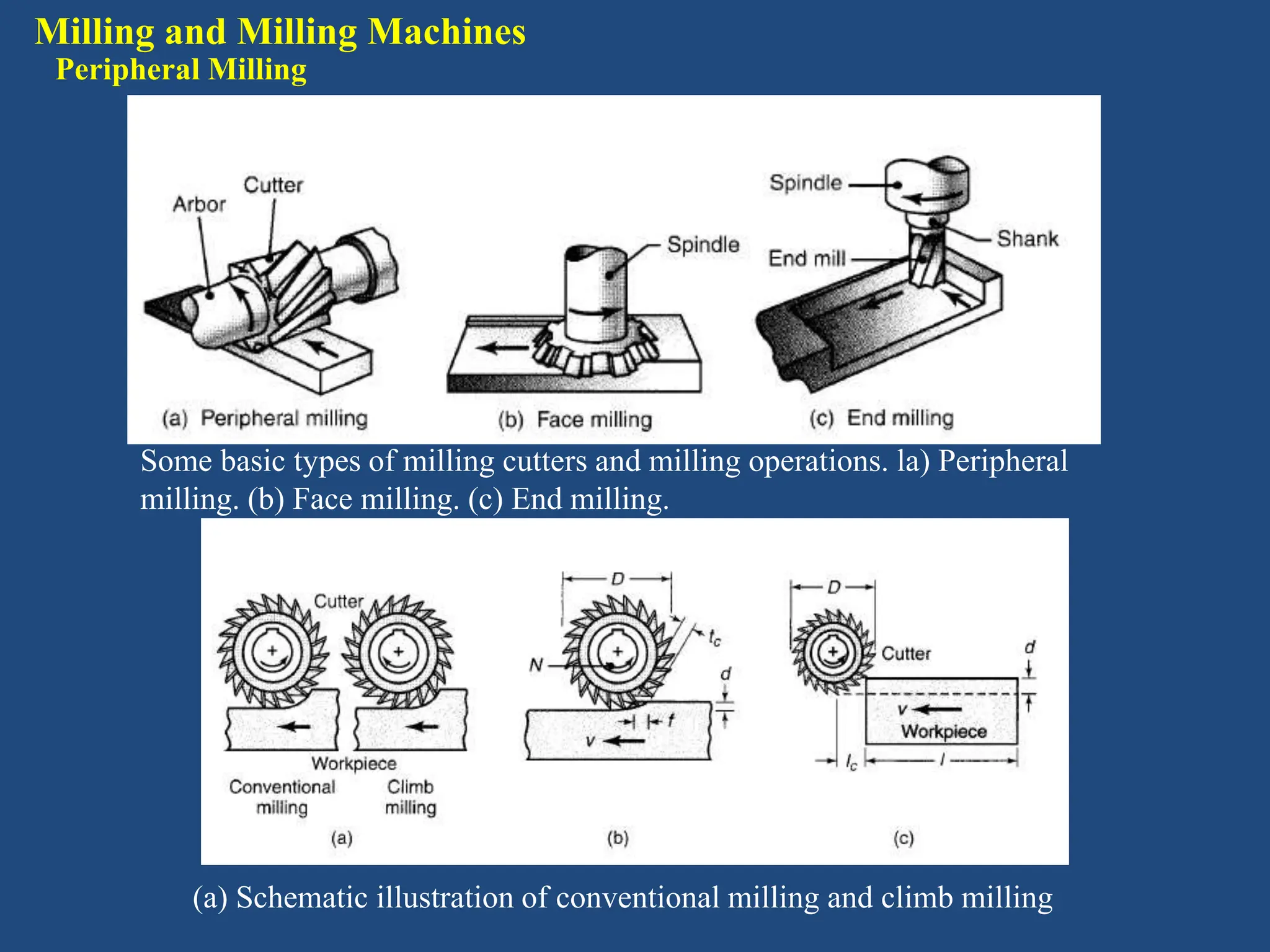
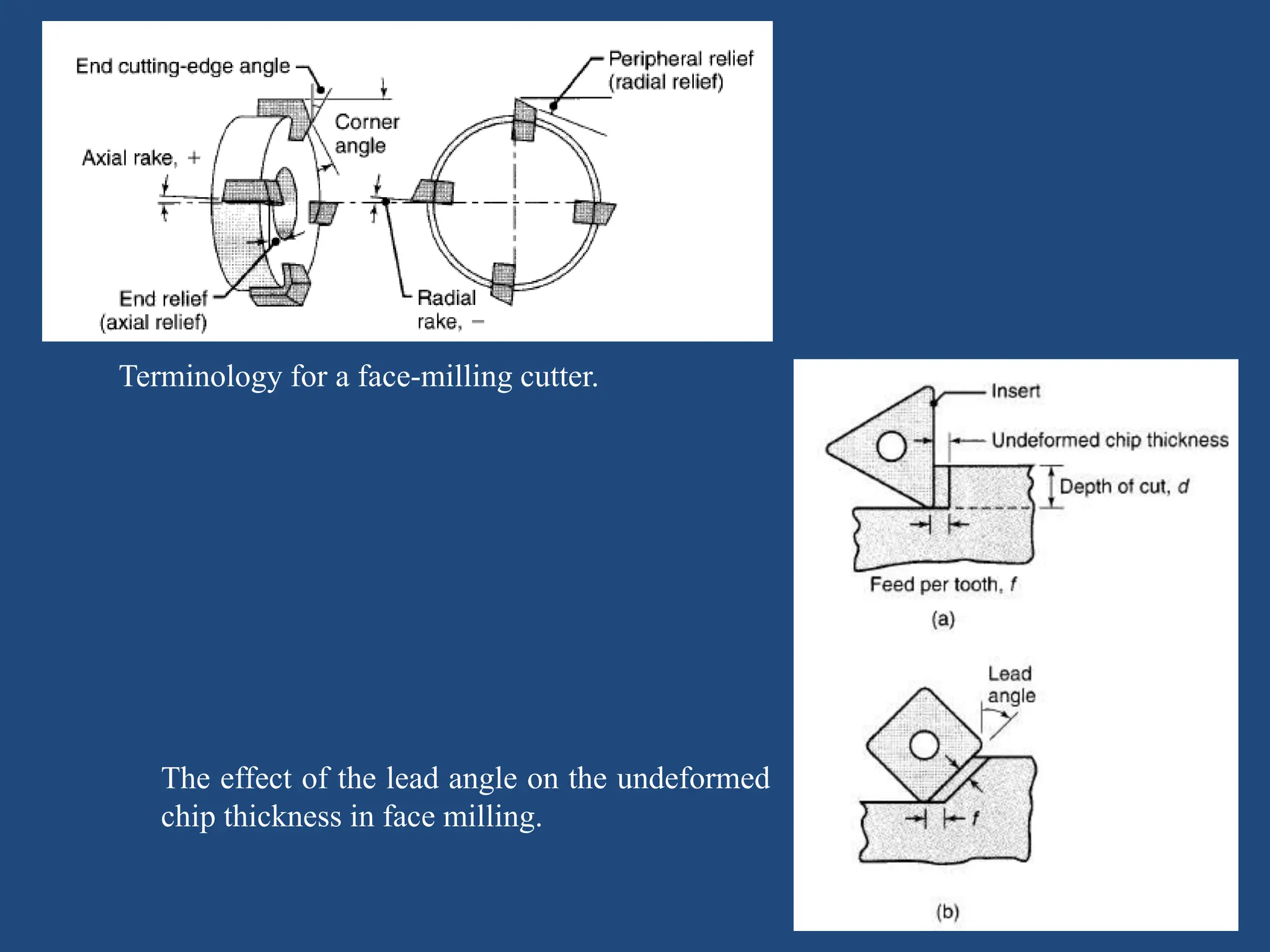
The document discusses various machining processes including milling, broaching, and gear manufacturing. It provides details on different types of milling such as peripheral milling, face milling, and end milling. Various milling cutters and parameters for milling operations are described. Broaching and broaching machines for internal and surface broaching are covered. Gear manufacturing by machining includes topics such as gear cutting, hobbing, bevel gear cutting, and gear grinding processes. Design considerations and the economics of gear machining in relation to gear quality are also summarized.