This document summarizes Lotfi Zadeh's 1965 paper that introduced fuzzy set theory. It defines fuzzy sets as sets with imprecise or unclear boundaries, where elements can partially belong through degrees of membership between 0 and 1. It provides key definitions for fuzzy sets, including complement, subset, union, intersection and algebraic operations. Convex combinations and fuzzy relations are also introduced. The document concludes with a definition for convex fuzzy sets.





![ Let the universal set be denoted by X and its elements by x i.e. X= {x}.
We define a set A on X such that 𝐴 ⊂ 𝑋. We define the term grade of
membership denoted by fA(x) which represents the information
regarding the extent of belongingness of x to set A.
If 𝑥 ∈ 𝑋, if fA(x)= 0 or 1 only and no intermediate value, then the set A
is called the crisp set and if the value of fA x belongs to the closed
interval [0, 1], then A is called the Fuzzy set. Eg: For the set X= set of
real numbers close to 1, we have fA 0 = 0; fA 10 = 0.2; fA 500 = 1
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN CRISP
SETS & FUZZY SETS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fuzzysets-151211062911/85/Fuzzy-sets-6-320.jpg)

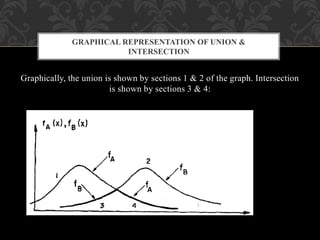

![ Let A, B & Λ be three FSs, then their convex combination is denoted by
𝐴, 𝐵; Λ = Λ𝐴 + Λ′ 𝐵
𝑤ℎ𝑒𝑟𝑒Λ′ is the complement of Λ
Or in terms of the membership function as:
𝑓 𝐴,𝐵;Λ 𝑥 = 𝑓Λ 𝑥 𝑓𝐴 𝑥 + [1 − 𝑓Λ 𝑥 ]𝑓𝐵(𝑥)
A basic property of convex combination of A, B and Λ is given by:
𝐴 ∩ 𝐵 ⊂ 𝐴, 𝐵; Λ ⊂ 𝐴 ∪ 𝐵 ∀Λ
CONVEX COMBINATION](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fuzzysets-151211062911/85/Fuzzy-sets-10-320.jpg)


![ A fuzzy set A is called the convex iff
𝑓𝐴 𝜆𝑥1 + 1 − 𝜆 𝑥2 ≥ 𝑀𝑖𝑛[𝑓𝐴 𝑥1 , 𝑓𝐴 𝑥2 ]
∀𝑥1, 𝑥2 ∈ 𝑋 𝑎𝑛𝑑𝜆 ∈ [0,1]
However the above definition does not imply that 𝑓𝐴(𝑥) must be a
convex function of 𝑥.
CONVEXITY](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fuzzysets-151211062911/85/Fuzzy-sets-13-320.jpg)
