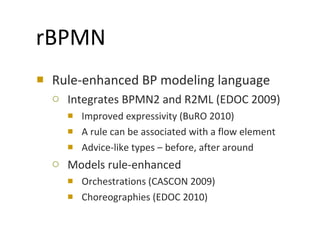
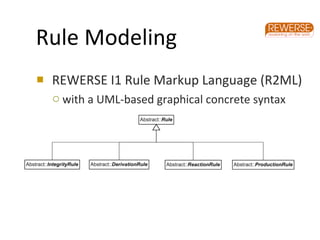
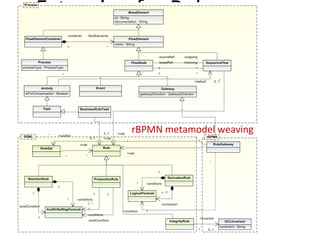
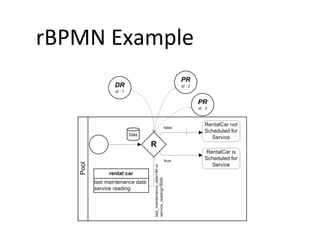
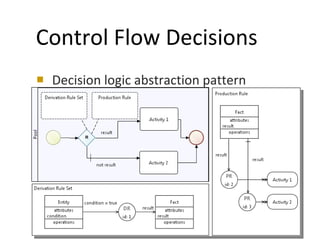
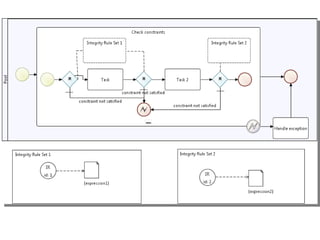
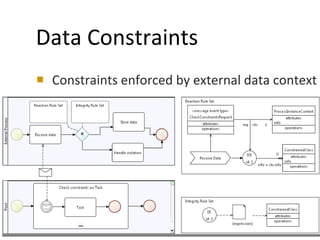
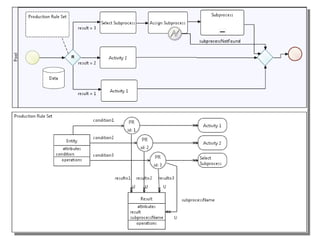
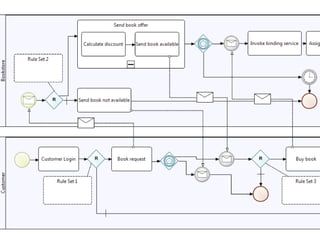
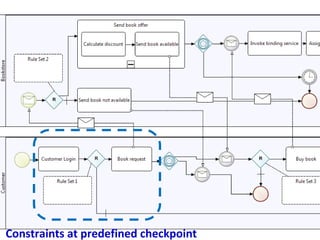
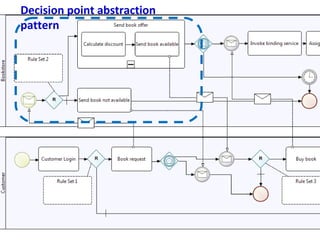
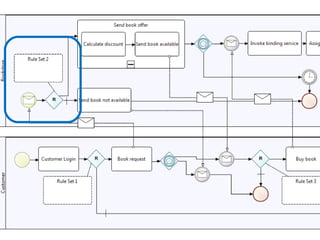
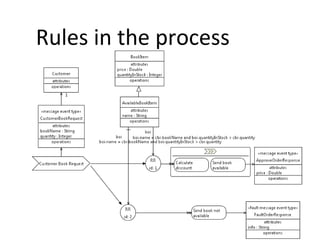
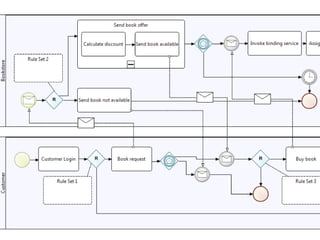
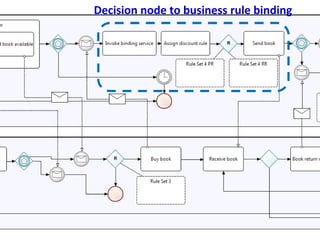
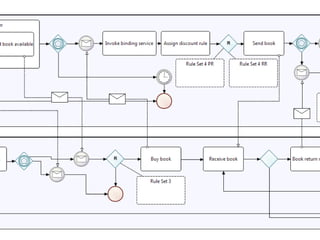
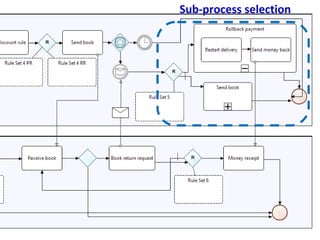
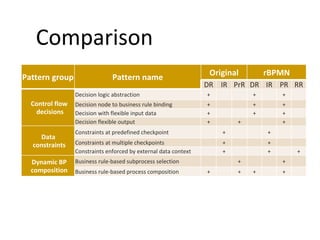
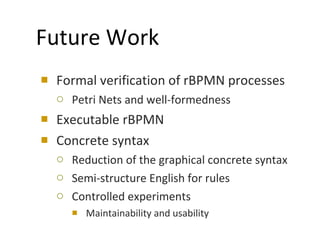
The document discusses the integration of business rules within flexible business process modeling, focusing on the development of a rule-enhanced business process modeling language that combines BPMN2 and R2ML. It outlines various modeling patterns for decision logic and data constraints, along with a book store case study to illustrate the process. The research aims to improve expressivity and flexibility in business process modeling while addressing existing integration challenges.


![Motivation Modeling flexible business process Integration of rules in processes Patterns for Rules in BPs [Graml et al., 2007] Control flow decisions Control flow decisions Rule types DR IR PrR Control flow decisions Decision logic abstraction + Decision node to business rule binding + Decision with flexible input data + Decision flexible output + + Data constraints Constraints at predefined checkpoint + Constraints at multiple checkpoints + Constraints enforced by external data context + Dynamic BP composition Business rule-based subprocess selection + Business rule-based process composition + +](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gasevicedoc2011ss-110831082911-phpapp02/85/Modeling-Flexible-Business-Processes-with-Business-Rule-Patterns-3-320.jpg)