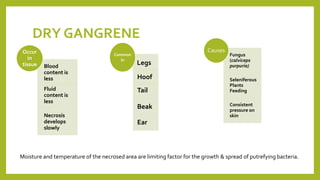
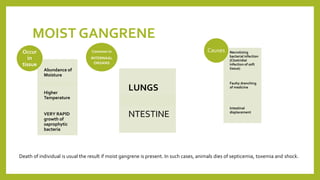
This document discusses gangrene, which is defined as the invasion and petrification of necrotic tissue by saprophytic bacteria. It commonly occurs in the lungs, intestines, and extremities. There are two main types of gangrene - dry gangrene and moist gangrene. Dry gangrene occurs where moisture and temperature limit bacterial growth, resulting in a dry, shriveled appearance. Moist gangrene occurs where moisture and heat allow rapid bacterial growth in tissues like the lungs and intestines, often resulting in death from sepsis, toxemia and shock. The document describes the gross and microscopic appearances of both dry and moist gangrene.