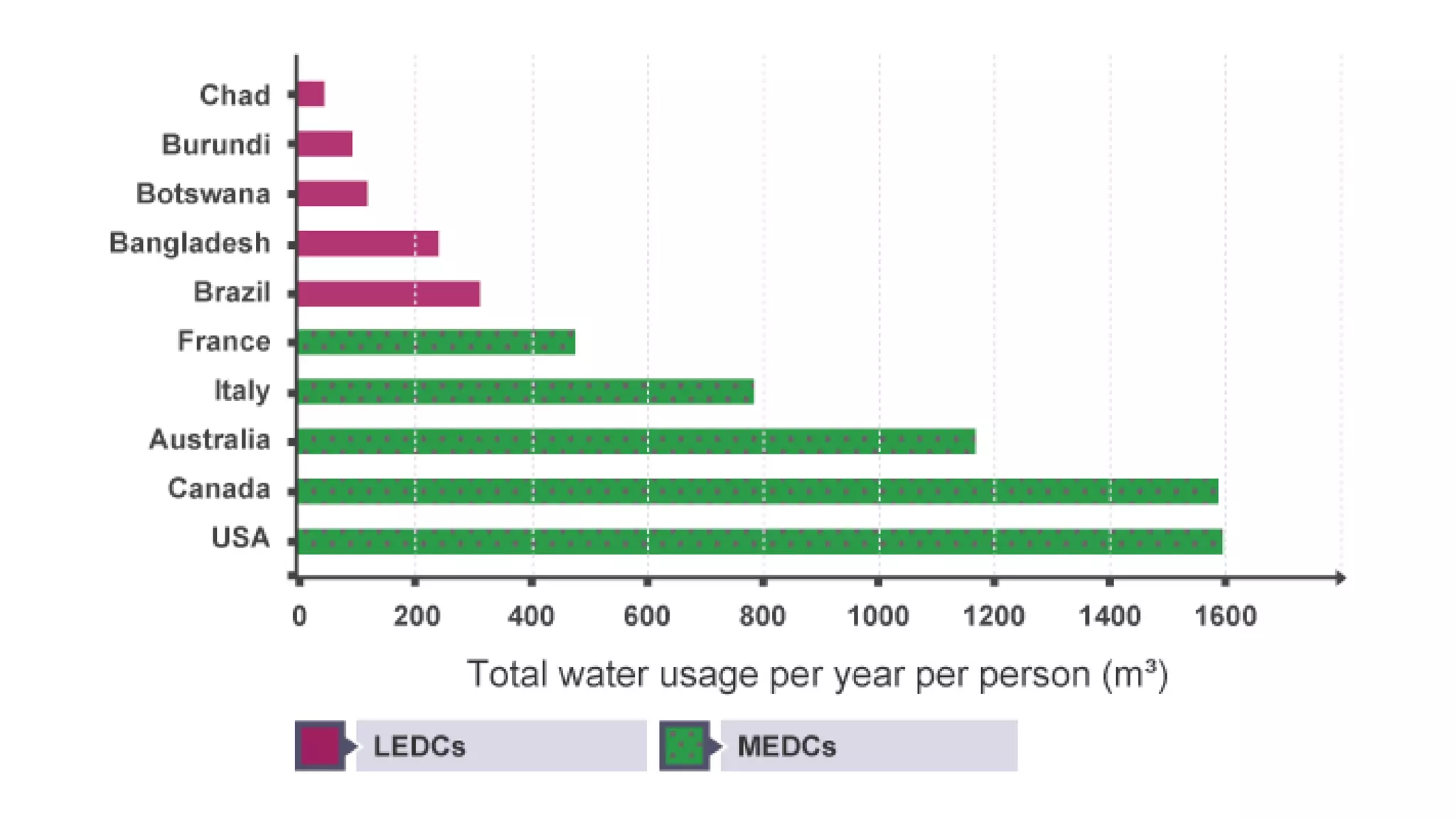
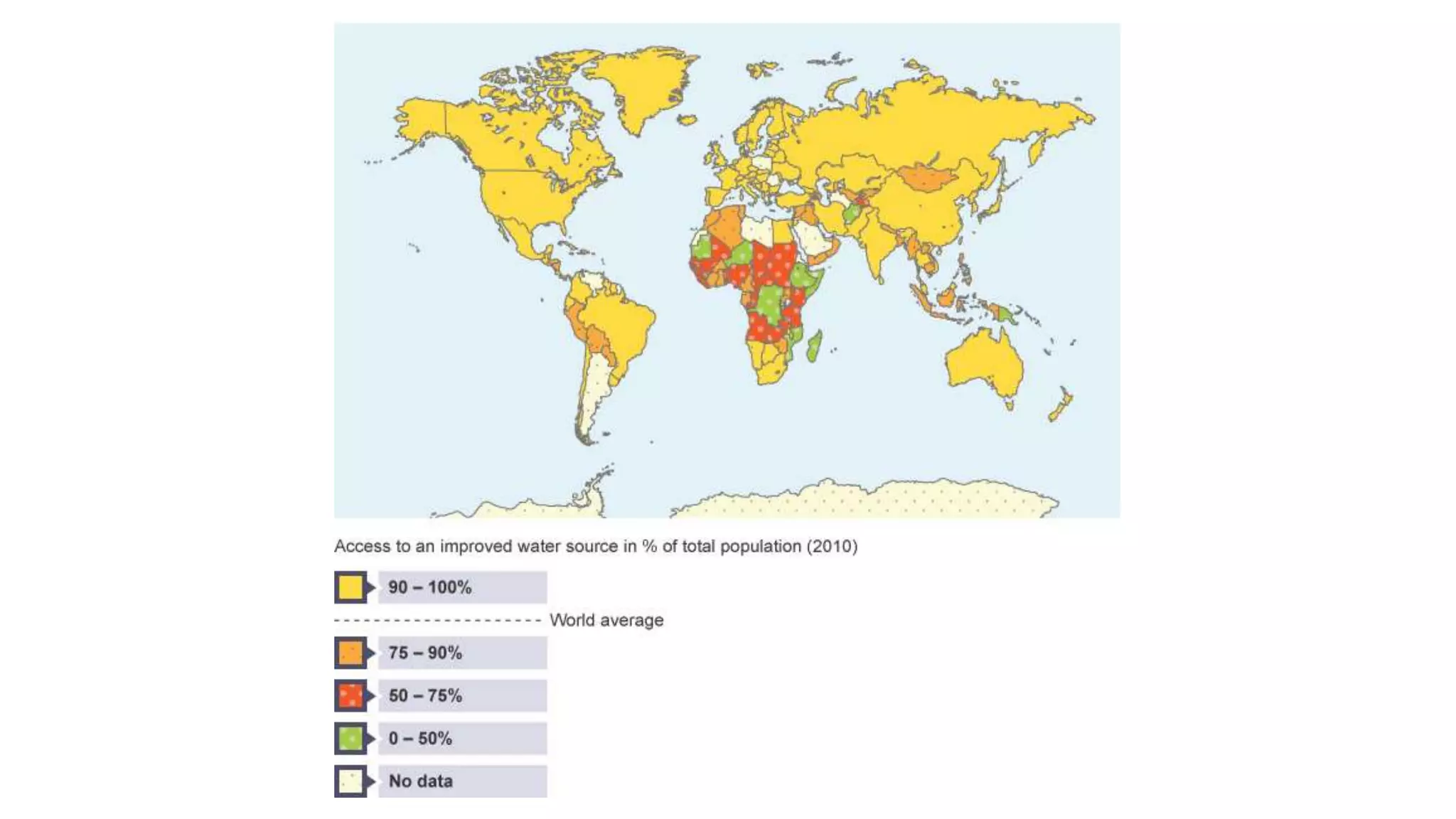
The document discusses global water usage, highlighting disparities between more economically developed countries (MEDCs) and less economically developed countries (LEDCs). It explores the significance of water management strategies, case studies from the UK, Nigeria, and Indonesia, and the challenges faced in both regions regarding access to clean water and proper sanitation. The need for sustainable improvement initiatives, such as community-led sanitation projects and appropriate technology, is emphasized to address water supply issues and enhance health outcomes.