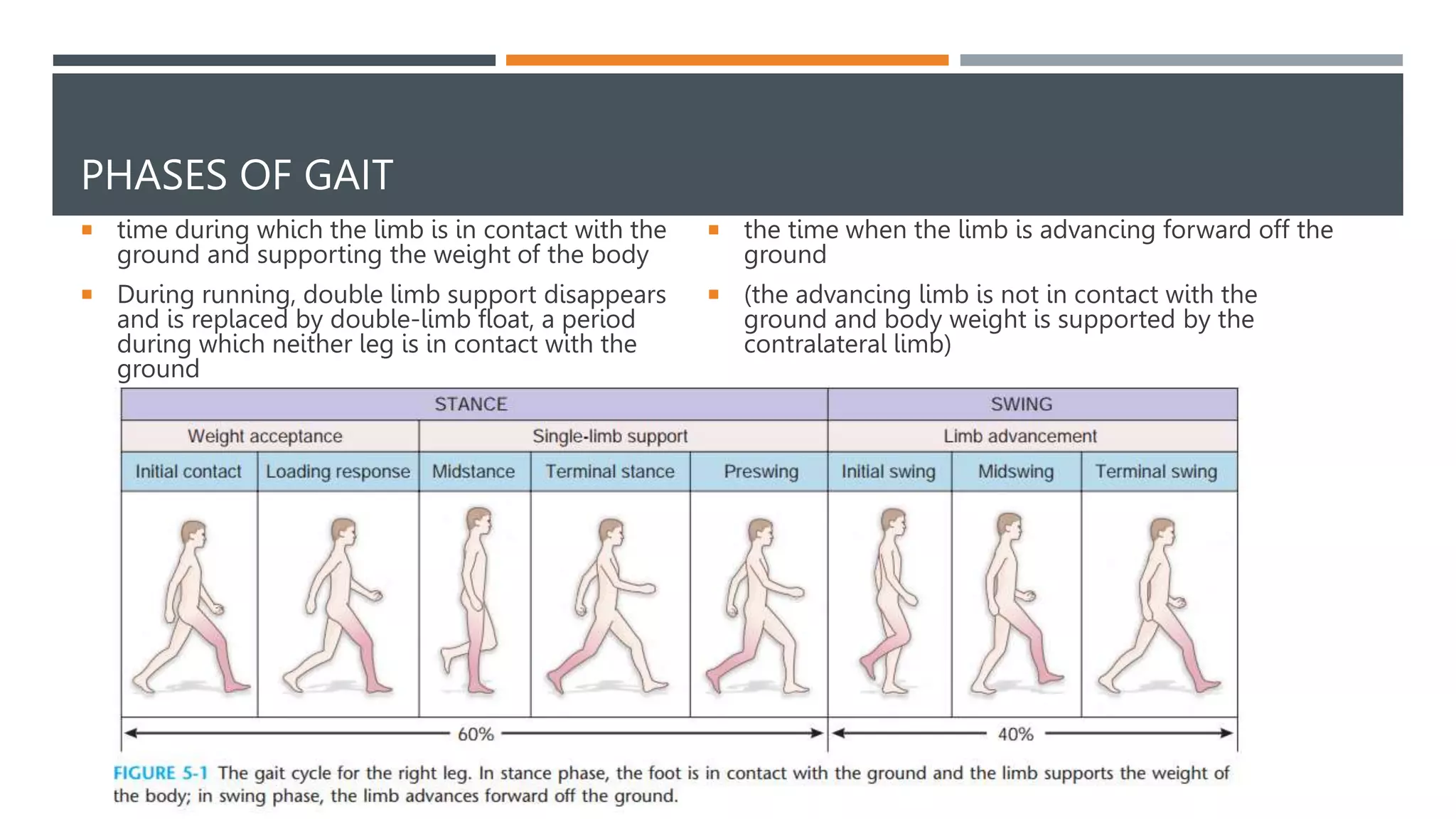
This document provides an overview of gait analysis. It discusses the phases of gait, temporal parameters, neurological control, kinematics, kinetics, and how to assess gait. Abnormal gaits such as hemiplegic, diplegic, neuropathic, myopathic, Parkinsonian, ataxic, sensory ataxic, choreiform, and antalgic gaits are described. The document is intended as an educational guide for orthopedic residents on evaluating a patient's gait.