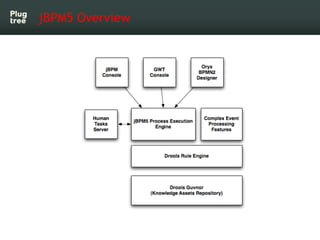
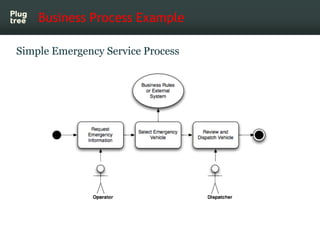
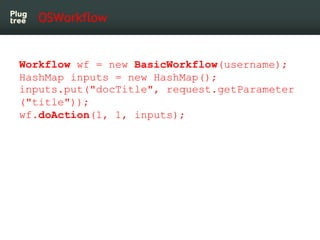
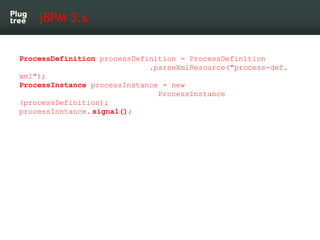
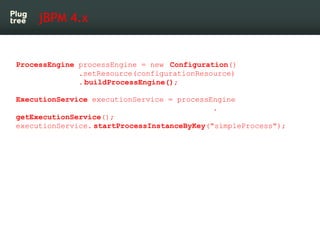
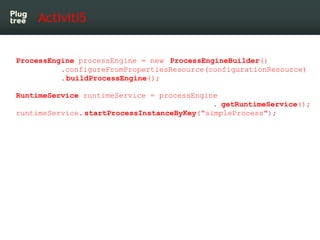
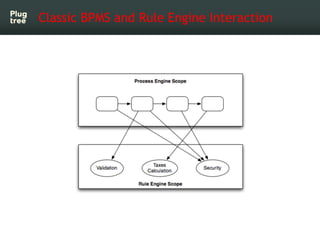
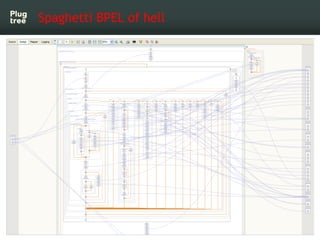
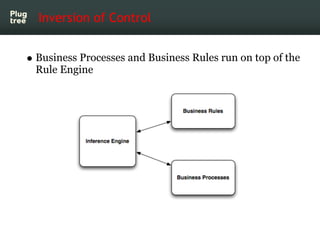
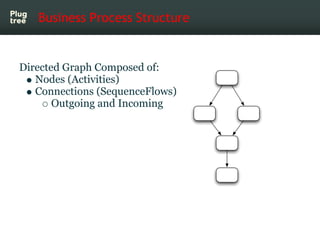
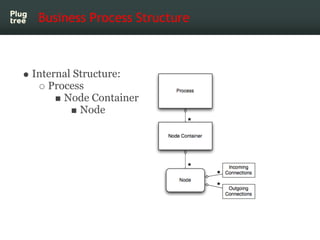
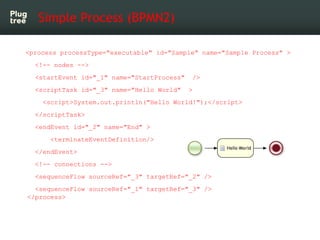
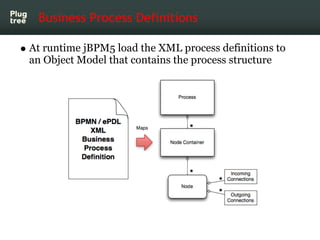
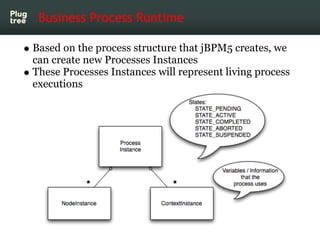
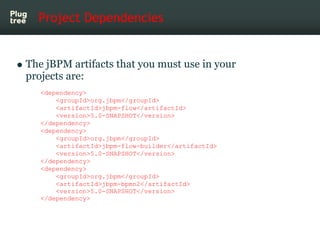
The document provides an introduction to jBPM5, a business process management system that runs on top of the Drools rule engine, highlighting its development history, features, and competitive advantages. It emphasizes the benefits of integrating business processes with rule-based systems and outlines the components necessary for developing applications using jBPM5. Additionally, it includes links for further documentation and resources related to jBPM5 training and usage.