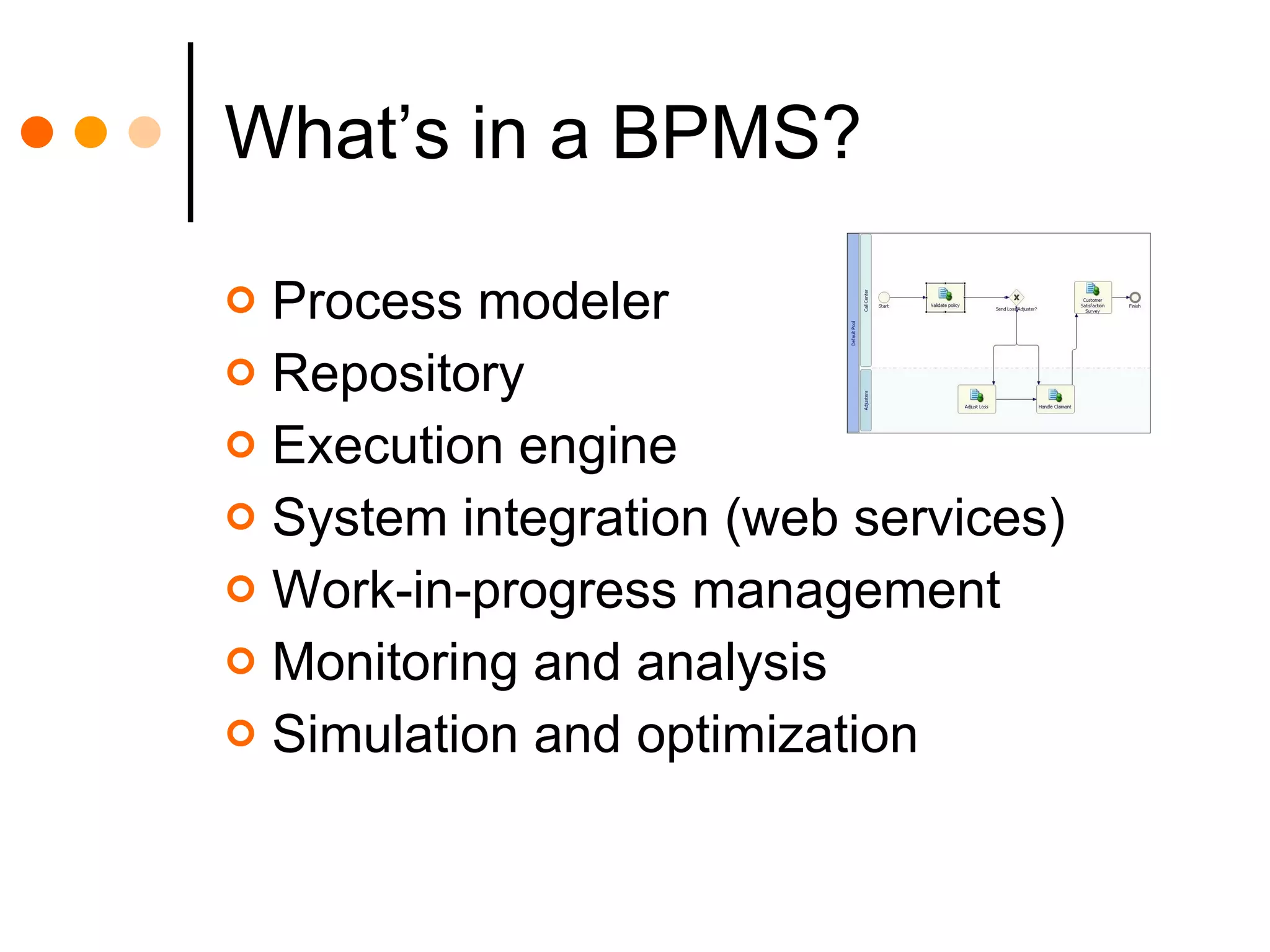
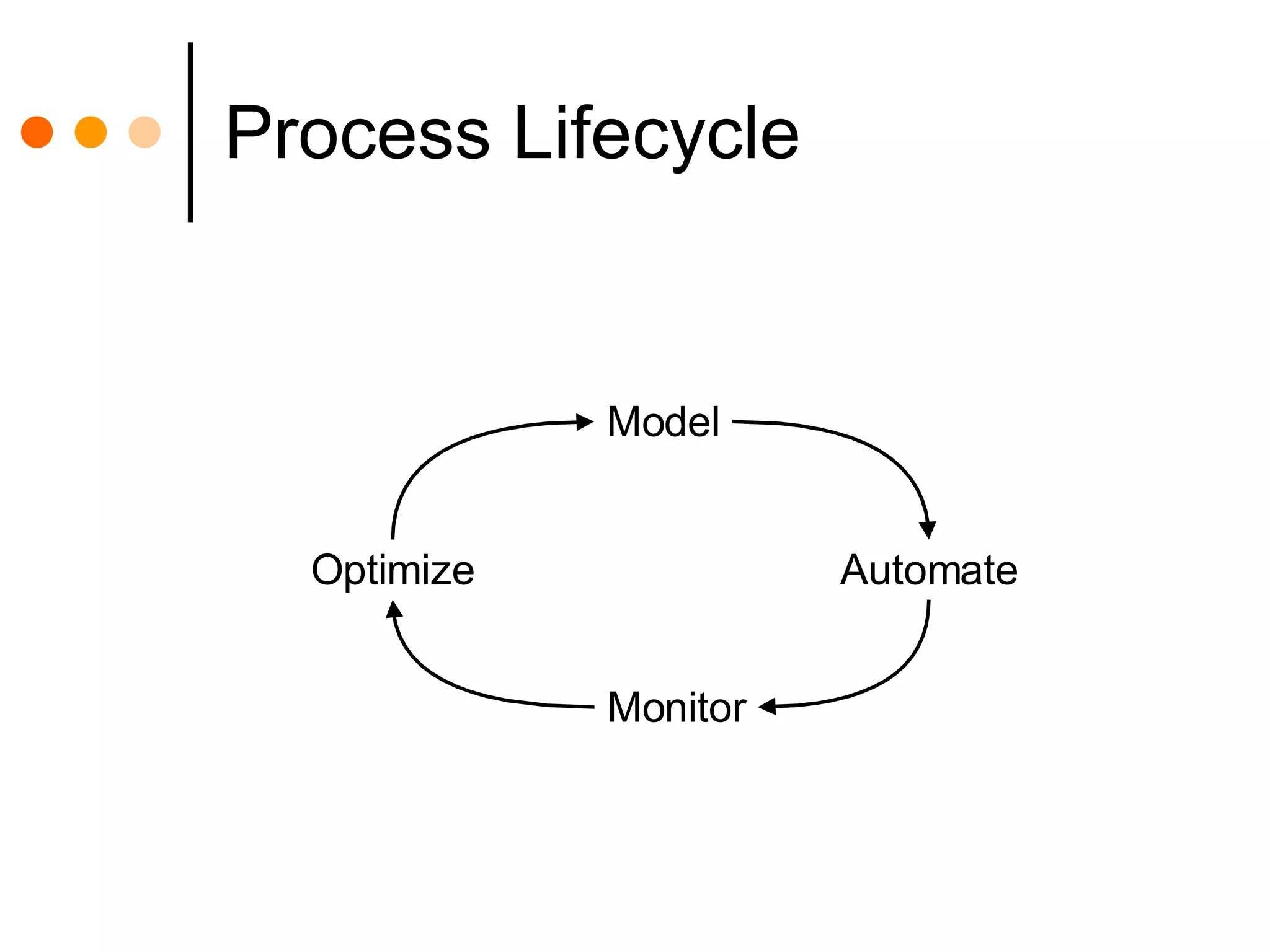
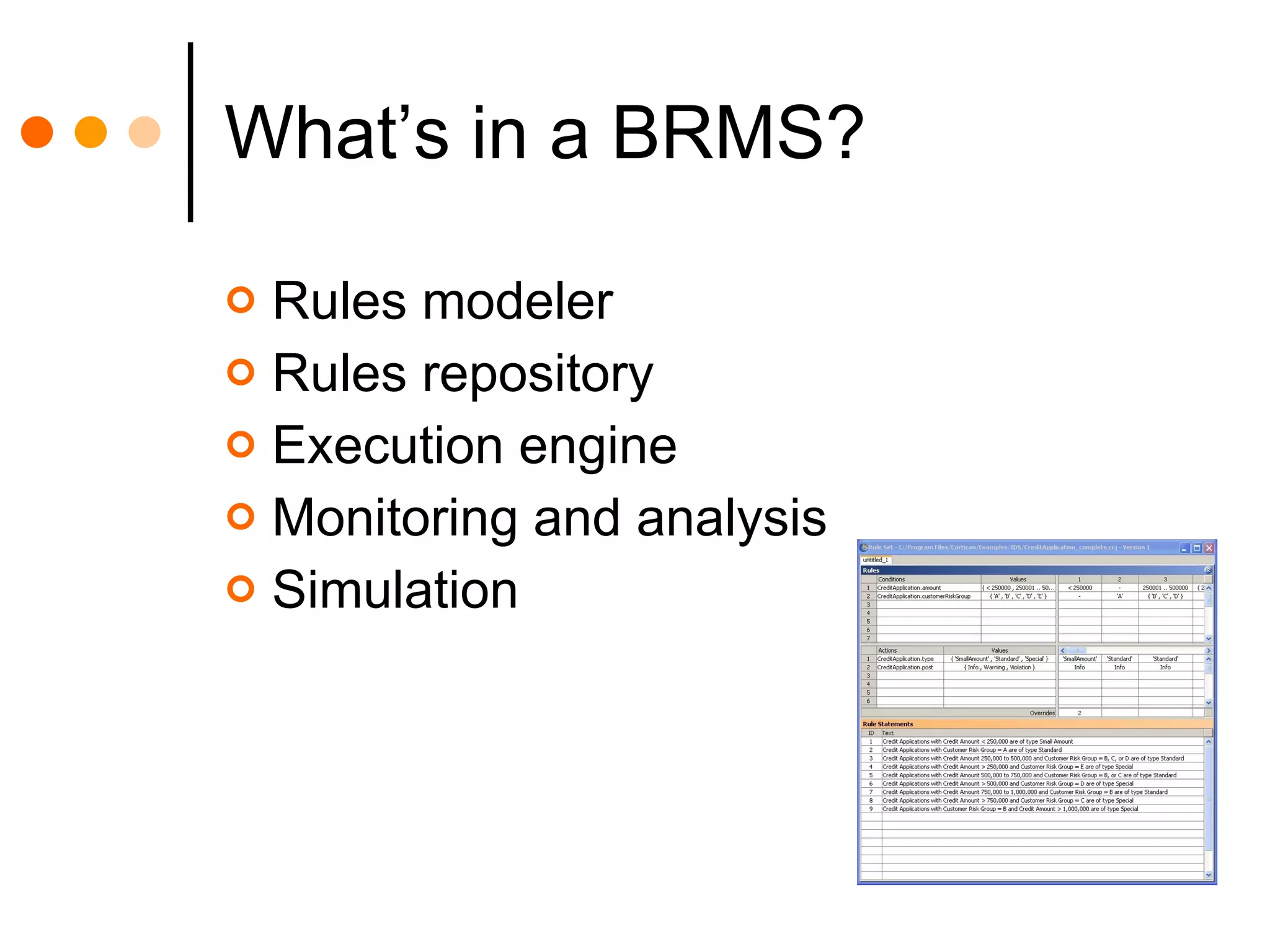
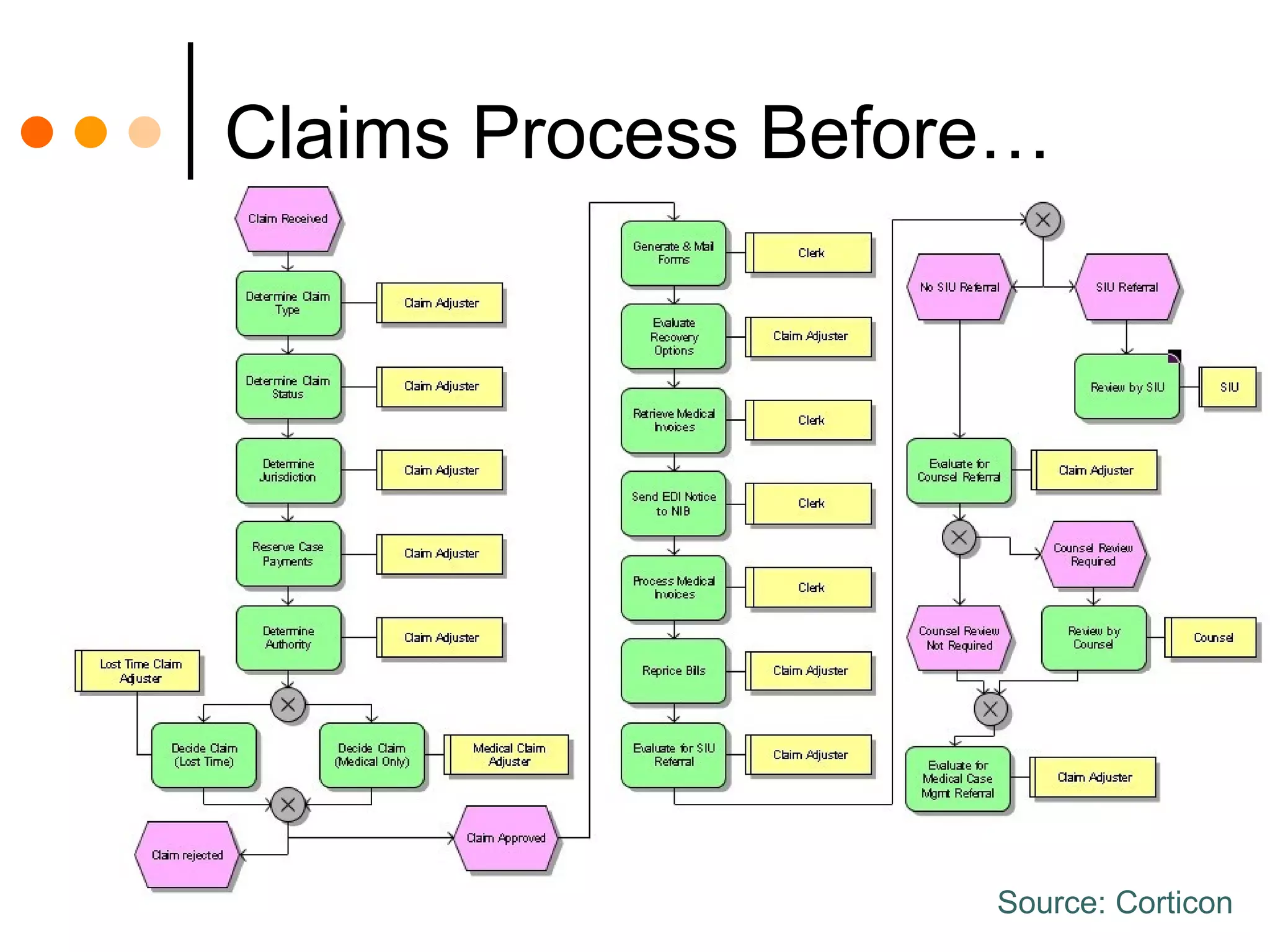
This document discusses how combining business process management (BPM) and business rules management (BRM) can improve business processes. BPM is used to manage cross-functional business processes, while BRM is used to manage business policies and rules. Integrating BPM and BRM allows rules that define decisions to be separated from business processes, improving process flexibility and agility. When rules are changed, it does not require redeploying entire processes. The key benefits are full rule functionality, reuse of rules across processes, and the ability to change rules without changing business processes. However, integrating separate BPM and BRM systems can also present challenges.