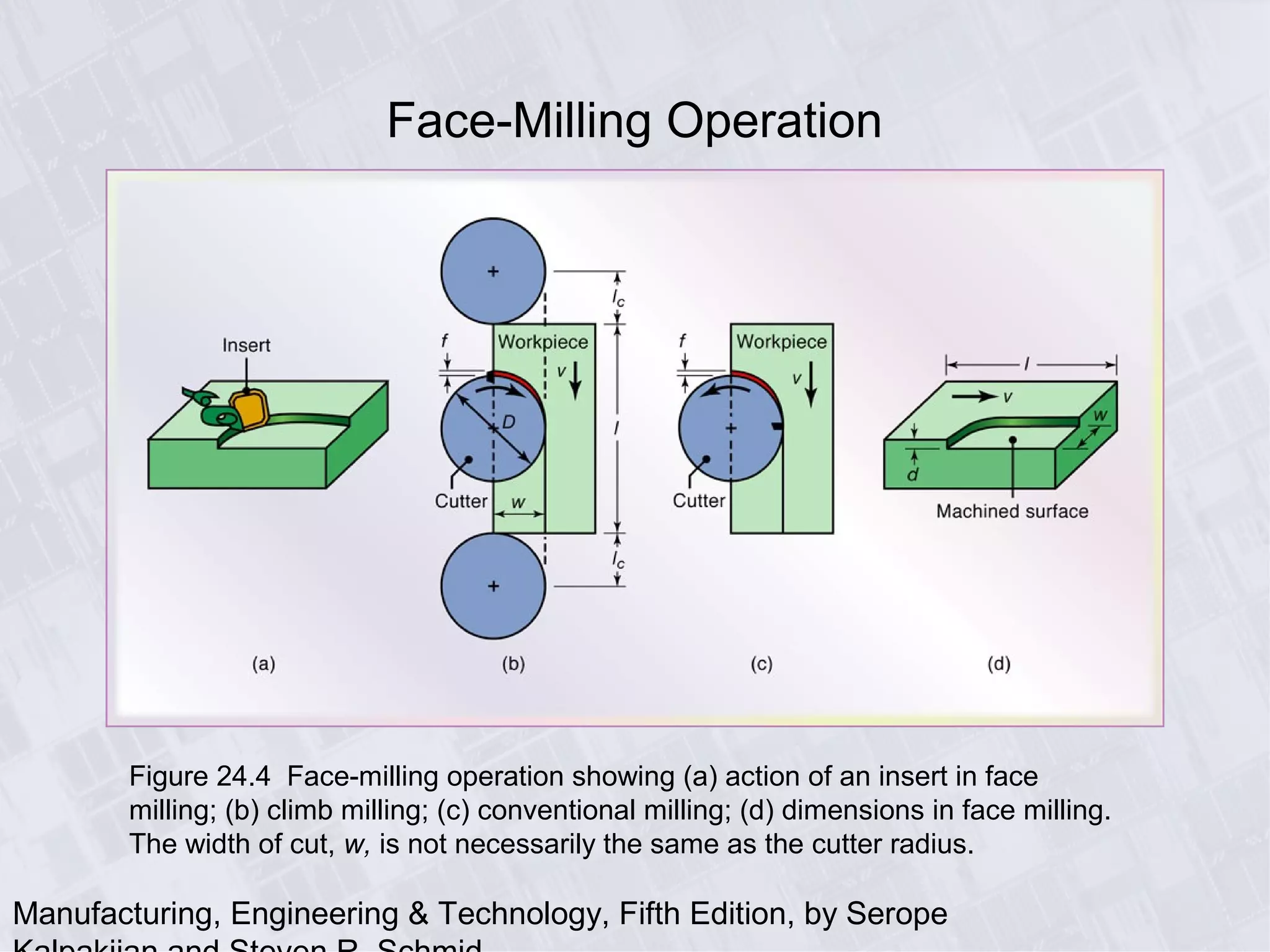
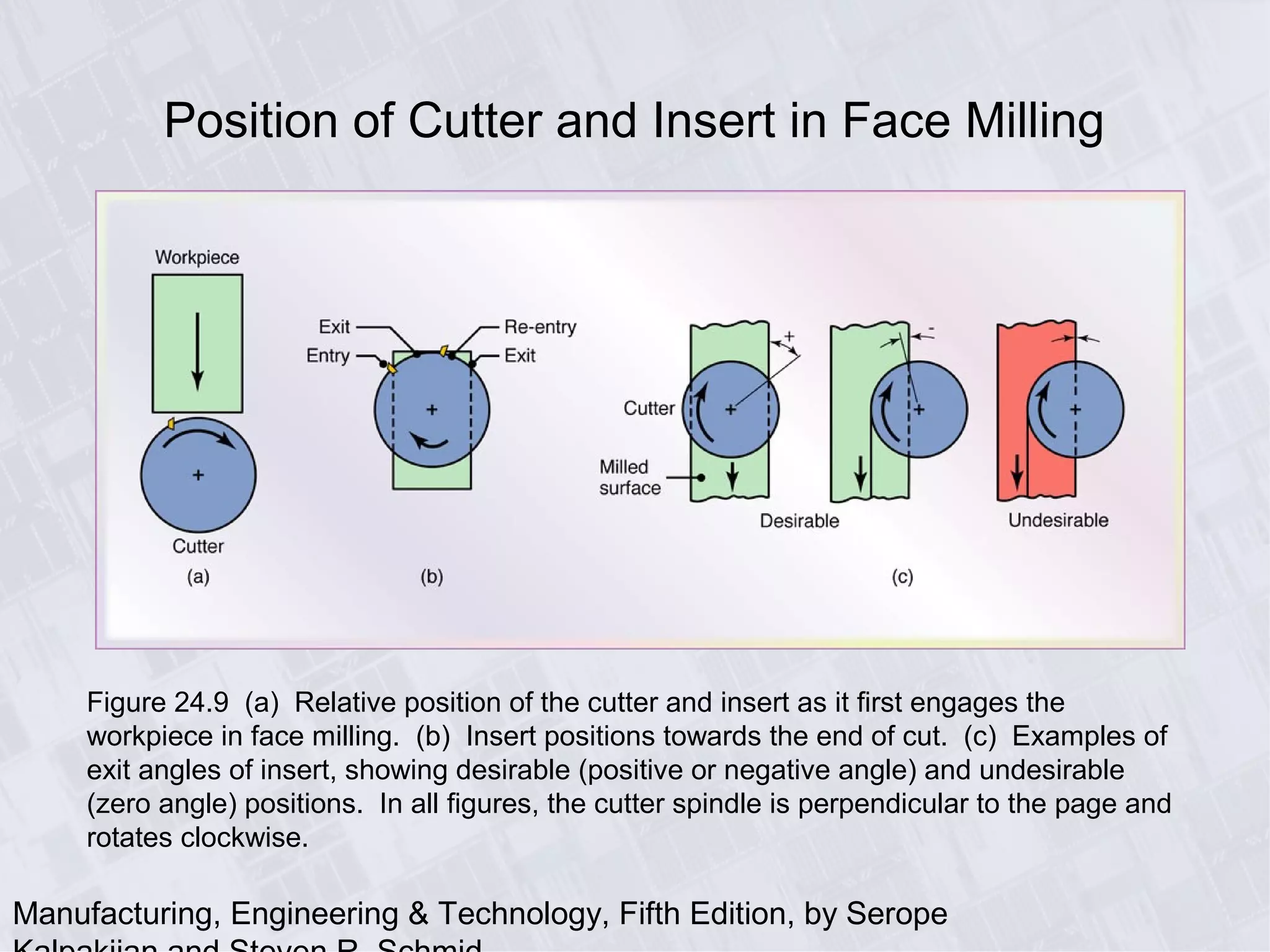
