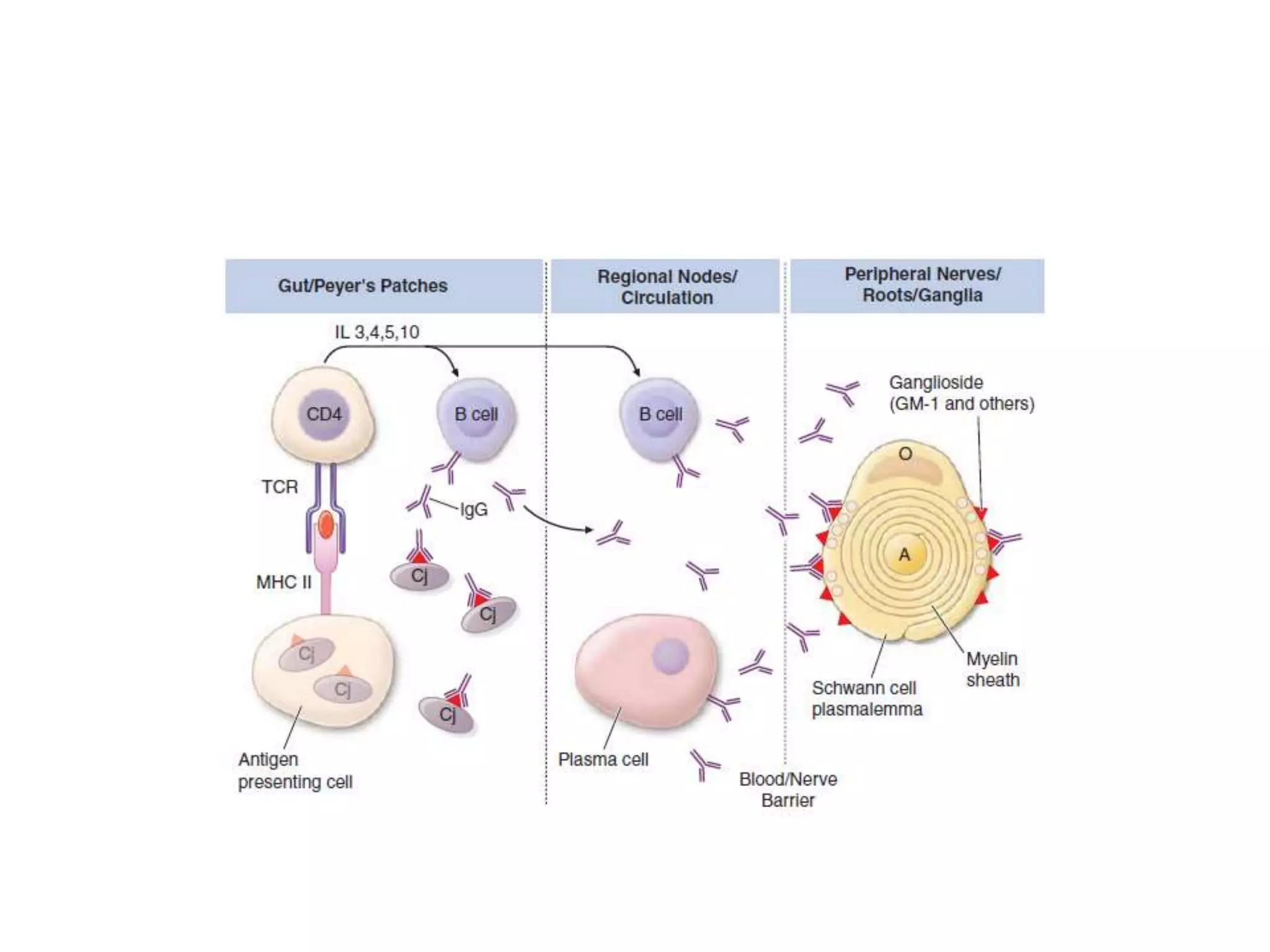
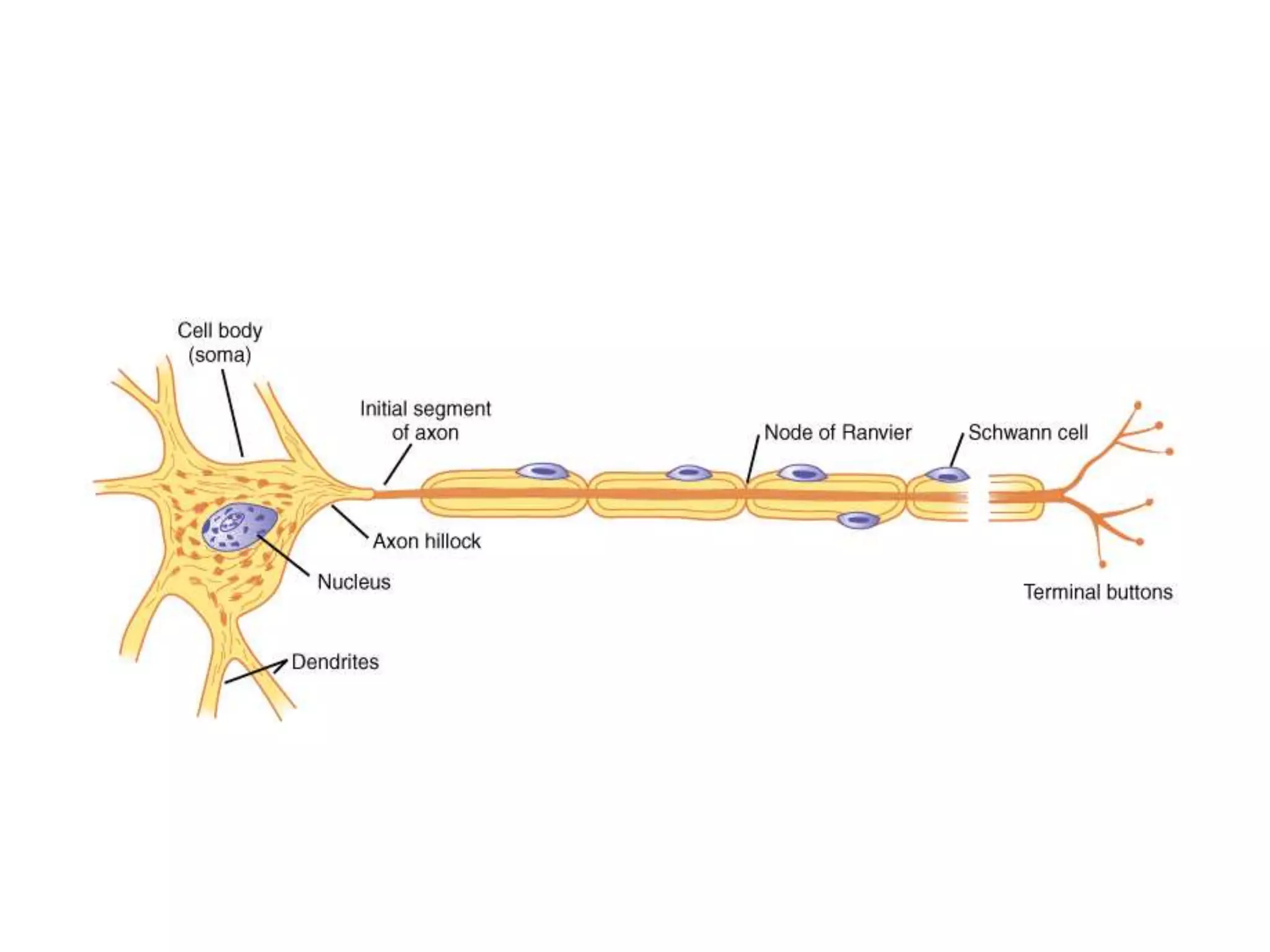
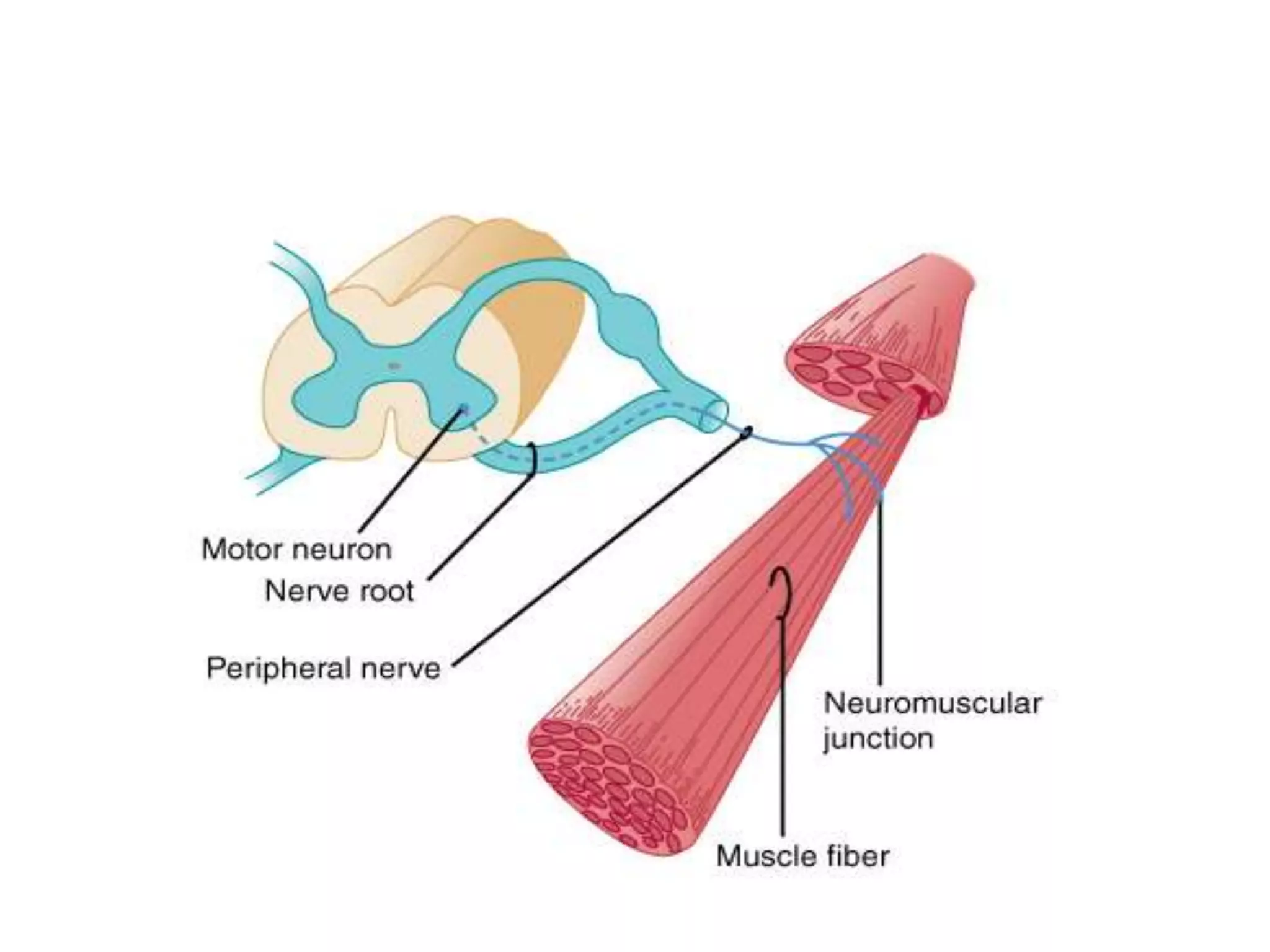
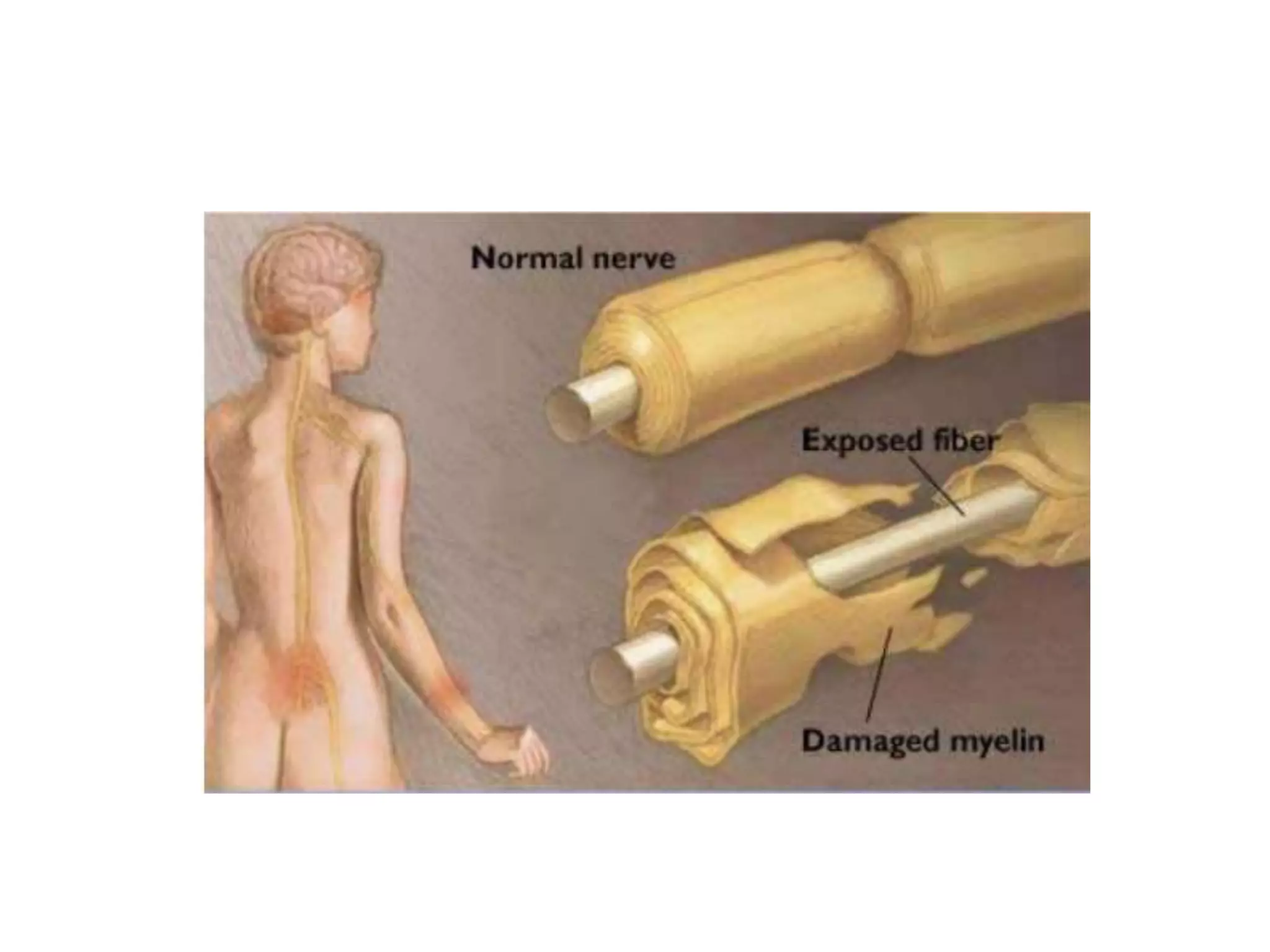
