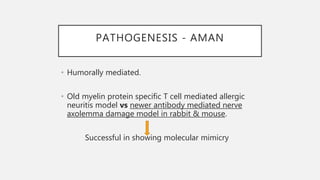
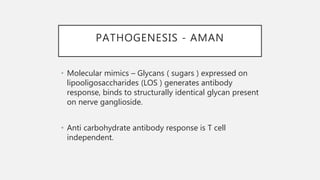
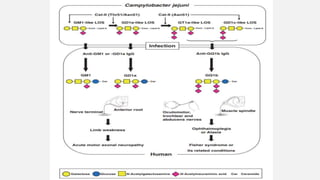
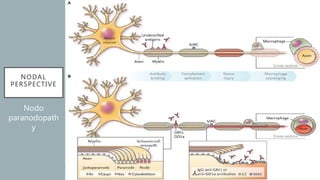
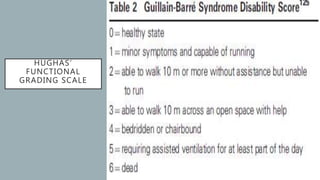
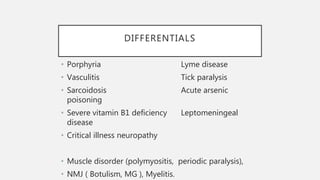
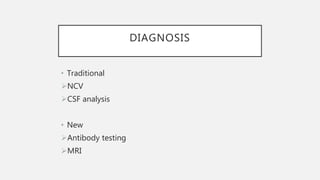
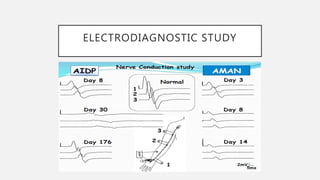
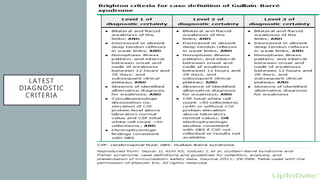
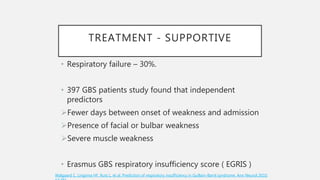
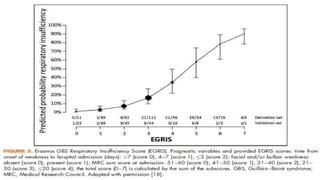
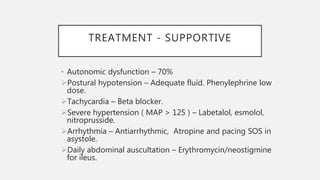
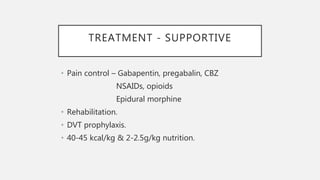
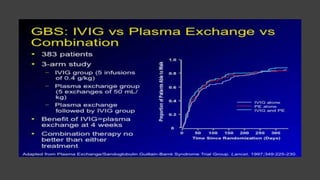
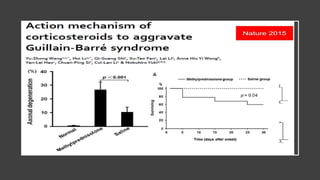
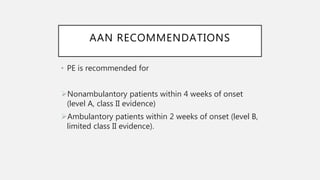
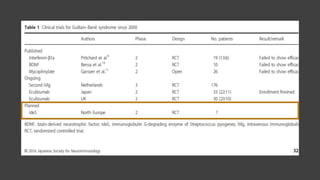
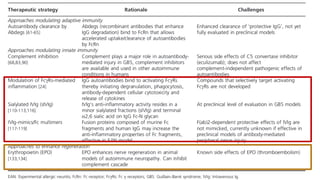
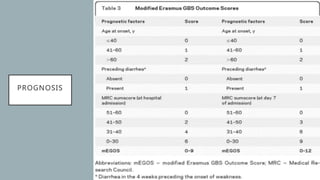
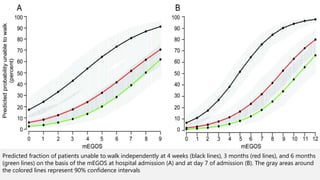
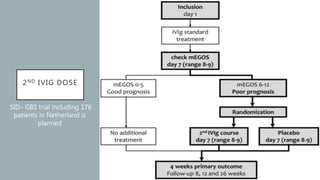
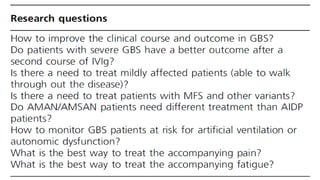
This document provides an overview of recent advances in the pathogenesis and management of Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS). It discusses the variants of GBS (AIDP and AMAN), their pathogenesis involving molecular mimicry and antibody responses, clinical manifestations, diagnostic criteria and tests, treatment including immunotherapy options, prognostic indicators, and novel immunomodulatory approaches being studied.