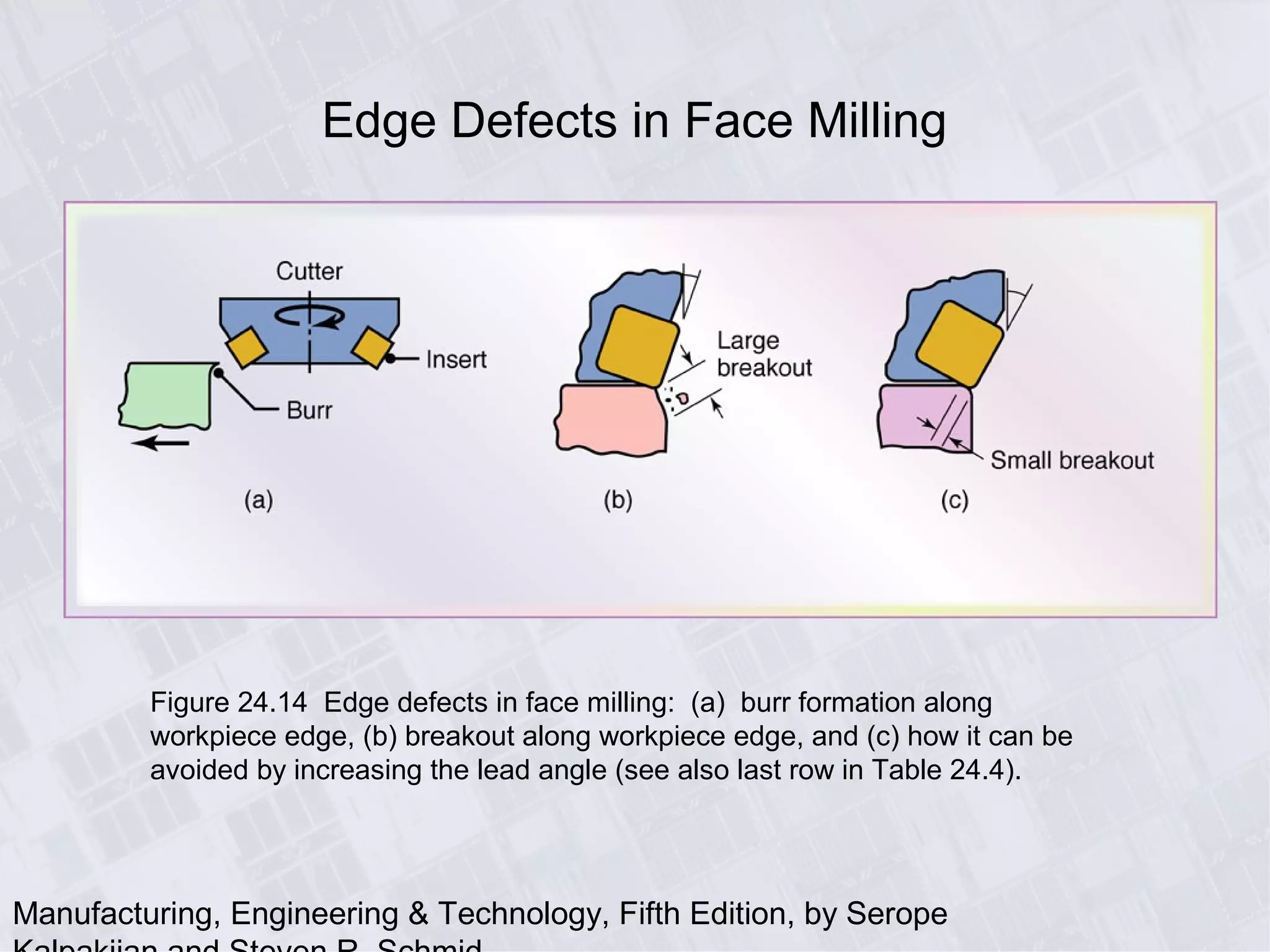
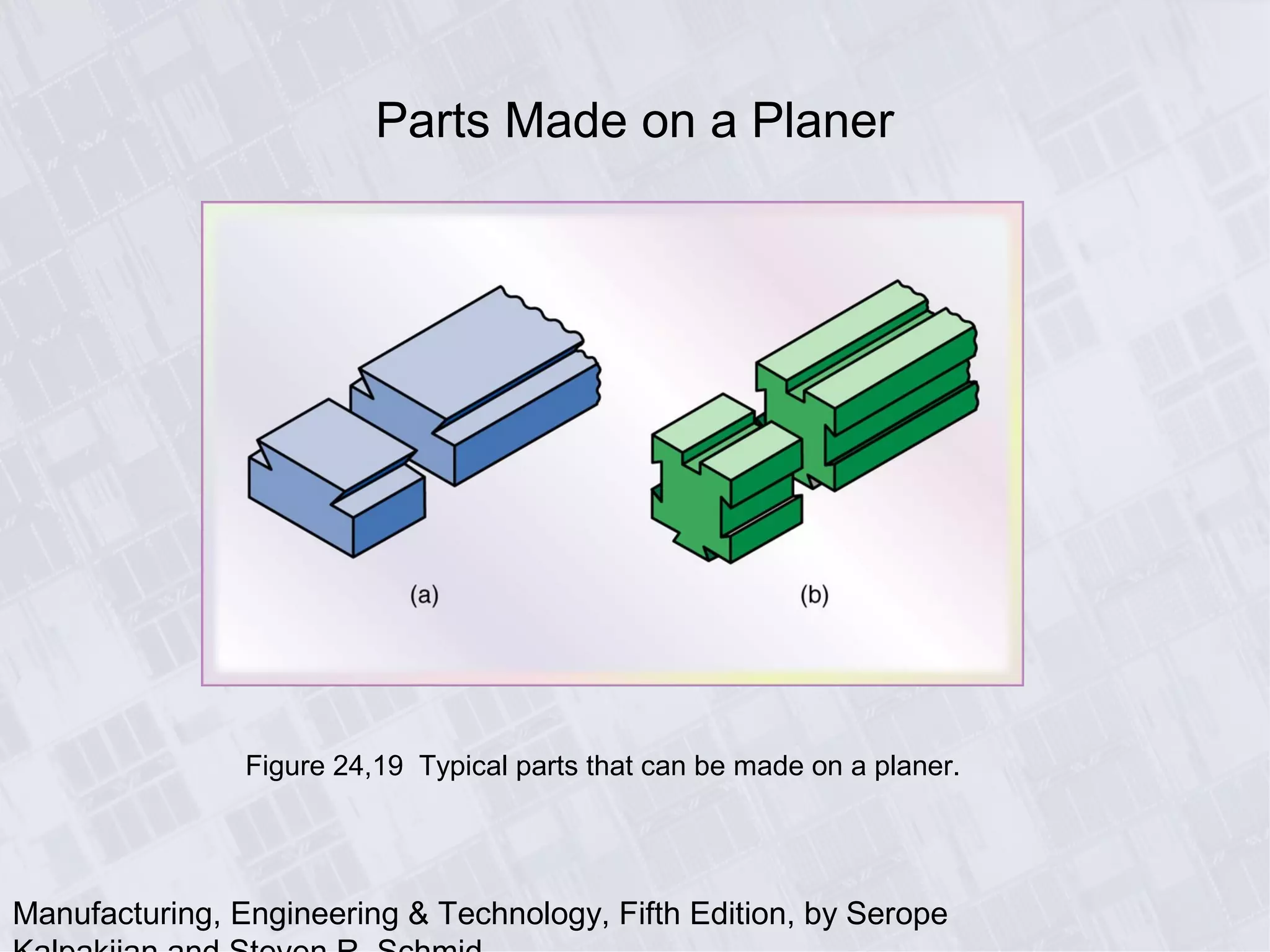
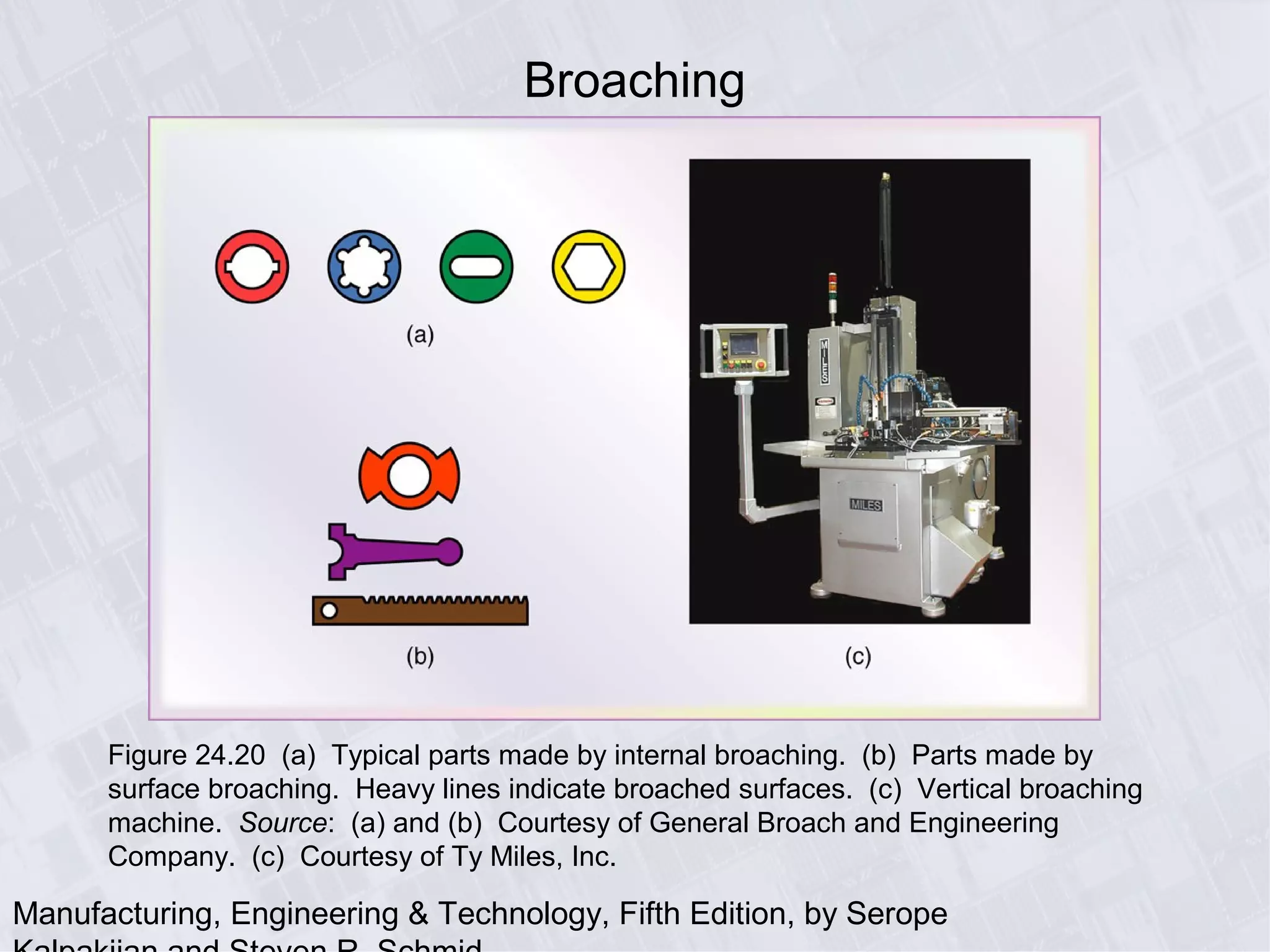