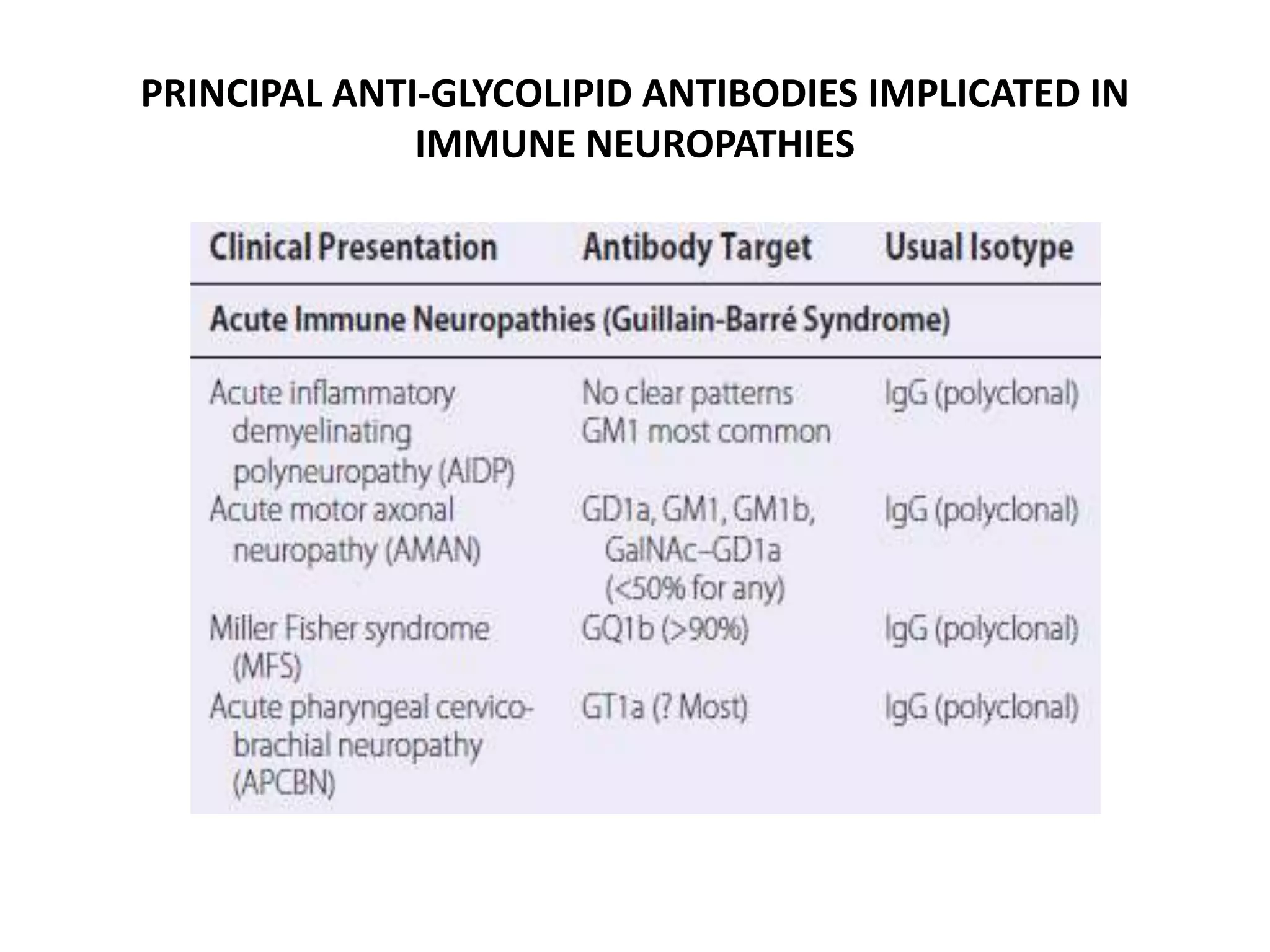
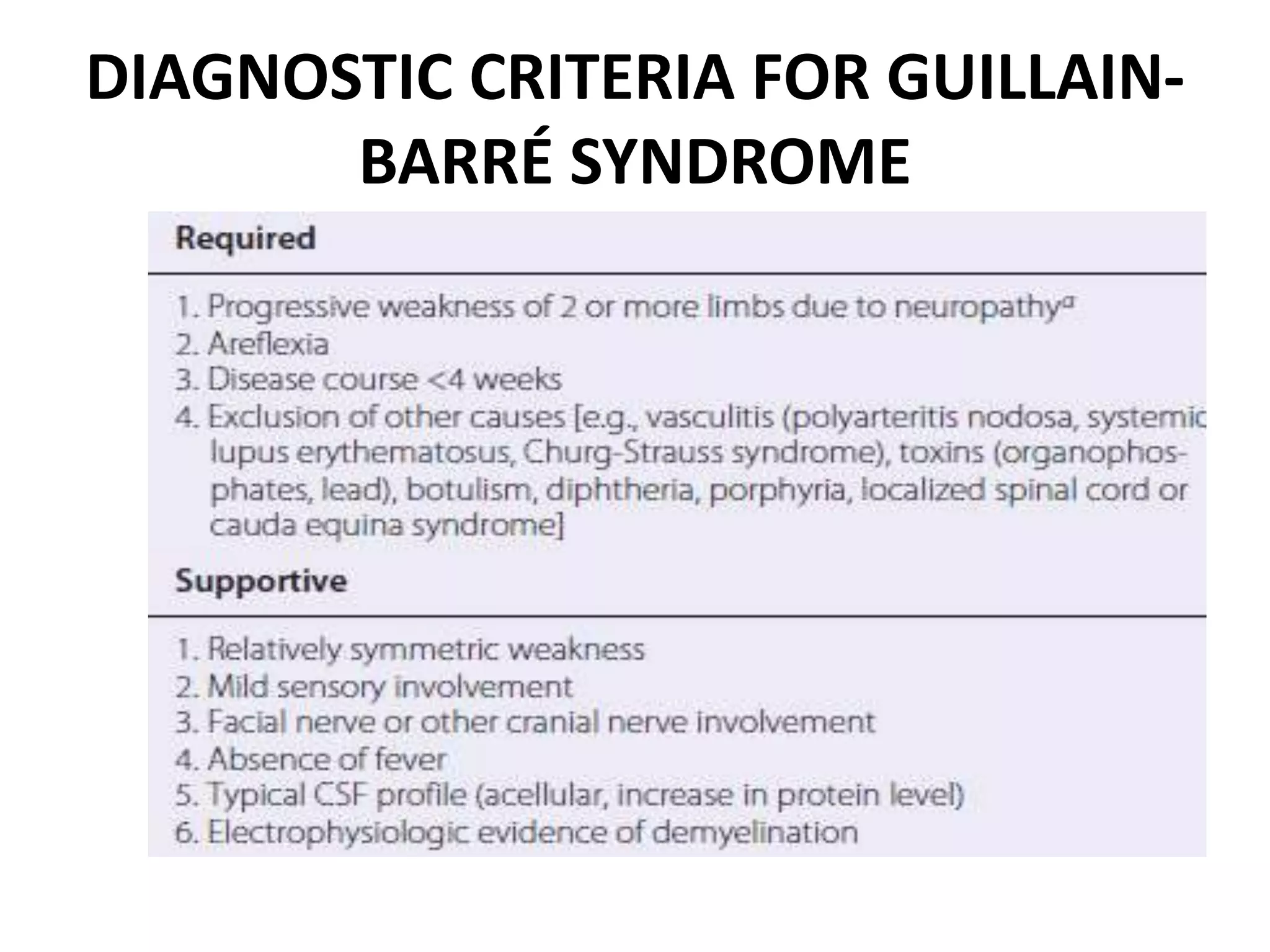
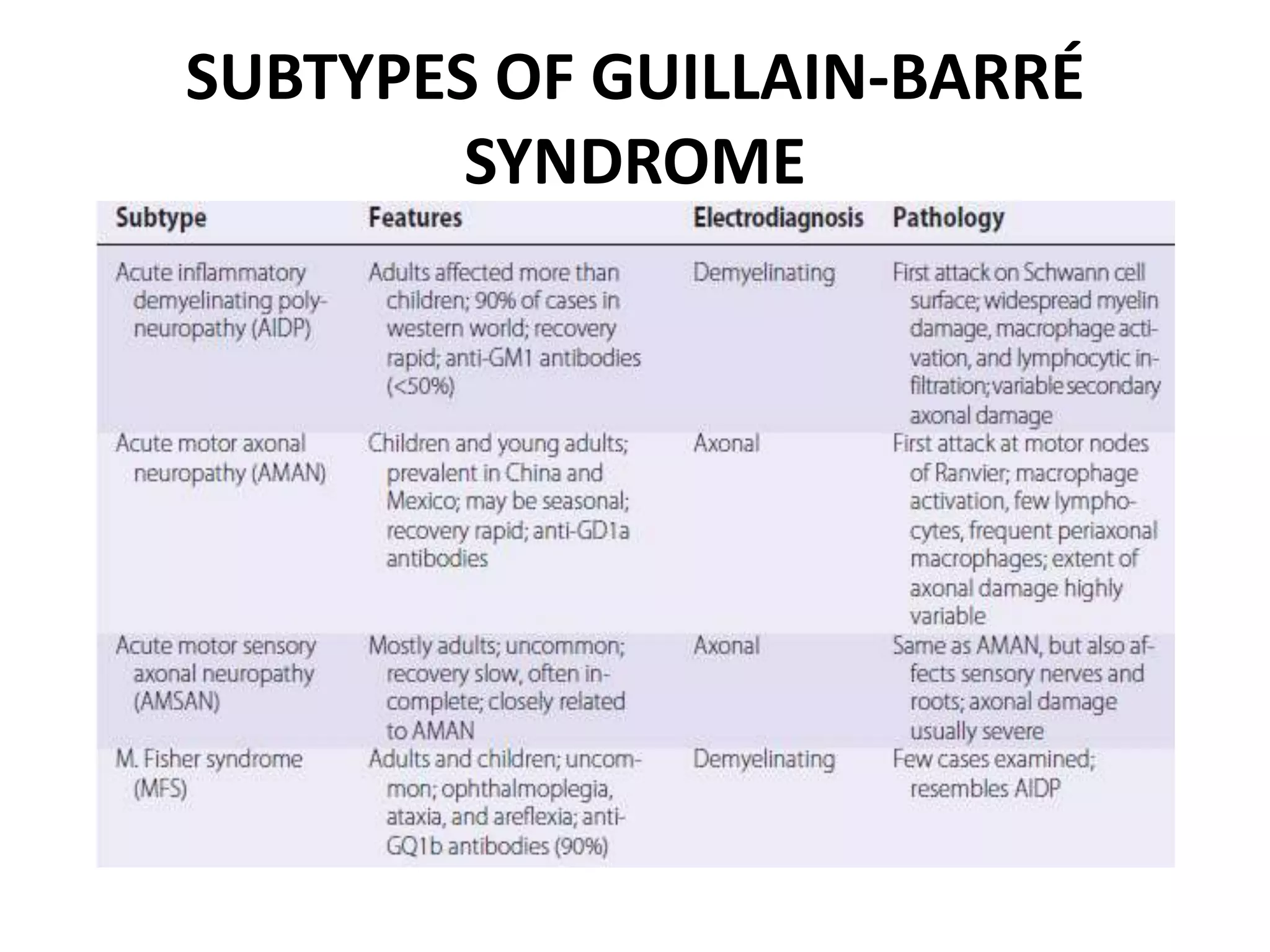
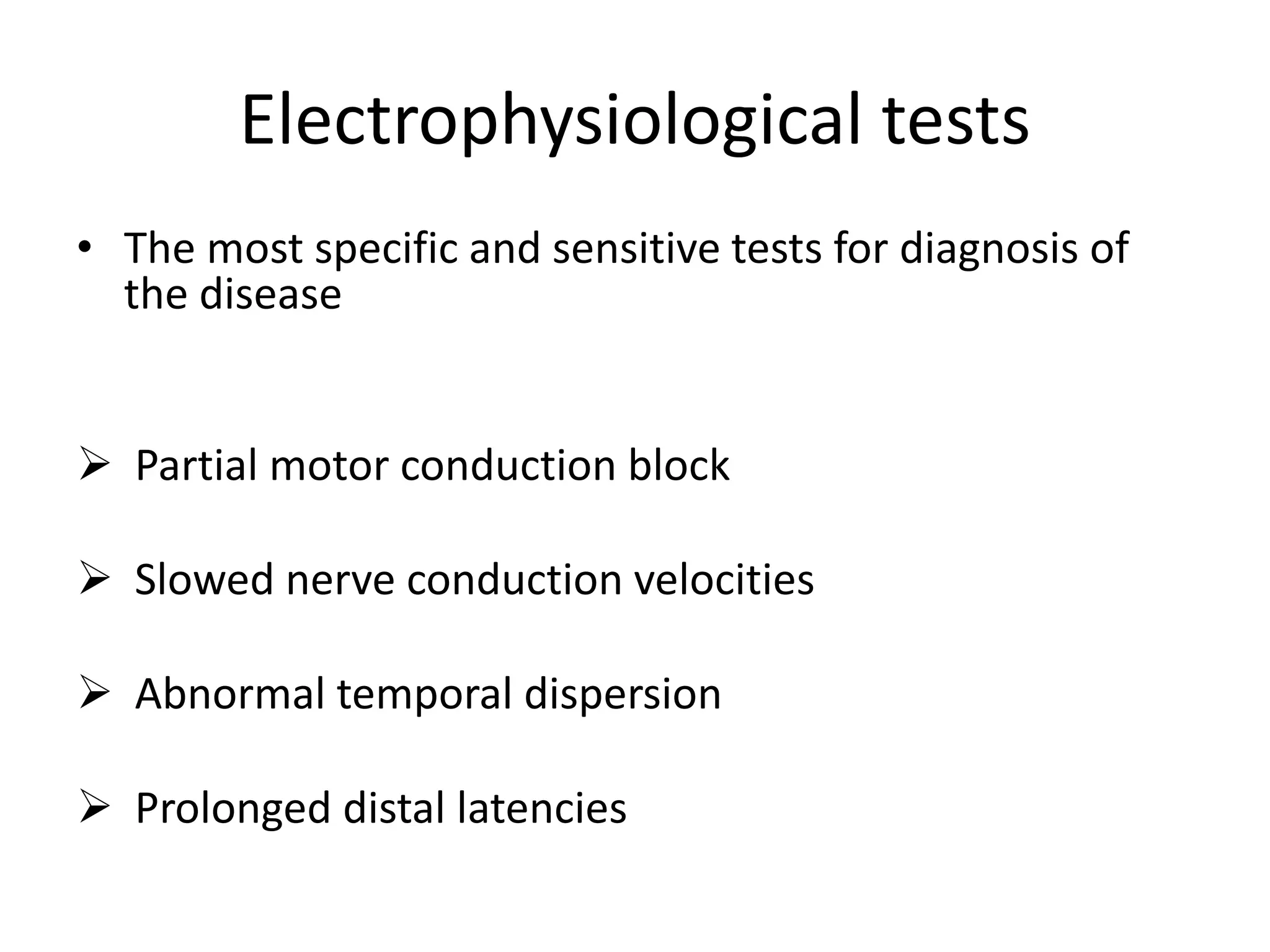
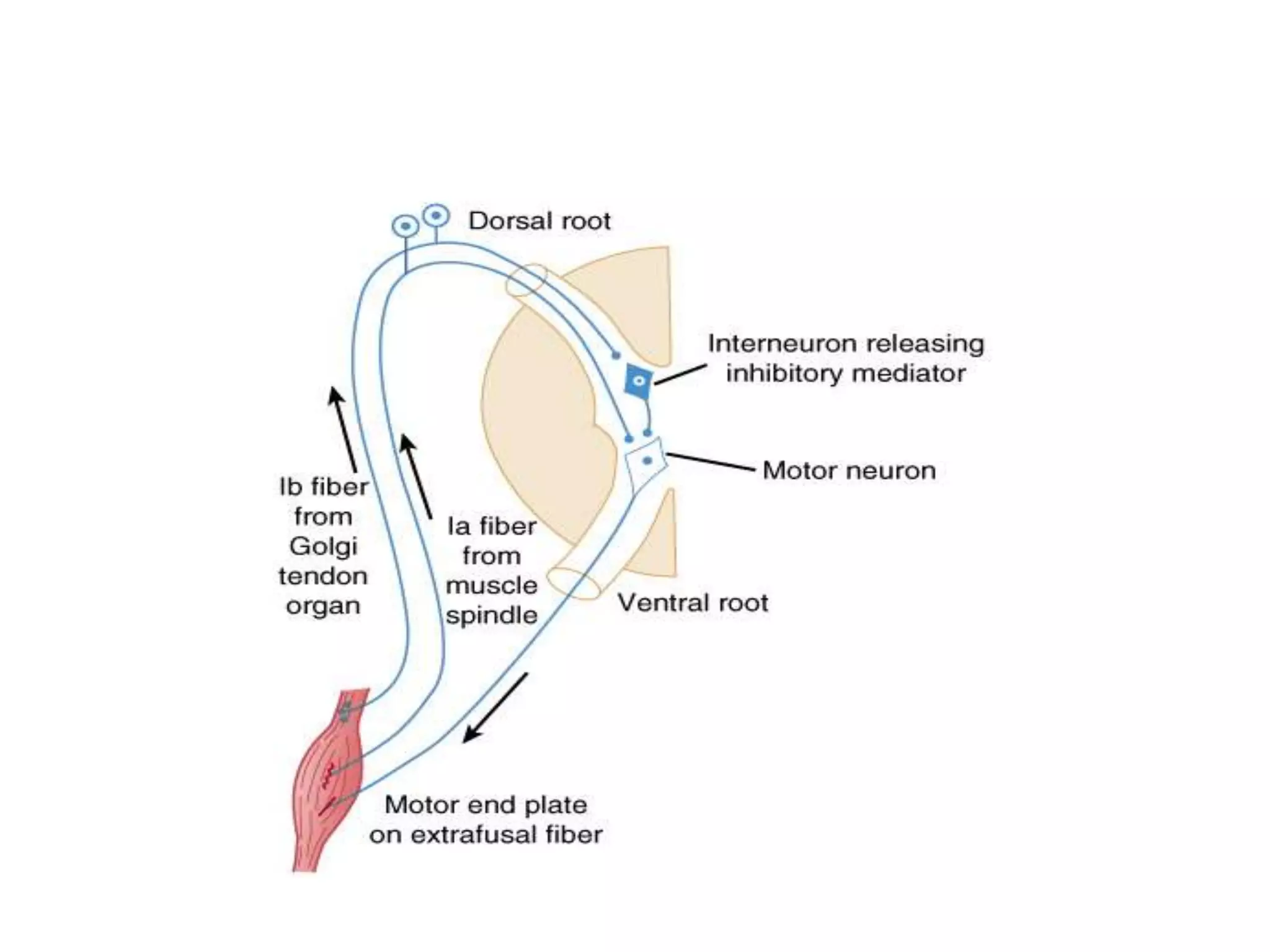
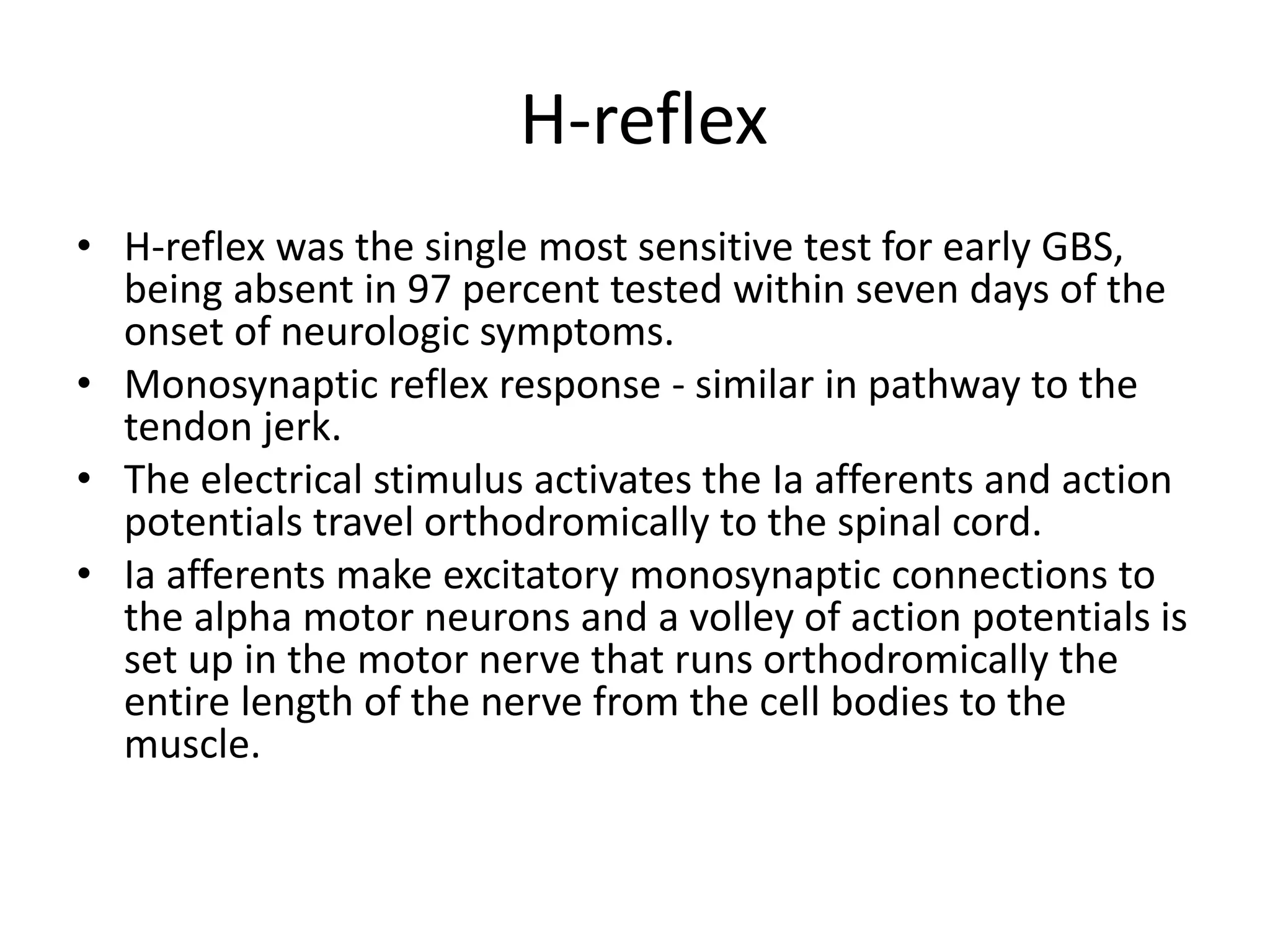
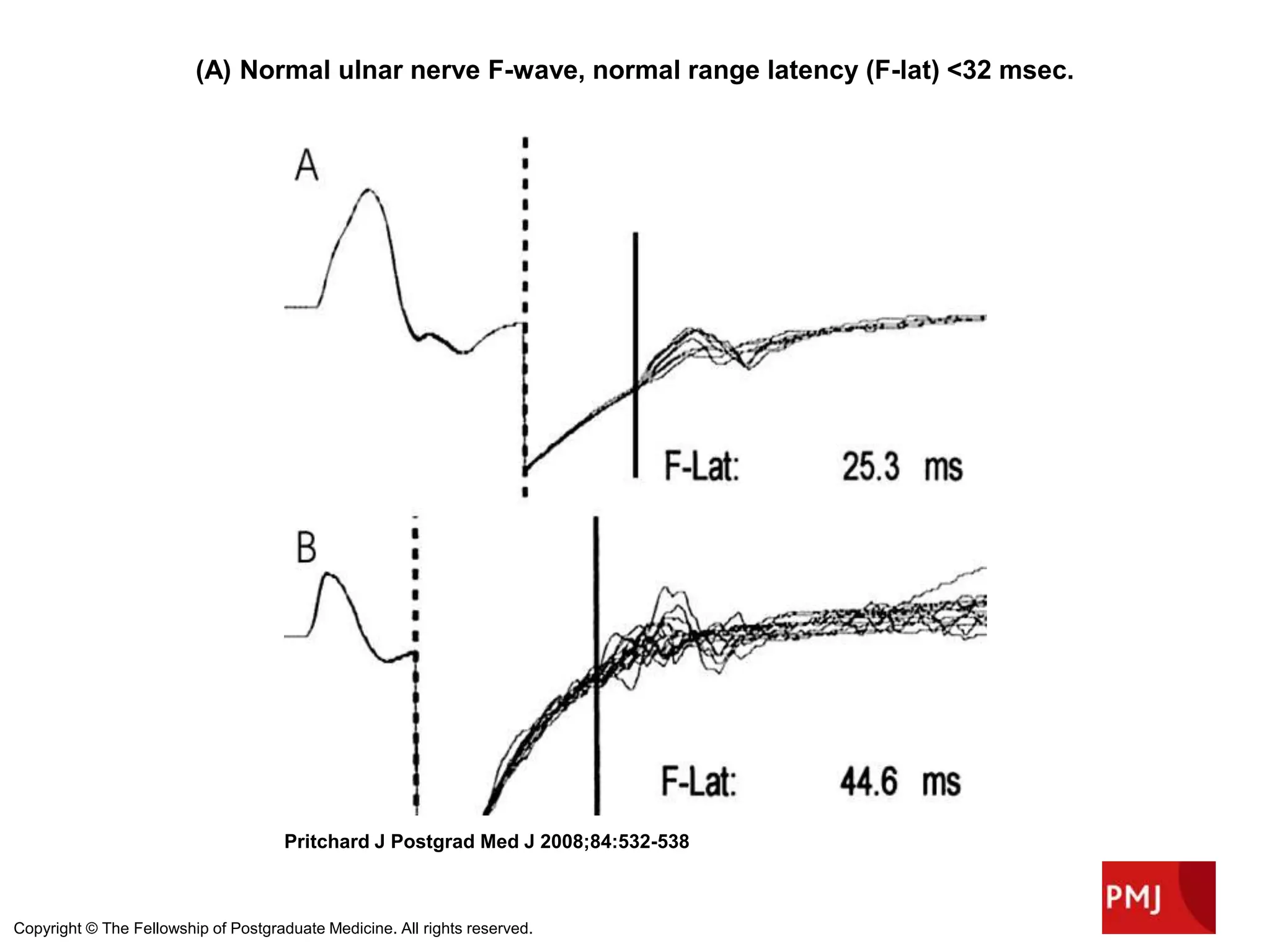
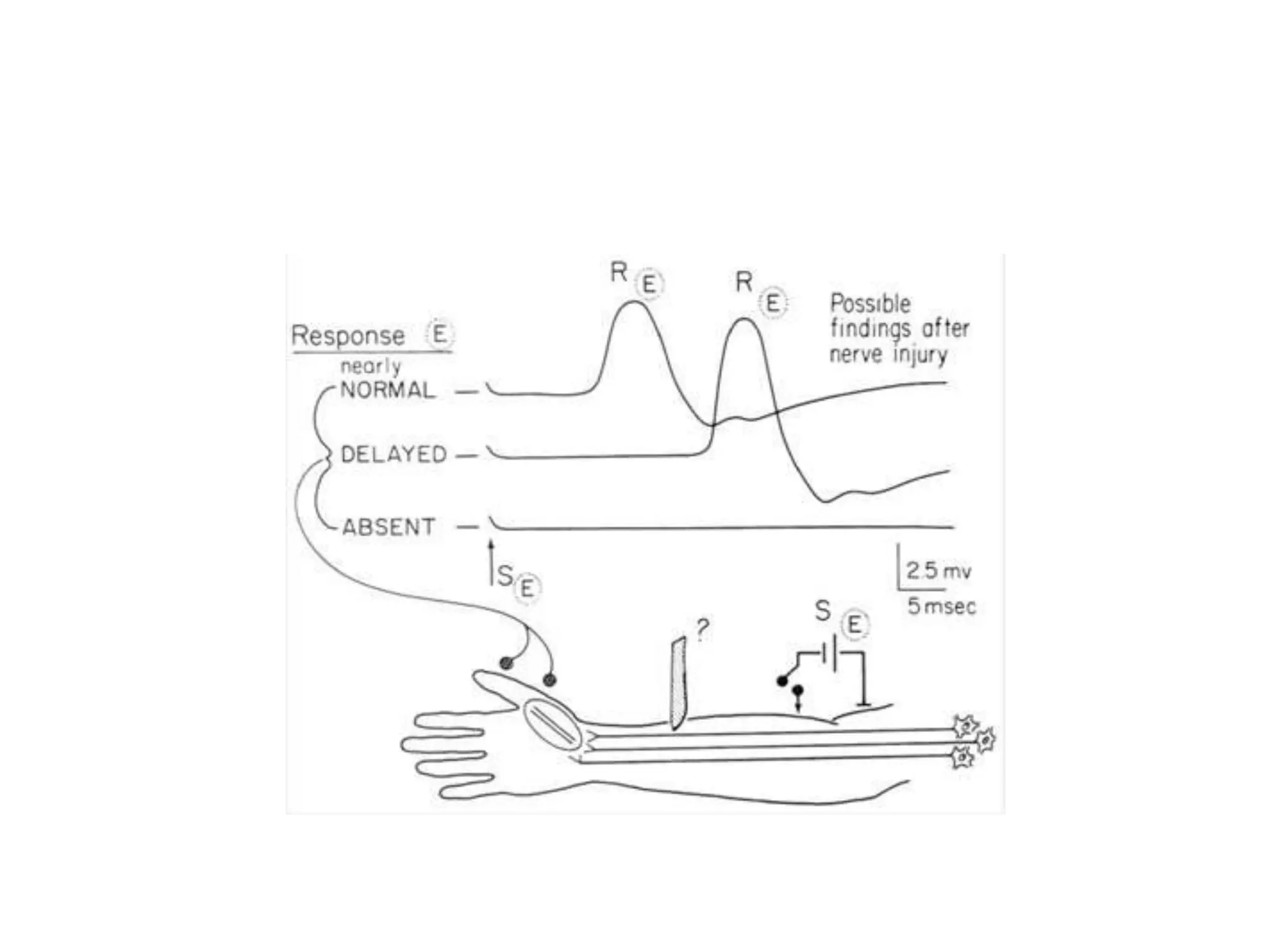