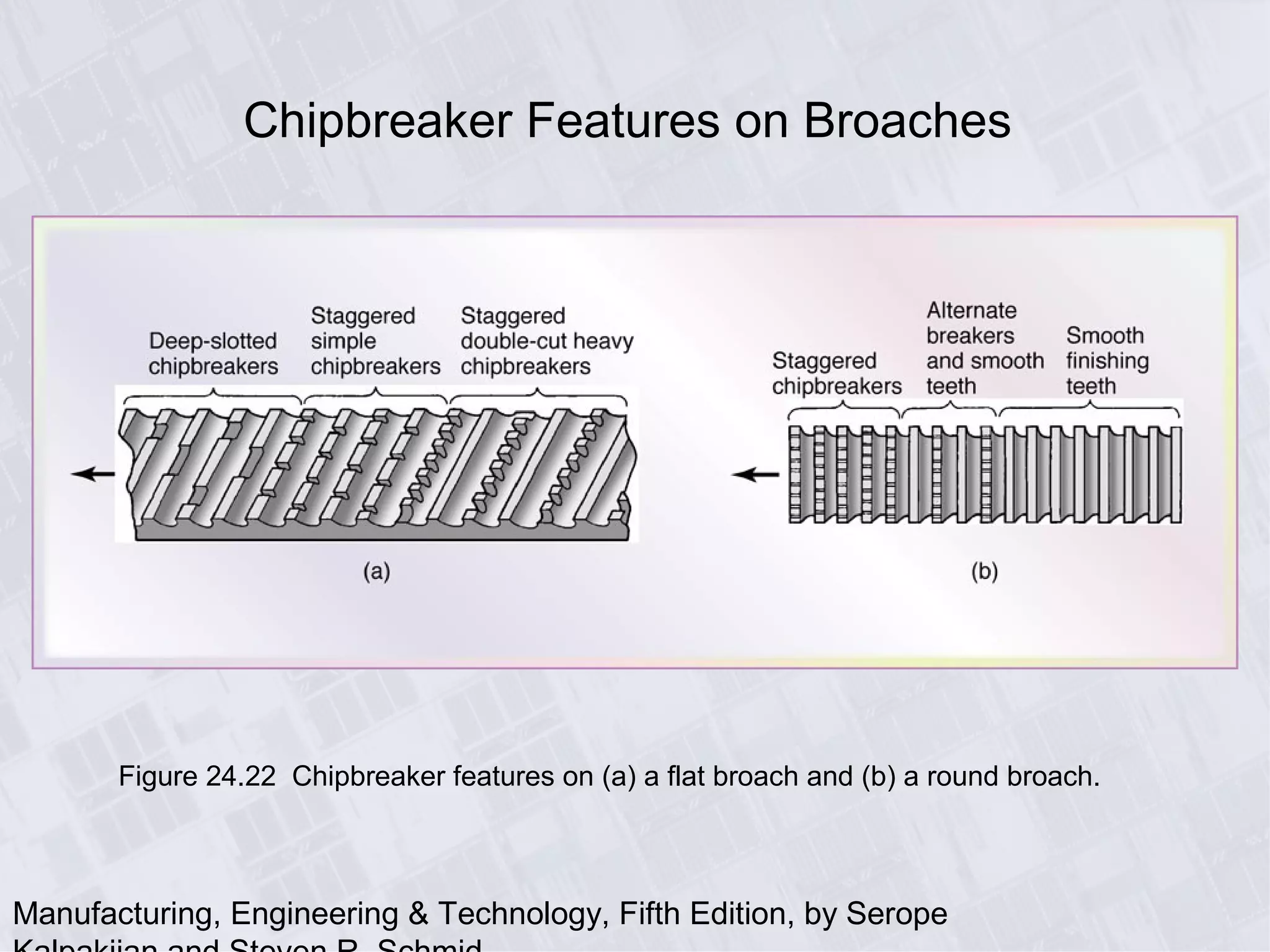
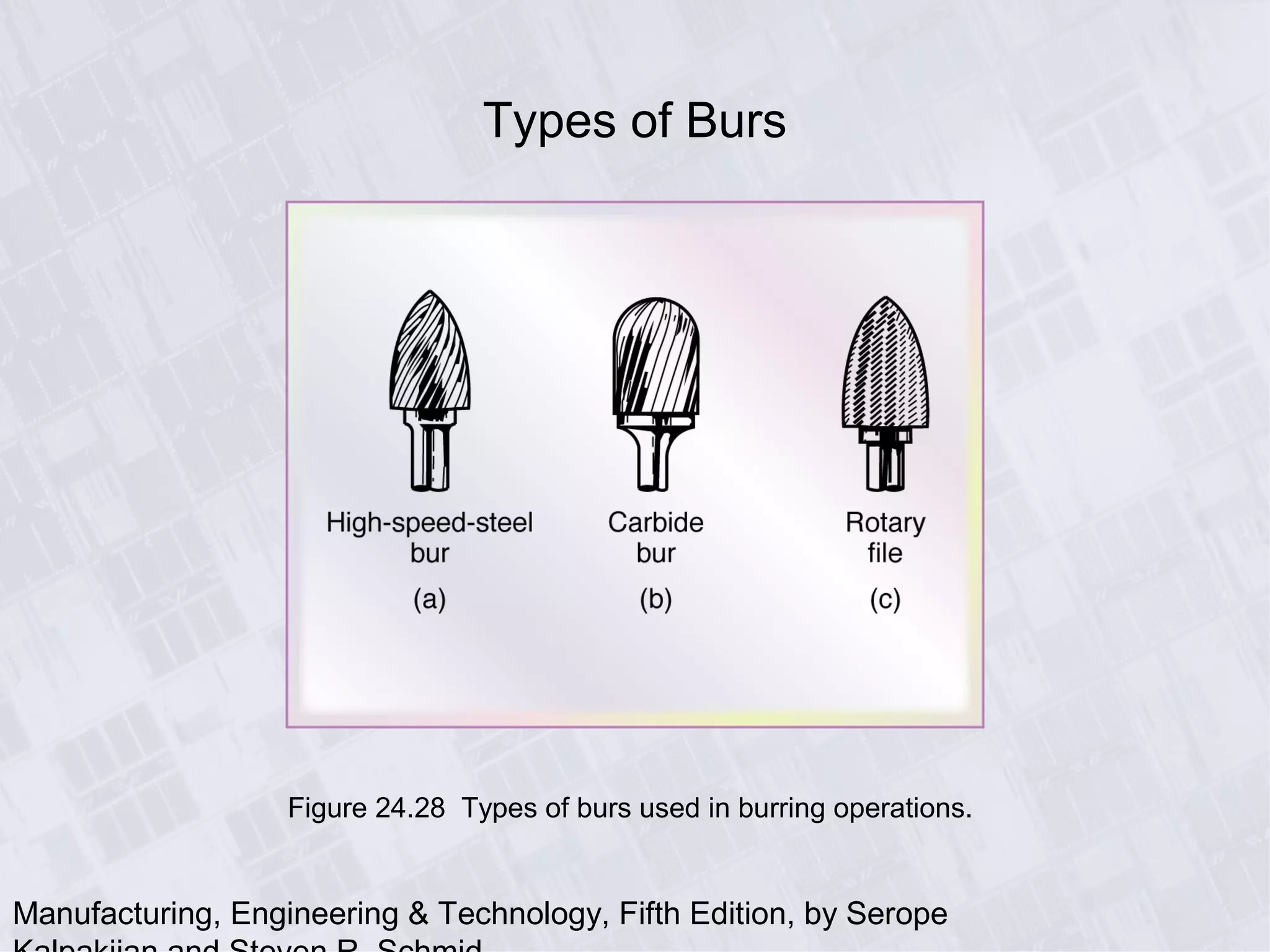