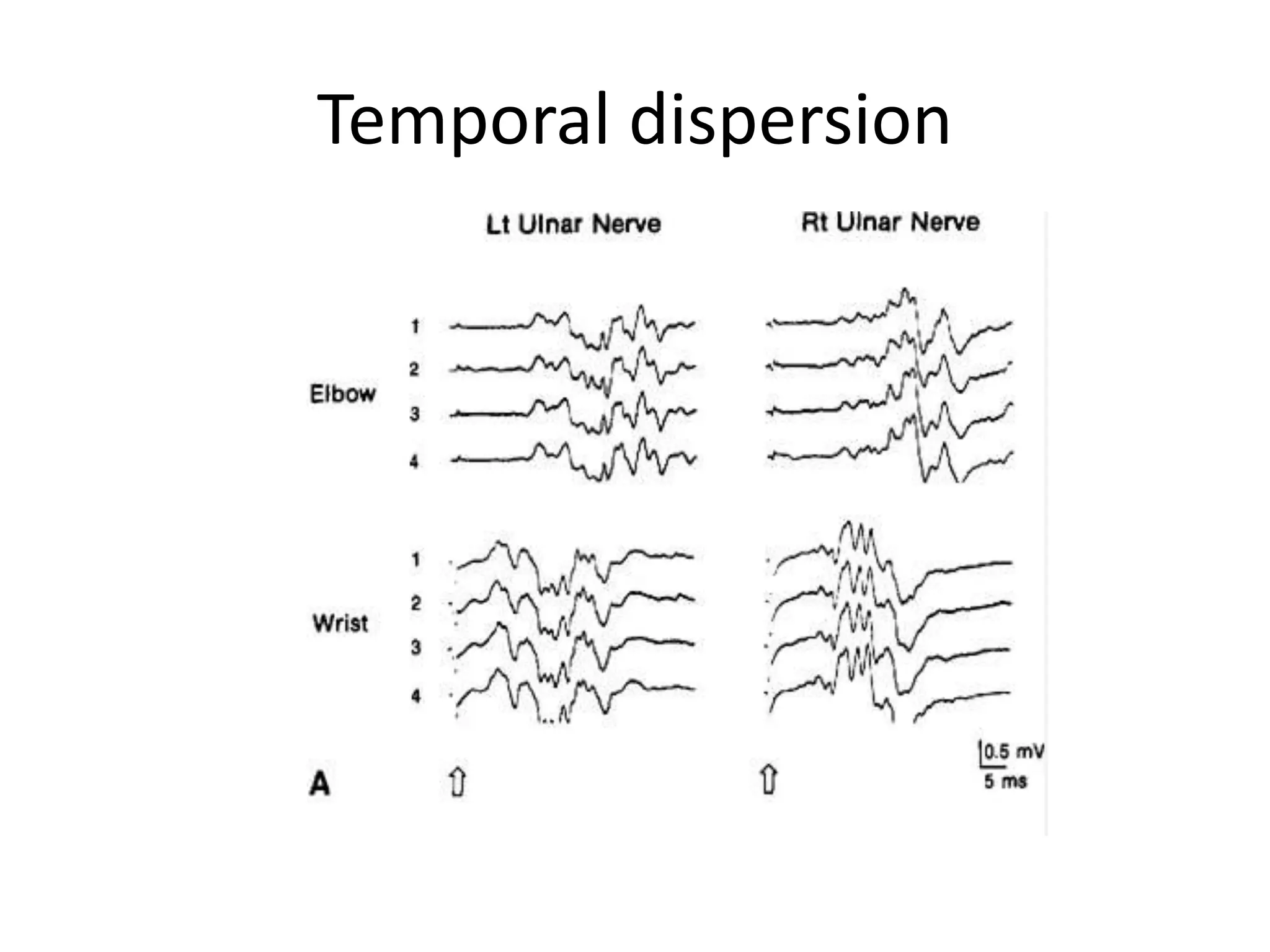
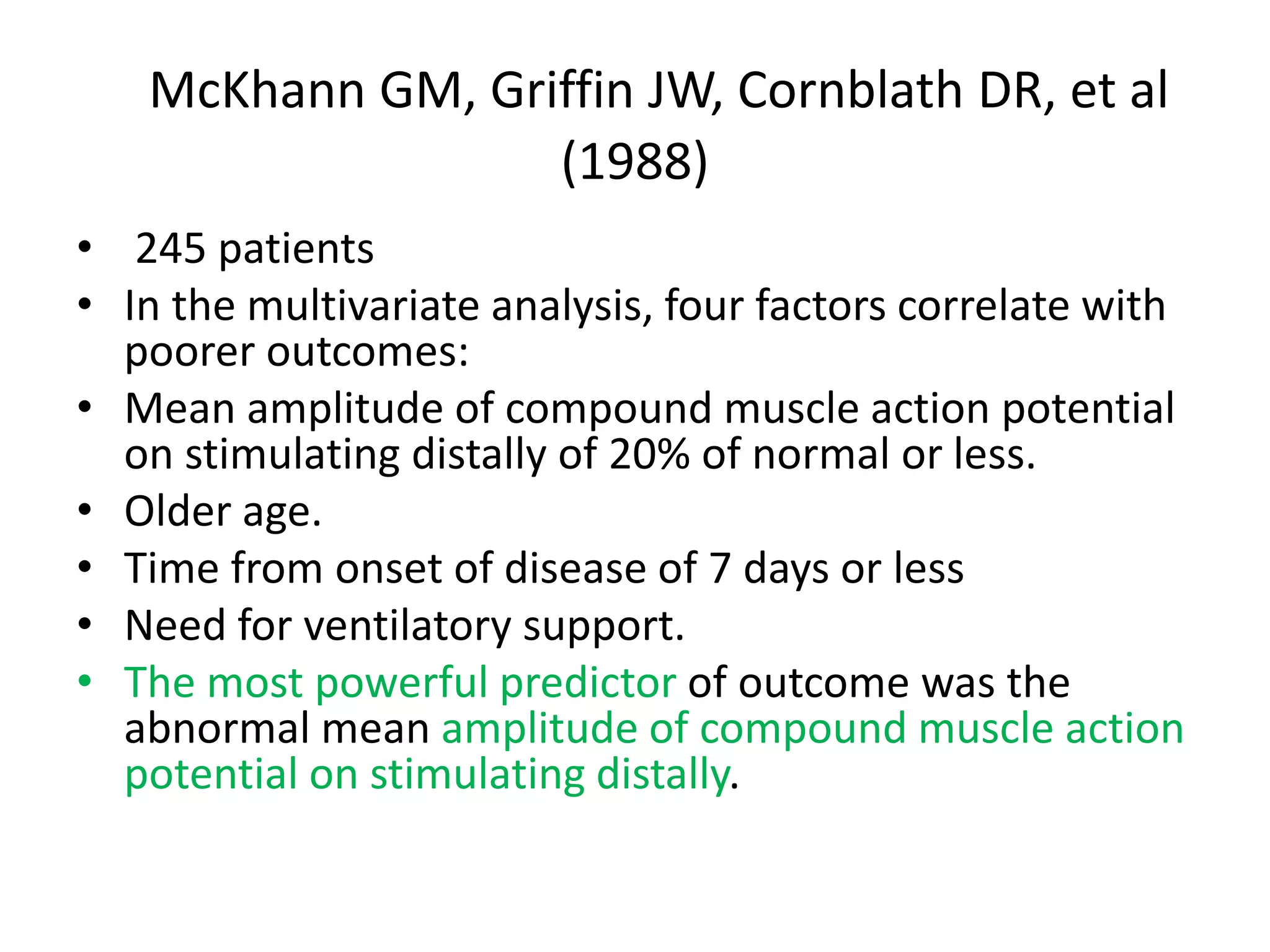
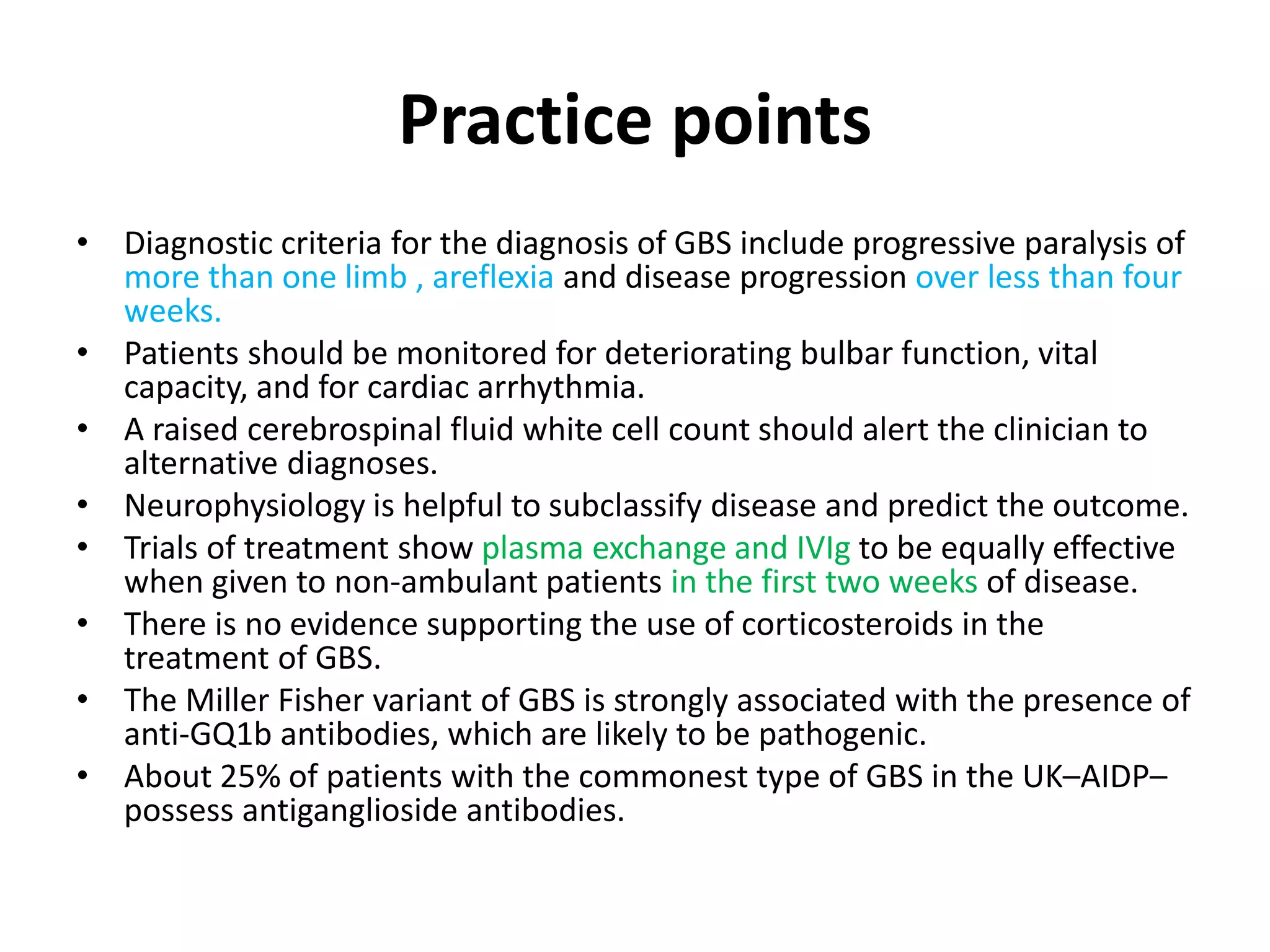
Guillain-Barre Syndrome is an acute immune-mediated inflammatory disorder of the peripheral nervous system. It was first described in 1859 and 1916. Clinical features include progressive weakness starting in the legs in most cases and sometimes the arms or face. Facial weakness and respiratory impairment occur in about half of patients. Electrophysiological tests are important for diagnosis and show features like conduction block, slowed conduction velocities and prolonged latencies. Prognostic factors include age, preceding gastroenteritis, disability level at nadir, and evidence of axonal damage on electrophysiology. Most patients recover fully but some have residual deficits.