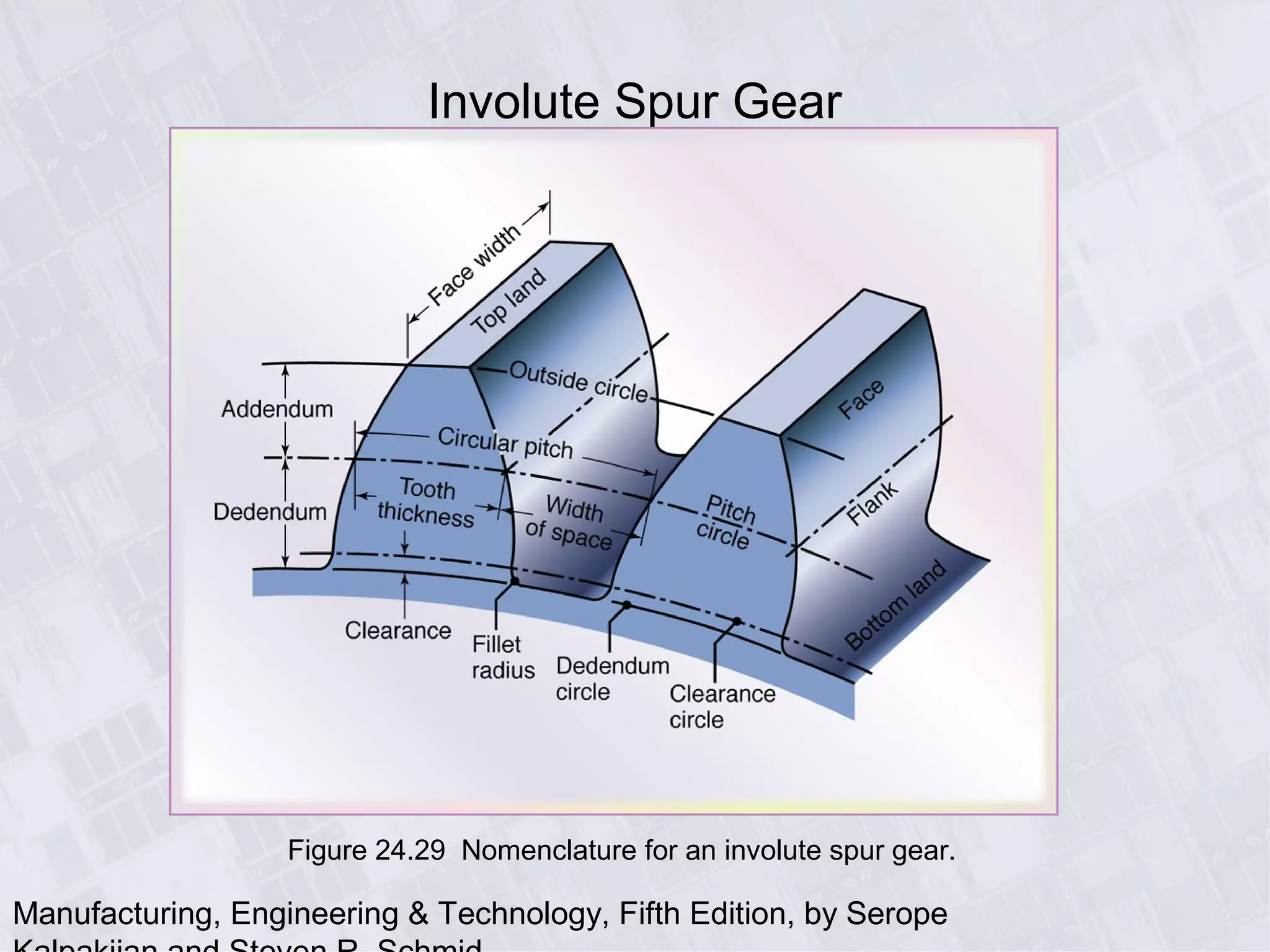
This chapter discusses various machining processes used to produce different shapes, including milling, broaching, sawing, and filing. It provides details on milling operations using different cutters and parameters. Broaching and gear manufacturing processes are also covered, along with the types of parts that can be made using these processes. The chapter includes diagrams illustrating machining terminology, operations, and the effects of different parameters.